Magnetism - TeacherWeb
... • The earliest magnets were found naturally in the mineral magnetite which is abundant the rock-type lodestone. These magnets were used by the ancient peoples as compasses to guide sailing vessels. • Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of a magnetic material due to the arrangement of i ...
... • The earliest magnets were found naturally in the mineral magnetite which is abundant the rock-type lodestone. These magnets were used by the ancient peoples as compasses to guide sailing vessels. • Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of a magnetic material due to the arrangement of i ...
marcelo.loewe
... E. Ferrer, V.de la Incera and X. J. Wen (arXiiv: 1407.3503) have considered this problem for the the strong magnetic field scenario (no temperature), finding an anisotropic behavior where the coupling decreases with B . ...
... E. Ferrer, V.de la Incera and X. J. Wen (arXiiv: 1407.3503) have considered this problem for the the strong magnetic field scenario (no temperature), finding an anisotropic behavior where the coupling decreases with B . ...
Electromagnetism - juan-roldan
... • Electromagnets can easily be made at home with a copper wire, a nail, and a battery. • Wrap the wire around the nail and hook it to the positive and negative ends of the battery. • Suddenly the nail is magnetic and can attract iron objects. ...
... • Electromagnets can easily be made at home with a copper wire, a nail, and a battery. • Wrap the wire around the nail and hook it to the positive and negative ends of the battery. • Suddenly the nail is magnetic and can attract iron objects. ...
FGT3_ConcepTestsch28 quiz
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
PHY 231 Lecture 29 (Fall 2006)
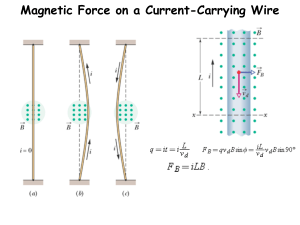
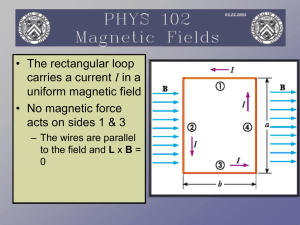
... The magnetic force is exerted on each moving charge in the wire The total force is the sum of all the magnetic forces on all the individual charges producing the current F = B I ℓ sin θ θ is the angle between B and the direction of I The direction is found by the right hand rule, placing your fi ...
... The magnetic force is exerted on each moving charge in the wire The total force is the sum of all the magnetic forces on all the individual charges producing the current F = B I ℓ sin θ θ is the angle between B and the direction of I The direction is found by the right hand rule, placing your fi ...
Electromagnetic Induction
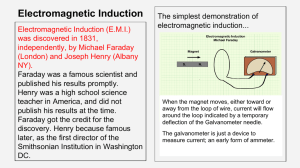
... Faraday’s Law Faraday discovered the physical phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
... Faraday’s Law Faraday discovered the physical phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.