Electromagnetic Induction
... proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the open area A of the loop. Such a loop is called a search coil. Thus, if we produce a varying magnetic field, and thus a varying flux, we can detect it using a search coil connected to a galvanometer. A varying magnetic field is produced ...
... proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the open area A of the loop. Such a loop is called a search coil. Thus, if we produce a varying magnetic field, and thus a varying flux, we can detect it using a search coil connected to a galvanometer. A varying magnetic field is produced ...
Building Blocks - The SPS Observer
... field. tric current is passed through this wire. . . . the effect will be that of a characterizing Studying toroids yielded new Studying insights toroids has fundamental yielded insights Atoms, into fund for be used as curlmeters to detect the curl of magnetic fields. The curl of a magnetic ¶ inare ...
... field. tric current is passed through this wire. . . . the effect will be that of a characterizing Studying toroids yielded new Studying insights toroids has fundamental yielded insights Atoms, into fund for be used as curlmeters to detect the curl of magnetic fields. The curl of a magnetic ¶ inare ...
Nicholas_Callan - University College Cork
... coils could give large electrical shocks and Callan used this as another way of testing battery power. He persuaded his students to take shocks from the coils and he gauged the power of the battery from their reactions. One student named William Walsh, who later became Archbishop of Dublin, was rend ...
... coils could give large electrical shocks and Callan used this as another way of testing battery power. He persuaded his students to take shocks from the coils and he gauged the power of the battery from their reactions. One student named William Walsh, who later became Archbishop of Dublin, was rend ...
Slide
... Nd:Yag laser (600 mJ/pp, 10 ns pulse length, Power -> 10ns of MW!!) Provides energy for dye laser ...
... Nd:Yag laser (600 mJ/pp, 10 ns pulse length, Power -> 10ns of MW!!) Provides energy for dye laser ...
Errors and Limitations of the Magnetic Compass
... There is no practical way of eliminating the effects of the local field. If the points at which the measurements have been made are 50 miles apart, and declination values are averaged over groups of about nine stations (three by three) the effects of the local field are uncorrelated at neighbouring ...
... There is no practical way of eliminating the effects of the local field. If the points at which the measurements have been made are 50 miles apart, and declination values are averaged over groups of about nine stations (three by three) the effects of the local field are uncorrelated at neighbouring ...
Conceptual Physical Science 5e — Chapter 9
... A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field, and it is zero when motion is parallel to the field. ...
... A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field, and it is zero when motion is parallel to the field. ...
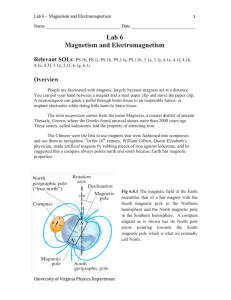
Lab 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Galileo
... In 1750 John Michell, an English physicist and astronomer, found that magnetic poles obey the inverse-square law, and his results were confirmed by Charles Coulomb. The subjects of magnetism and electricity developed almost independently of each other until 1820, when a Danish physicist named Hans C ...
... In 1750 John Michell, an English physicist and astronomer, found that magnetic poles obey the inverse-square law, and his results were confirmed by Charles Coulomb. The subjects of magnetism and electricity developed almost independently of each other until 1820, when a Danish physicist named Hans C ...
Maxwell, Hertz, the Maxwellians, and the Early History of
... set forth in his "Thought on Ray Vibrations." The electromagnetic theory of light, ac proposed by him, is the same in substance as that which I have begun to develop in this paper, except that in 1846 there were no data to calculate the velocity of propagation." III. MAXWELL'S ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY ...
... set forth in his "Thought on Ray Vibrations." The electromagnetic theory of light, ac proposed by him, is the same in substance as that which I have begun to develop in this paper, except that in 1846 there were no data to calculate the velocity of propagation." III. MAXWELL'S ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY ...
Ch7 sec1
... 10 different locations near the bar magnet. 2. Compare Oersted’s experiment with a single wire and compass and your investigation with a wire and compass. 3. Suppose 100 compasses were placed on a horizontal surface to surround a vertical current-carrying wire. Describe the pattern of directions in ...
... 10 different locations near the bar magnet. 2. Compare Oersted’s experiment with a single wire and compass and your investigation with a wire and compass. 3. Suppose 100 compasses were placed on a horizontal surface to surround a vertical current-carrying wire. Describe the pattern of directions in ...
Electromagnetic Theory - National Open University of Nigeria
... The basic equations of electromagnetism are the four Maxwell’s equations and the Lorentz force law. In principle, these together with Newton’s second law of motion are enough to completely determine the motion of an assembly of charges given the initial positions and velocities of all the charges. I ...
... The basic equations of electromagnetism are the four Maxwell’s equations and the Lorentz force law. In principle, these together with Newton’s second law of motion are enough to completely determine the motion of an assembly of charges given the initial positions and velocities of all the charges. I ...
Motors and Generators
... The bipolar nature of the pulses (above and below the centre axis,) is because the magnet first approaches and then retreats from the turns in the coil, generating a current in one direction and then the other. Eddy current magic The unmagnetised projectile did exactly what was expected - it fell un ...
... The bipolar nature of the pulses (above and below the centre axis,) is because the magnet first approaches and then retreats from the turns in the coil, generating a current in one direction and then the other. Eddy current magic The unmagnetised projectile did exactly what was expected - it fell un ...
Chapter 8: Magnetism and Its Uses
... produced by an electric current. Explain how an electromagnet produces a magnetic field. Describe how electromagnets are used. Explain how an electric motor operates. ...
... produced by an electric current. Explain how an electromagnet produces a magnetic field. Describe how electromagnets are used. Explain how an electric motor operates. ...
Kapittel 26
... current and corresponding field. According to Lenz’s law, the induced current creates an induced field that opposes the change in flux. Solve: (a) When magnet 1 is close to the solenoid there is flux to the left through the solenoid. As magnet 1 moves away there is less flux to the left. The induced ...
... current and corresponding field. According to Lenz’s law, the induced current creates an induced field that opposes the change in flux. Solve: (a) When magnet 1 is close to the solenoid there is flux to the left through the solenoid. As magnet 1 moves away there is less flux to the left. The induced ...
12.6 The Direct Current Motor
... reliable and economical. However, the brushes in these designs make contact with the split rings and can wear out. Also, brush designs often produce small sparks as the brushes go past the splits. There is a design that does not use brushes. 1. Research brushless motor designs and their applications ...
... reliable and economical. However, the brushes in these designs make contact with the split rings and can wear out. Also, brush designs often produce small sparks as the brushes go past the splits. There is a design that does not use brushes. 1. Research brushless motor designs and their applications ...
The Coriolis Force in Maxwell`s Equations
... of the 1861 paper, and the combination would be referred to as the Ampère/Maxwell equation. In a modern day textbook, the addition of Maxwell’s displacement current to equation [C] would not be explained in terms of total electric current as per Maxwell’s 1861 derivation, but rather in terms of addi ...
... of the 1861 paper, and the combination would be referred to as the Ampère/Maxwell equation. In a modern day textbook, the addition of Maxwell’s displacement current to equation [C] would not be explained in terms of total electric current as per Maxwell’s 1861 derivation, but rather in terms of addi ...
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics
... Astrophysical objects are distant and most of them have extreme environments such that none of the modern day probes would survive in them. Since we have access to the radiation emitted by them, we should gain an understanding of the properties of the astrophysical source by observing these radiatio ...
... Astrophysical objects are distant and most of them have extreme environments such that none of the modern day probes would survive in them. Since we have access to the radiation emitted by them, we should gain an understanding of the properties of the astrophysical source by observing these radiatio ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.