Phys11U_Unit 5_Ch13_transmittal_July12
... Discovery of Electromagnetic Induction In Section 12.2 you learned that a constant electric current will produce a magnetic field, so it would be logical to assume the opposite—that a constant magnetic field will produce an electric current in a conductor sitting in that constant magnetic field. It ...
... Discovery of Electromagnetic Induction In Section 12.2 you learned that a constant electric current will produce a magnetic field, so it would be logical to assume the opposite—that a constant magnetic field will produce an electric current in a conductor sitting in that constant magnetic field. It ...
Meetings in Physics 2005
... parameters along the depth of soil profiles. Magnetic susceptibility variations within small test area of 8.4ha is mapped at a grid of 6m using portable field kappameter KT6. Statistical significance of the data is evaluated through standard descriptive statistic, using 10 replicate measurements at ...
... parameters along the depth of soil profiles. Magnetic susceptibility variations within small test area of 8.4ha is mapped at a grid of 6m using portable field kappameter KT6. Statistical significance of the data is evaluated through standard descriptive statistic, using 10 replicate measurements at ...
and magnetism - Ms. Athena Klock Science Teacher Pine Middle
... predict, based on the findings of the previous test, which objects will be attracted to the magnet. Upon actual testing, they will discover that only some of the metals in Bag B are attracted. 3. Discuss the fact that only ferromagnetic materials (materials containing iron, cobalt nickel and/or rare ...
... predict, based on the findings of the previous test, which objects will be attracted to the magnet. Upon actual testing, they will discover that only some of the metals in Bag B are attracted. 3. Discuss the fact that only ferromagnetic materials (materials containing iron, cobalt nickel and/or rare ...
MHD seismology as a tool to diagnose the coronae of X
... s interpreted as a fundamental fast-kink mode of magnetoacoustic waves. These oscillations can be highly dispersive and can be a useful candidate for the localized heating of the corona of ξ-Boo. It should be noted that it is a binary K-Dwarf with the magnetized atmosphere and flaring activities. Ob ...
... s interpreted as a fundamental fast-kink mode of magnetoacoustic waves. These oscillations can be highly dispersive and can be a useful candidate for the localized heating of the corona of ξ-Boo. It should be noted that it is a binary K-Dwarf with the magnetized atmosphere and flaring activities. Ob ...
The surprising role of magnetism on the phase stability of Fe
... structures at low temperatures. Question 1 can now be addressed as follows. At 0 K, the ferromagnetic ordering in the BCC α phase causes the internal energy (and enthalpy) of that phase to be lower than the internal energy (and enthalpy) of the antiferromagnetic (and paramagnetic) FCC phase, i.e. Hα ...
... structures at low temperatures. Question 1 can now be addressed as follows. At 0 K, the ferromagnetic ordering in the BCC α phase causes the internal energy (and enthalpy) of that phase to be lower than the internal energy (and enthalpy) of the antiferromagnetic (and paramagnetic) FCC phase, i.e. Hα ...
PHY 380L Introduction to Plasma Physics Richard Fitzpatrick
... eventually achieved). In the process, he developed the theory of plasma sheaths; the boundary layers which form between ionized plasmas and solid surfaces. He also discovered that certain regions of a plasma discharge tube exhibit periodic variations of the electron density, which we nowadays term L ...
... eventually achieved). In the process, he developed the theory of plasma sheaths; the boundary layers which form between ionized plasmas and solid surfaces. He also discovered that certain regions of a plasma discharge tube exhibit periodic variations of the electron density, which we nowadays term L ...
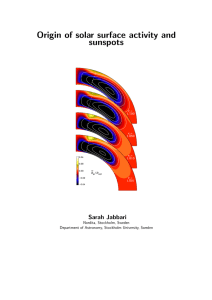
Origin of solar surface activity and sunspots Sarah Jabbari Nordita, Stockholm, Sweden
... collapse of small flux tubes. He found a critical value for the magnetic field strength needed to get such field concentrations. For a field stronger than a certain critical value, the magnetic field will suppress convection. He computed this critical value for the solar convection zone to be about ...
... collapse of small flux tubes. He found a critical value for the magnetic field strength needed to get such field concentrations. For a field stronger than a certain critical value, the magnetic field will suppress convection. He computed this critical value for the solar convection zone to be about ...
FALL 2015 PHYS 1252 Department of Physics & Astronomy, UGA
... Collaboration OK. Go to: http://www.smartphysics.com Enroll in: 2015FALL - DR. G - PHYS 1252: Studio Physics II for Engineers There will be three (3) midterm exams on selected chapters, and one (1) cumulative final exam. No make-ups or re-scheduling permitted. One (1) standard sheet cont ...
... Collaboration OK. Go to: http://www.smartphysics.com Enroll in: 2015FALL - DR. G - PHYS 1252: Studio Physics II for Engineers There will be three (3) midterm exams on selected chapters, and one (1) cumulative final exam. No make-ups or re-scheduling permitted. One (1) standard sheet cont ...
Collisionless interaction of an energetic laser produced plasma C. Constantin
... Meyer and Thiell 1984). While this regime is interesting in itself one can see that these conditions are not maintained long enough for a shock to form (i.e. NT ,⊥ < 1 and NT ,/ < 10). A simple scaling analysis shows that a small ion mass is required for shock formation. Using the standard relation ...
... Meyer and Thiell 1984). While this regime is interesting in itself one can see that these conditions are not maintained long enough for a shock to form (i.e. NT ,⊥ < 1 and NT ,/ < 10). A simple scaling analysis shows that a small ion mass is required for shock formation. Using the standard relation ...
Observations of ubiquitous compressive waves in the Sun`s
... field is much longer than the plasma flows that generate the visible structuring. Waves may be present in the atmosphere even when the magnetic field is not outlined by an intensity enhancement; however, they are far more difficult to identify directly. These intensity enhancements suggest a greater ...
... field is much longer than the plasma flows that generate the visible structuring. Waves may be present in the atmosphere even when the magnetic field is not outlined by an intensity enhancement; however, they are far more difficult to identify directly. These intensity enhancements suggest a greater ...
Correlation Between Nitrogen and Oxygen Content in Planetary
... definite polar nebula, just for reference. Ten hours of observation time were reserved at the University of Arizona’s 90inch Bok telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. This telescope’s large mirror and its spectrograph were used to take exposures of each nebula. The spectrograph separates the ...
... definite polar nebula, just for reference. Ten hours of observation time were reserved at the University of Arizona’s 90inch Bok telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. This telescope’s large mirror and its spectrograph were used to take exposures of each nebula. The spectrograph separates the ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.