File - Science with Ms. C
... An _______________ ______________ changes electrical energy to mechanical energy. It contains an electromagnet that rotates between the poles of a magnet. The coil of the electromagnet is connected to a _________________ or other source of electric current. When an electric current flows thr ...
... An _______________ ______________ changes electrical energy to mechanical energy. It contains an electromagnet that rotates between the poles of a magnet. The coil of the electromagnet is connected to a _________________ or other source of electric current. When an electric current flows thr ...
Rotational Work
... perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is sufficiently large that the person will not slip. a) What is the magnitude of the normal force on ...
... perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is sufficiently large that the person will not slip. a) What is the magnitude of the normal force on ...
PowerPoint slides - Physics 420 UBC Physics Demonstrations
... • At maximum speed, Vback should be equal for both coils • So 6*2πfrLB = 6*2πfrLB • 2f1 = f2 • Top speed of the 3 turn coil should be about twice that of the 6 turn coil. Is it? ...
... • At maximum speed, Vback should be equal for both coils • So 6*2πfrLB = 6*2πfrLB • 2f1 = f2 • Top speed of the 3 turn coil should be about twice that of the 6 turn coil. Is it? ...
Useful Motor/Torque Equations for EML2322L
... Our goal is to find a realistic range for Tm, the motor torque. As calculated above, Tw would be the maximum amount of torque the motor could transfer to the ground before the wheel begins to slip (ie Tm, max). Typically, we desire μw > μa, so the wheel does not slip/slide across the floor, but rat ...
... Our goal is to find a realistic range for Tm, the motor torque. As calculated above, Tw would be the maximum amount of torque the motor could transfer to the ground before the wheel begins to slip (ie Tm, max). Typically, we desire μw > μa, so the wheel does not slip/slide across the floor, but rat ...
PHY 1114: Physics I Practice Problem Think about it
... following quantities is zero, constant (but not zero), or changing: a. Velocity ...
... following quantities is zero, constant (but not zero), or changing: a. Velocity ...
Understand Ohm`s law in both microscopic
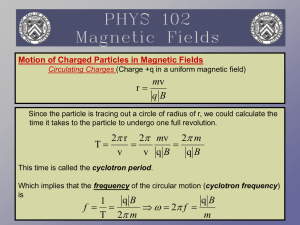
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
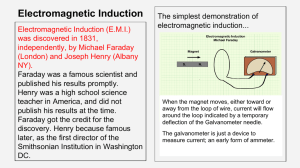
L15 Electromagnetic induction and inductance
... Electric motors: The inverse of generators, current leads to motion. If the torque is constant, why doesn’t the loop get faster and faster? The rotating loop produces an induced EMF which opposes the original current, and the torque is reduced (a back EMF). So we get a balance between work done and ...
... Electric motors: The inverse of generators, current leads to motion. If the torque is constant, why doesn’t the loop get faster and faster? The rotating loop produces an induced EMF which opposes the original current, and the torque is reduced (a back EMF). So we get a balance between work done and ...
Solenoids
... Right Hand Rule for magnetic fields around curved wires 1. Curve your fingers. 2. Place them along wire loop so that your fingers point in direction of current. 3. Your thumb gives the direction of the magnetic field in the center of the loop, where it is straight. 4. Field lines curve around and m ...
... Right Hand Rule for magnetic fields around curved wires 1. Curve your fingers. 2. Place them along wire loop so that your fingers point in direction of current. 3. Your thumb gives the direction of the magnetic field in the center of the loop, where it is straight. 4. Field lines curve around and m ...
Slide 1 - Robotics Academy
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...
HSC Physics - Motors and Generators Verbs
... magnetic flux density. For example, if the North pole of a magnet is moving towards a coil, the current must flow in such a way that a ‘North’ pole is produced at that end. Electric motors use an input voltage to produce an electric current in a coil to make the coil rotate in the external magne ...
... magnetic flux density. For example, if the North pole of a magnet is moving towards a coil, the current must flow in such a way that a ‘North’ pole is produced at that end. Electric motors use an input voltage to produce an electric current in a coil to make the coil rotate in the external magne ...
P6F
... external circuit. The brushes touch the spinning slip rings, which maintain electrical contact between the coil and the external circuit. At the power station Electricity is a useful form of energy. It allows energy to be transmitted over long distances easily through cables, and it allows energy to ...
... external circuit. The brushes touch the spinning slip rings, which maintain electrical contact between the coil and the external circuit. At the power station Electricity is a useful form of energy. It allows energy to be transmitted over long distances easily through cables, and it allows energy to ...
Magnetism - West Ashley Advanced Studies Magnet
... ● It contains an electromagnet that rotates between the poles of a magnet. ● The coil of the electromagnet is connected to a battery or other source of electric current. ● When an electric current flows through the wire in the electromagnet, a magnetic field is produced in the coil. ● Like poles of ...
... ● It contains an electromagnet that rotates between the poles of a magnet. ● The coil of the electromagnet is connected to a battery or other source of electric current. ● When an electric current flows through the wire in the electromagnet, a magnetic field is produced in the coil. ● Like poles of ...
uploaded to our site here
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...
DC Motors - Robotics Academy
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...
... – A permanent magnet that doesn’t move, called the stator. – An electromagnet (usually wound bare wire) – A frame on which the electromagnet is wound, called the armature – A set of brushes for transferring voltage to the armature Vex 1.0 © 2005 Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy Inc. ...