Lecture_7_Magnets and Magnetism print
... • Determines direction of magnetic field • Imagine grasping conductor with right hand • Thumb in direction of current flow (not electron flow) • Fingers curl in the direction of magnetic field DO NOT USE LEFT HAND RULE IN BOOK ...
... • Determines direction of magnetic field • Imagine grasping conductor with right hand • Thumb in direction of current flow (not electron flow) • Fingers curl in the direction of magnetic field DO NOT USE LEFT HAND RULE IN BOOK ...
6. Magnetism
... Generally, domains cancel – no magnetic effects An external field aligns domains (non-random) A strong magnetic field can make other ferromagnetic materials into permanent magnets ...
... Generally, domains cancel – no magnetic effects An external field aligns domains (non-random) A strong magnetic field can make other ferromagnetic materials into permanent magnets ...
4 Electromagnetism
... Electric current as flow of electric charges Drift velocity and current Magnetic force on a moving charge Hall voltage a Explanation of Hall effect b Derivation of Hall voltage c Characteristics of conductors revealed by Hall voltage Measuring magnetic fields by a Hall probe ...
... Electric current as flow of electric charges Drift velocity and current Magnetic force on a moving charge Hall voltage a Explanation of Hall effect b Derivation of Hall voltage c Characteristics of conductors revealed by Hall voltage Measuring magnetic fields by a Hall probe ...
Magnetism - TeacherWeb
... The direction the north pole of a compass would point when placed at that location ...
... The direction the north pole of a compass would point when placed at that location ...
practice exam solutions
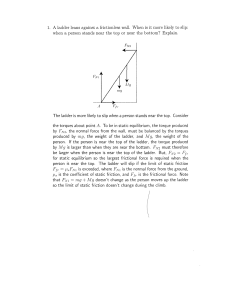
... person is near the top. The ladder will slip if the limit of static friction Ffr = /l,,,F'Nl is exceeded, where Fm is the normal force from the ground, 1"8 is the coefficient of static friction, and Ffr is the frictional force. Note that FNl = /7I,g + j\{g doesn't change as the person moves up the l ...
... person is near the top. The ladder will slip if the limit of static friction Ffr = /l,,,F'Nl is exceeded, where Fm is the normal force from the ground, 1"8 is the coefficient of static friction, and Ffr is the frictional force. Note that FNl = /7I,g + j\{g doesn't change as the person moves up the l ...
Lecture 18 - UConn Physics
... An instrument based on induced emf has been used to measure projectile speeds up to 6 km/s. A small magnet is imbedded in the projectile, as shown in Figure below. The projectile passes through two coils separated by a distance d. As the projectile passes through each coil a pulse of emf is induced ...
... An instrument based on induced emf has been used to measure projectile speeds up to 6 km/s. A small magnet is imbedded in the projectile, as shown in Figure below. The projectile passes through two coils separated by a distance d. As the projectile passes through each coil a pulse of emf is induced ...
Electromagnetism
... A light bulb needs a continuous flow of electricity. It takes energy to separate the charges. You can provide electrical energy by rubbing some materials together. However, electrical energy can be better generated and stored for later use with a battery or other item. Current – how much electrical ...
... A light bulb needs a continuous flow of electricity. It takes energy to separate the charges. You can provide electrical energy by rubbing some materials together. However, electrical energy can be better generated and stored for later use with a battery or other item. Current – how much electrical ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. • Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. • Permanent magnets are difficult ...
... iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. • Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. • Permanent magnets are difficult ...
Lesson 1 Magnets
... 4. When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself. 5. Iron is a SOFT magnetic material;it is easily magnetised but easily loses its magnetism. 6. Steel is a HARD magnetic material; it is hard to magnetise but keeps its magnetism. 7. The magnetic field around a bar magnet i ...
... 4. When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself. 5. Iron is a SOFT magnetic material;it is easily magnetised but easily loses its magnetism. 6. Steel is a HARD magnetic material; it is hard to magnetise but keeps its magnetism. 7. The magnetic field around a bar magnet i ...
Lecture 11
... the previous chapters, we have studied that an electric charge sets up an electric field that affects other electric charges. Here, we might expect that a magnetic charge sets up a magnetic field that can then affect other magnetic charges. Such a magnetic charge is called a magnetic monopole (a new ...
... the previous chapters, we have studied that an electric charge sets up an electric field that affects other electric charges. Here, we might expect that a magnetic charge sets up a magnetic field that can then affect other magnetic charges. Such a magnetic charge is called a magnetic monopole (a new ...
Preparation PHYS2425 Magnetism lab. Charges cause
... Charges cause electric fields. We saw in the first part of the semester that electric field lines start at positive charges and end up at negative charges. We say in physics positive charges are the sources of the electric field lines and negative charges are the sinks. So electric charges create a ...
... Charges cause electric fields. We saw in the first part of the semester that electric field lines start at positive charges and end up at negative charges. We say in physics positive charges are the sources of the electric field lines and negative charges are the sinks. So electric charges create a ...
Magnetism - BAschools.org
... when inside of a strong magnetic field but lose their magnetism outside of it paperclips, nails, other soft ...
... when inside of a strong magnetic field but lose their magnetism outside of it paperclips, nails, other soft ...
em induction
... The net magnetic flux is zero through a closed surface. B field lines cannot begin or end at any point. If they did, monopoles would exist ...
... The net magnetic flux is zero through a closed surface. B field lines cannot begin or end at any point. If they did, monopoles would exist ...
Electrodynamic constraints on homogeneity and RF power deposition in multiple...
... Correction of B1 inhomogeneities and management of SAR are among the most difficult challenges faced by in-vivo ultra high field MR applications. The use of multiple independently driven transmit elements, which enables fine control over the distribution of electromagnetic fields, has been explored ...
... Correction of B1 inhomogeneities and management of SAR are among the most difficult challenges faced by in-vivo ultra high field MR applications. The use of multiple independently driven transmit elements, which enables fine control over the distribution of electromagnetic fields, has been explored ...
Technology Brief 27 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
... on, the outlier molecules align with that magnetic field. When the pulse turns off, they relax back to their original state. As they relax, their spin precesses (becomes tipped like a toy top slowing down) and produces yet another magnetic field, which returns to and is picked up by the same coil th ...
... on, the outlier molecules align with that magnetic field. When the pulse turns off, they relax back to their original state. As they relax, their spin precesses (becomes tipped like a toy top slowing down) and produces yet another magnetic field, which returns to and is picked up by the same coil th ...
Q.5. What is a magnetic field?
... Q.26. When does the direction of induced current in an AC generator changes? Q.27. What is an electromagnet? Q.28. Which scientist suggested that the magnet must also exert an equal and opposite force on the current carrying conductor? Q.29. Which rule gives the direction of the motion of a current ...
... Q.26. When does the direction of induced current in an AC generator changes? Q.27. What is an electromagnet? Q.28. Which scientist suggested that the magnet must also exert an equal and opposite force on the current carrying conductor? Q.29. Which rule gives the direction of the motion of a current ...