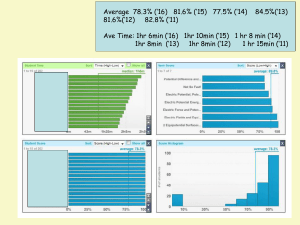
Chapter28 - Academic Program Pages
... 79. A proton, a deuteron (q = +e, m = 2.0 u), and an alpha particle (q = +2e, m = 4.0 u) are accelerated through the same potential difference and then enter the same region of uniform magnetic field B, moving perpendicular to B. What is the ratio of (a) the proton’s kinetic energy Kp to the alpha p ...
... 79. A proton, a deuteron (q = +e, m = 2.0 u), and an alpha particle (q = +2e, m = 4.0 u) are accelerated through the same potential difference and then enter the same region of uniform magnetic field B, moving perpendicular to B. What is the ratio of (a) the proton’s kinetic energy Kp to the alpha p ...
Magnetostatics – Magnetic Flux Density
... From this characteristic of magnetic fields, it is easy to see that the net magnetic flux passing through a Gaussian surface (a closed surface as shown in Figure 3.26) must be zero. What goes into the surface must come back out. Thus we have Gauss’s law for static magnetic fields ...
... From this characteristic of magnetic fields, it is easy to see that the net magnetic flux passing through a Gaussian surface (a closed surface as shown in Figure 3.26) must be zero. What goes into the surface must come back out. Thus we have Gauss’s law for static magnetic fields ...
Study Guide
... 27. Draw a picture of the magnetic domains in a magnetic. 28. The north pole of a compass points to which geographic pole? Explain your answer. 29. How can you adjust the coil wires on an electromagnet to make the electromagnet stronger? 30. Give an example of a ferromagnetic material. 31. Explain t ...
... 27. Draw a picture of the magnetic domains in a magnetic. 28. The north pole of a compass points to which geographic pole? Explain your answer. 29. How can you adjust the coil wires on an electromagnet to make the electromagnet stronger? 30. Give an example of a ferromagnetic material. 31. Explain t ...
fourth nine weeks
... mirrors, prisms, tuning forks, optical illusions, lights, color, musical instruments, common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...
... mirrors, prisms, tuning forks, optical illusions, lights, color, musical instruments, common household items to demonstrate sound and light qualities. Post assessment – quiz ...
Electromagnetism - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... -magnitite (loadstone) is a special mineral found on Earth & is magnetized by exposure to Earth's magnetic field ...
... -magnitite (loadstone) is a special mineral found on Earth & is magnetized by exposure to Earth's magnetic field ...
The Earth`s Magnetic Field!
... a conductive body in the presence of a magnetic field acts to regenerate that magnetic field. • In computer simulations, it is observed that magnetic field lines can sometimes become tangled and disorganized through the chaotic motions of liquid metal in the Earth's core. • In some simulations, this ...
... a conductive body in the presence of a magnetic field acts to regenerate that magnetic field. • In computer simulations, it is observed that magnetic field lines can sometimes become tangled and disorganized through the chaotic motions of liquid metal in the Earth's core. • In some simulations, this ...
Magnetic Induction
... • Once a current is established in a circuit, self inductance will tend to keep the current going even after the circuit is turned off… • No it isn't perpetual motion. • The current will decay to zero in a short time, but not instantly. ...
... • Once a current is established in a circuit, self inductance will tend to keep the current going even after the circuit is turned off… • No it isn't perpetual motion. • The current will decay to zero in a short time, but not instantly. ...
9J Force Fields and Electromagnets
... An atom consists of a central nucleus with small particles called electrons moving around it. An atom normally has no overall charge because it has the same number of positive and negative charges. When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If t ...
... An atom consists of a central nucleus with small particles called electrons moving around it. An atom normally has no overall charge because it has the same number of positive and negative charges. When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If t ...
Magic Magnets
... Only a few substances have atoms in which the magnets line up their forces. When some metals are put in a magnetic field all of its atoms line up which is how the iron nail became a temporary magnet. Objects, like the iron nail, that become temporarily magnetized are made of ferromagnetic material. ...
... Only a few substances have atoms in which the magnets line up their forces. When some metals are put in a magnetic field all of its atoms line up which is how the iron nail became a temporary magnet. Objects, like the iron nail, that become temporarily magnetized are made of ferromagnetic material. ...
Magnetic Force - WordPress.com
... positive charge is in the direction opposite the direction of the magnetic force exer ted on a negative charge moving in the ...
... positive charge is in the direction opposite the direction of the magnetic force exer ted on a negative charge moving in the ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.