A Review of Self Inductance
... Self - Inductance • Faraday postulated that a magnetic field consists of lines of force surrounding the current-carrying conductor. • Think of these lines as elastic bands that ...
... Self - Inductance • Faraday postulated that a magnetic field consists of lines of force surrounding the current-carrying conductor. • Think of these lines as elastic bands that ...
File
... 21.1 – Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnetic Forces - Magnetic force is the force a magnet exerts on another magnet, on a metal (iron) or on moving charges. - 1 aspect of electromagnetic force - Acts over a distance - Magnetic poles – all magnets have 2 – N and S…these are regions where the magnetic ...
... 21.1 – Magnets and Magnetic Fields Magnetic Forces - Magnetic force is the force a magnet exerts on another magnet, on a metal (iron) or on moving charges. - 1 aspect of electromagnetic force - Acts over a distance - Magnetic poles – all magnets have 2 – N and S…these are regions where the magnetic ...
Magnetic Fields
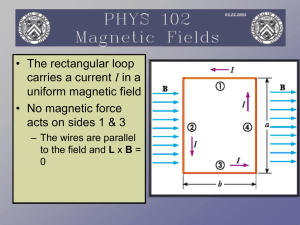
... • The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the ...
... • The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop • The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop • τ = IA x B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the ...
M - BIAC – Duke
... • Gradient magnetic fields change gradually over space and can change quickly over time (thousands of times per second) ...
... • Gradient magnetic fields change gradually over space and can change quickly over time (thousands of times per second) ...
Magnets - Science with Ms. C
... Know that magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that applies a force, a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af fects magnetic materials (includi ...
... Know that magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that applies a force, a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af fects magnetic materials (includi ...
Spintronics Integrating magnetic materials with semiconductors
... Making MEMS • How to make a MEMS device - deposit and etch out materials • Introduction to Micro-machining - Wet and Dry etching - Bulk and surface micro-machining • What kinds of materials are used in MEMS? ...
... Making MEMS • How to make a MEMS device - deposit and etch out materials • Introduction to Micro-machining - Wet and Dry etching - Bulk and surface micro-machining • What kinds of materials are used in MEMS? ...
Electromagnets & magnetism
... of aluminum, nickel, and colbalt) and have a persistent magnetic field Retain magnetic properties better than other materials A strong current is used to align the domains of the alloy Once the domains are lined up, they ...
... of aluminum, nickel, and colbalt) and have a persistent magnetic field Retain magnetic properties better than other materials A strong current is used to align the domains of the alloy Once the domains are lined up, they ...
chapter – 5 magnetic effects of electric current and
... • Third pillar of Maxwel’s electromagnetic theory is the fact that magnetic field lines form closed loops. • Toroid : If a solenoid is bent in the form a circle and its two ends are connected to each other, then the device is called a toroid. OR A device prepared by closely winding an insulated con ...
... • Third pillar of Maxwel’s electromagnetic theory is the fact that magnetic field lines form closed loops. • Toroid : If a solenoid is bent in the form a circle and its two ends are connected to each other, then the device is called a toroid. OR A device prepared by closely winding an insulated con ...
ch29
... solenoid. The back portions of five turns are shown, as are the magnetic field lines due to a current through the solenoid. Each turn produces circular magnetic field lines near itself. Near the solenoid’s axis, the field lines combine into a net magnetic field that is directed along the axis. The c ...
... solenoid. The back portions of five turns are shown, as are the magnetic field lines due to a current through the solenoid. Each turn produces circular magnetic field lines near itself. Near the solenoid’s axis, the field lines combine into a net magnetic field that is directed along the axis. The c ...
PHYS_3342_111511
... The small magnetism is of two kinds: • Diamagnetics are repelled from magnetic fields • Paramagnetics are attracted towards magnetic fields This is unlike the electric effect in matter, which always causes dielectrics to be attracted. ...
... The small magnetism is of two kinds: • Diamagnetics are repelled from magnetic fields • Paramagnetics are attracted towards magnetic fields This is unlike the electric effect in matter, which always causes dielectrics to be attracted. ...
ECE 341: Electromagnetic Fields I Concepts: Maxwell’s Equations
... forms, and boundary conditions to solve complex static and low-frequency electromagnetic-field problems Can mathematically model electric and magnetic properties of material media in relation with field equations Understands how electromagnetic material properties can be exploited in engineering app ...
... forms, and boundary conditions to solve complex static and low-frequency electromagnetic-field problems Can mathematically model electric and magnetic properties of material media in relation with field equations Understands how electromagnetic material properties can be exploited in engineering app ...
7 - web page for staff
... Analogy to Gauss’s law Use for magnetostatic’s problems with sufficient symmetry. Ampere’s circuital law – the integration of around any closed path is equal to the net current enclosed by that path. ...
... Analogy to Gauss’s law Use for magnetostatic’s problems with sufficient symmetry. Ampere’s circuital law – the integration of around any closed path is equal to the net current enclosed by that path. ...
01 - TBAISD Moodle
... to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft iron core is called a(n) a. electromagnet. c. magnetic core. b. maglev. d. magne ...
... to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft iron core is called a(n) a. electromagnet. c. magnetic core. b. maglev. d. magne ...
01 - Edublogs
... to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft iron core is called a(n) a. electromagnet. c. magnetic core. b. maglev. d. magne ...
... to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft iron core is called a(n) a. electromagnet. c. magnetic core. b. maglev. d. magne ...
Magnetism Notes - Brookwood High School
... of needle Cause needle to be deflected (like repel, etc.) Amount of deflection indicates amount of current ...
... of needle Cause needle to be deflected (like repel, etc.) Amount of deflection indicates amount of current ...
Lecture 12:introduction to B fields, aurora
... ASK1: 20 seconds of data at 32 fps 18:21:10 – 18:21:30 UT ...
... ASK1: 20 seconds of data at 32 fps 18:21:10 – 18:21:30 UT ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.