Microwave Methods and Detection Techniques for Electron Spin
... Electron spin resonance (ESR) originated more than sixty years ago, when Zavoisky (1945) reported the first successful measurement of ESR signals in several salts, copper sulfate and manganese sulfate [1]. ESR is applied whenever a system has unpaired electrons. For instance, it can be used to under ...
... Electron spin resonance (ESR) originated more than sixty years ago, when Zavoisky (1945) reported the first successful measurement of ESR signals in several salts, copper sulfate and manganese sulfate [1]. ESR is applied whenever a system has unpaired electrons. For instance, it can be used to under ...
UNIT - StudyGuide.PK
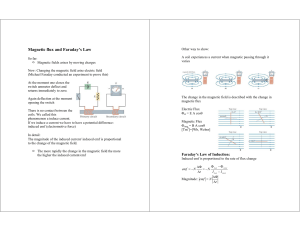
... Context This unit is a continuation of the work on magnetic fields to study aspects of electromagnetic induction. An introduction to alternating current is also included. Outline The concepts of flux and flux linkage are introduced so that electromagnetic induction may be studied. Aspects of alterna ...
... Context This unit is a continuation of the work on magnetic fields to study aspects of electromagnetic induction. An introduction to alternating current is also included. Outline The concepts of flux and flux linkage are introduced so that electromagnetic induction may be studied. Aspects of alterna ...
Your Comments
... Please explain the right hand rule when there are two wires and you are trying to find the direction of the force. I am getting confused with all these right hand rules. So do you have any age-old advice for Unofficial? After Tuesdays lecture I felt like I understood the torque stuff, but as soon as ...
... Please explain the right hand rule when there are two wires and you are trying to find the direction of the force. I am getting confused with all these right hand rules. So do you have any age-old advice for Unofficial? After Tuesdays lecture I felt like I understood the torque stuff, but as soon as ...
Solution Derivations for Capa #10
... D) Upon leaving the field, a clockwise current flows in the loop. E) Upon entering the field, a clockwise current flows in the loop. ANSWER: A) False, when the loop is moving out of the field, the left hand side will be out of the magnetic field so no force will be on it. The current will be moving ...
... D) Upon leaving the field, a clockwise current flows in the loop. E) Upon entering the field, a clockwise current flows in the loop. ANSWER: A) False, when the loop is moving out of the field, the left hand side will be out of the magnetic field so no force will be on it. The current will be moving ...
Applied field Mössbauer study of shape anisotropy in Fe nanowire
... to the expression K = M SHapp / 2具sin 典, where 0 ⬍ ⬍ / 2. Using M S of bulk Fe and the average 具sin 典 at different applied fields [Fig. 3(a)], one can estimate the average magnetic anisotropy constant K ⬇ 7.3⫻ 106 ergs/ cm3. The shape anisotropy constant is one order of magnitude larger than t ...
... to the expression K = M SHapp / 2具sin 典, where 0 ⬍ ⬍ / 2. Using M S of bulk Fe and the average 具sin 典 at different applied fields [Fig. 3(a)], one can estimate the average magnetic anisotropy constant K ⬇ 7.3⫻ 106 ergs/ cm3. The shape anisotropy constant is one order of magnitude larger than t ...
October 20th Induction and Inductance
... Checkpoint #3 – Four wire loops with edge lengths of either L or 2L. All loops move through uniform B field at same velocity. Rank the four loops according to maximum magnitude of induced emf, greatest first. ...
... Checkpoint #3 – Four wire loops with edge lengths of either L or 2L. All loops move through uniform B field at same velocity. Rank the four loops according to maximum magnitude of induced emf, greatest first. ...
Magnetohydrodynamic Effects in Gamma
... (if optical flashes are related the emission from RS) • The magnetic acceleration mechanism suggests that s and g are not independent parameters at the deceleration radius. • For high-s flow, ejecta would experience magnetic acceleration at small radii, before reaching the coasting regime; the coast ...
... (if optical flashes are related the emission from RS) • The magnetic acceleration mechanism suggests that s and g are not independent parameters at the deceleration radius. • For high-s flow, ejecta would experience magnetic acceleration at small radii, before reaching the coasting regime; the coast ...
Lecture 1
... electrification effects were not confined to just amber The electrification effects were a general phenomena ...
... electrification effects were not confined to just amber The electrification effects were a general phenomena ...
magnetic orientation by hatchling loggerhead sea turtles
... Hatchling loggerheads were obtained from a beach hatchery located about 30km south of Fort Pierce, Florida, USA. The hatchery consisted of 123 nests relocated from local beaches unsafe for hatchlings. All nests were moved to the hatchery within 24 h of natural deposition, positioned in a row paralle ...
... Hatchling loggerheads were obtained from a beach hatchery located about 30km south of Fort Pierce, Florida, USA. The hatchery consisted of 123 nests relocated from local beaches unsafe for hatchlings. All nests were moved to the hatchery within 24 h of natural deposition, positioned in a row paralle ...
Modeling of induced current into the human body by low
... low-frequency (up to 1 MHz) electromagnetic fields is the generation of induced currents inside the human body [1]. While the short-term effects of this exposure are well known, there is no convincing evidence of (possibly hazardous) long-term effects of the electromagnetic fields on the human health ...
... low-frequency (up to 1 MHz) electromagnetic fields is the generation of induced currents inside the human body [1]. While the short-term effects of this exposure are well known, there is no convincing evidence of (possibly hazardous) long-term effects of the electromagnetic fields on the human health ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... function of time? Note: At time t = 0 s, the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. ...
... function of time? Note: At time t = 0 s, the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.