12: Electromagnetic Induction
... change in flux so EMF is zero for an instant. - As magnet exits, Lenz’s law tells us that the current must flow in the opposite direction so as to oppose motion. reversed EMF - Max induced EMF occurs on exit because magnet is moving fastest. - t2 is smaller due to greater speed. ...
... change in flux so EMF is zero for an instant. - As magnet exits, Lenz’s law tells us that the current must flow in the opposite direction so as to oppose motion. reversed EMF - Max induced EMF occurs on exit because magnet is moving fastest. - t2 is smaller due to greater speed. ...
BASANT`S SCIENCE ACADEMY A compass needle is a small bar
... List the properties of magnetic lines of force. The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows. (a) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole. (b) They merge at the south pole. (c) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole. (d) Magnetic l ...
... List the properties of magnetic lines of force. The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows. (a) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole. (b) They merge at the south pole. (c) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole. (d) Magnetic l ...
Electromagnetic Demos
... For more details visit: https://vimeo.com/20847392 A copper or aluminium calorimeter balanced on a point could also be used for this demonstration. This demonstration is from the Applied Electricity section of the syllabus Applications Induction motors are used in speedometers, tachometers and some ...
... For more details visit: https://vimeo.com/20847392 A copper or aluminium calorimeter balanced on a point could also be used for this demonstration. This demonstration is from the Applied Electricity section of the syllabus Applications Induction motors are used in speedometers, tachometers and some ...
2731-AQA Physics P3.3 SoW Keeping things moving
... efficient,the electrical power output would equal the electrical power input. Vp x Ip = Vs x Is i) Switch mode transformers operate at a high frequency, often between 50 kHz and 200 kHz. j) Switch mode transformers are much lighter and smaller than traditional transformers working from a 50 Hz mains ...
... efficient,the electrical power output would equal the electrical power input. Vp x Ip = Vs x Is i) Switch mode transformers operate at a high frequency, often between 50 kHz and 200 kHz. j) Switch mode transformers are much lighter and smaller than traditional transformers working from a 50 Hz mains ...
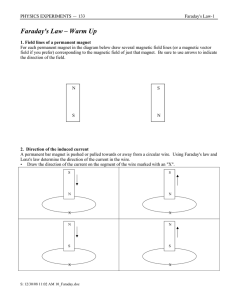
Faraday`s Law – Warm Up
... solenoid to an AC power supply (ACV < 1 V) and place it inside the medium coil. The changing flux is now due to the changing direction of the current through the solenoid, which changes the direction of the magnetic field. The AC power supply should be set to a frequency of 60 Hz; so you will need t ...
... solenoid to an AC power supply (ACV < 1 V) and place it inside the medium coil. The changing flux is now due to the changing direction of the current through the solenoid, which changes the direction of the magnetic field. The AC power supply should be set to a frequency of 60 Hz; so you will need t ...
Ferrites and accessories – toroids – R 12.5 x 7.50 x 5.00
... in the core, the lower is the value for the initial permeability. Thus the embedding medium should have the greatest possible elasticity. For detailed information see chapter “Definitions”, section 8.2. Heating up Ferrites can run hot during operation at higher flux densities and higher frequencies. ...
... in the core, the lower is the value for the initial permeability. Thus the embedding medium should have the greatest possible elasticity. For detailed information see chapter “Definitions”, section 8.2. Heating up Ferrites can run hot during operation at higher flux densities and higher frequencies. ...