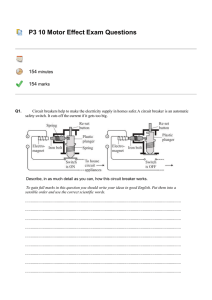
Experiment 10 Magnetic Fields and Induction
... 2. Connect the solenoid to a DC power supply of 15 V. Divide this voltage by the total resistance of the solenoid and the resistor to obtain the current I through the solenoid. The resistance of the solenoid is also labeled on it. Now you have all the information for your theoretical calculations. 3 ...
... 2. Connect the solenoid to a DC power supply of 15 V. Divide this voltage by the total resistance of the solenoid and the resistor to obtain the current I through the solenoid. The resistance of the solenoid is also labeled on it. Now you have all the information for your theoretical calculations. 3 ...
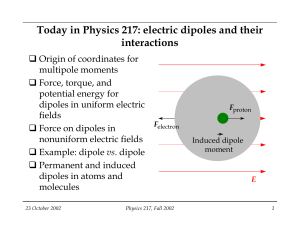
Today in Physics 217: electric dipoles and their interactions
... Dipole vs. dipole: force and torque Griffiths problems 4.5 and 4.29: Two perfect (infinitesimal) dipoles p1 and p2 are perpendicular and lie a distance r apart. What is the torque on p1 (about its center) due to p2? What is the torque on p2 (about its center) due to p1? What are the forces on each, ...
... Dipole vs. dipole: force and torque Griffiths problems 4.5 and 4.29: Two perfect (infinitesimal) dipoles p1 and p2 are perpendicular and lie a distance r apart. What is the torque on p1 (about its center) due to p2? What is the torque on p2 (about its center) due to p1? What are the forces on each, ...
Experiment 8: Magnetic Fields and Forces
... Are your observations of the magnetic field produced by the current consistent with the right-hand rule? Part 2 - Current Balance In this part of the lab you will investigate the magnetic force acting on a current carrying wire by observing the changes in a horseshoe magnet’s weight (Fg = mg). The c ...
... Are your observations of the magnetic field produced by the current consistent with the right-hand rule? Part 2 - Current Balance In this part of the lab you will investigate the magnetic force acting on a current carrying wire by observing the changes in a horseshoe magnet’s weight (Fg = mg). The c ...
Welcome to Physics 220! - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... induction independently of Henry. •Develops the transformer, motor, and generator. •Discovers the Faraday Effect of light - the rotation of the plane of polarization in magnetic fields. •Develops the First and Second Laws of Electrochemistry. •Discovers paramagnetism and ...
... induction independently of Henry. •Develops the transformer, motor, and generator. •Discovers the Faraday Effect of light - the rotation of the plane of polarization in magnetic fields. •Develops the First and Second Laws of Electrochemistry. •Discovers paramagnetism and ...
Module II – Discovering Electrical Phenomena
... When the iron is not magnetized, the domains are not aligned. Their magnetic effects cancel out. When the iron is magnetized, the domains line up. The greater the number of aligned domains, the stronger the magnet. ...
... When the iron is not magnetized, the domains are not aligned. Their magnetic effects cancel out. When the iron is magnetized, the domains line up. The greater the number of aligned domains, the stronger the magnet. ...
Lecture 1510
... If we plot the net field BM as function of the applied field Bo we get the loop shown in the figure known as a "hysteresis" loop. If we start with a unmagnetized ferromagnetic material the curve follows the path from point a to point b, where the magnetization saturates. If we reduce Bo the curve fo ...
... If we plot the net field BM as function of the applied field Bo we get the loop shown in the figure known as a "hysteresis" loop. If we start with a unmagnetized ferromagnetic material the curve follows the path from point a to point b, where the magnetization saturates. If we reduce Bo the curve fo ...
21.2 Electromagnetism
... fingers are oriented for a positive current and its magnetic field. Then, have students adapt the rule for positive charges moving in a magnetic field, as shown in Figure 8 (that is, the thumb points in the direction of the moving charge, the fingers extend in the direction of the magnetic field, an ...
... fingers are oriented for a positive current and its magnetic field. Then, have students adapt the rule for positive charges moving in a magnetic field, as shown in Figure 8 (that is, the thumb points in the direction of the moving charge, the fingers extend in the direction of the magnetic field, an ...
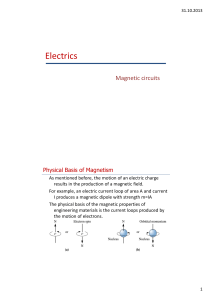
Electrics
... magnetic field in a ferromagnetic material, however, this approach has inaccuracy due to assumptions made in. • The magnetic circuit assumes that all flux are confined within the core, but in reality a small fraction of the flux escapes from the core into the surrounding low‐permeability air, and ...
... magnetic field in a ferromagnetic material, however, this approach has inaccuracy due to assumptions made in. • The magnetic circuit assumes that all flux are confined within the core, but in reality a small fraction of the flux escapes from the core into the surrounding low‐permeability air, and ...
The Power of Magnets
... magnet, which circulates around the magnet is a distinct pattern. The size of the magnetic field is related to the size of the magnet and its strength. The easiest way to view a magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet is to scatter iron filings around a bar magnet, which quickly orient themse ...
... magnet, which circulates around the magnet is a distinct pattern. The size of the magnetic field is related to the size of the magnet and its strength. The easiest way to view a magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet is to scatter iron filings around a bar magnet, which quickly orient themse ...
Magnetic Art
... of creating a Magnetic Art piece. They could create their magnetic art individually or in pairs. • Make sure the students have the collection of objects they brought from home. • Give each student or group a photocopy of the box template. Remind students that the solid lines are for cutting and the ...
... of creating a Magnetic Art piece. They could create their magnetic art individually or in pairs. • Make sure the students have the collection of objects they brought from home. • Give each student or group a photocopy of the box template. Remind students that the solid lines are for cutting and the ...