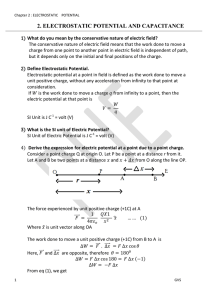
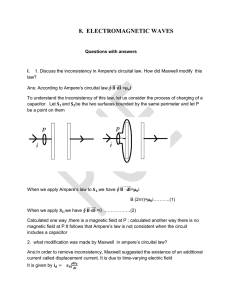
Homework Set #3 - Solutions
... Homework Problem Set 3 - Solutions Partial credit may be given even if the final answer is incorrect so please show all work! Question 1 (1 point) What is Lenz’s Law? To which basic principle of physics is it most closely related? 1) Lenz’s law = The induced current in a loop is in the direction tha ...
... Homework Problem Set 3 - Solutions Partial credit may be given even if the final answer is incorrect so please show all work! Question 1 (1 point) What is Lenz’s Law? To which basic principle of physics is it most closely related? 1) Lenz’s law = The induced current in a loop is in the direction tha ...
Lesson 10
... do work. Each piece of equipment creates a load when it is used. The load cannot exceed the available power. Electricity and magnetism are closely related phenomena. Magnetism induces electricity in a wire. The flow of electricity through a conductor creates a magnetic field. Photovoltaic cells may ...
... do work. Each piece of equipment creates a load when it is used. The load cannot exceed the available power. Electricity and magnetism are closely related phenomena. Magnetism induces electricity in a wire. The flow of electricity through a conductor creates a magnetic field. Photovoltaic cells may ...
Electromagnetism
... invisible lines of force. The first known magnets were natural ones, like lodestone. Scientists began to wonder if they could make artificial magnets, too. Artificial means something that is manmade. ...
... invisible lines of force. The first known magnets were natural ones, like lodestone. Scientists began to wonder if they could make artificial magnets, too. Artificial means something that is manmade. ...
Lesson 12. Topic “Magnetic effect of an electric current”. Grammar
... decided to establish the relation between a flow of current and a magnetic needle. It took him at least 13 years more to find out that a compass needle is deflected when brought near a wire through which the electric current flows. At last, during a lecture he adjusted, by chance, the wire parallel ...
... decided to establish the relation between a flow of current and a magnetic needle. It took him at least 13 years more to find out that a compass needle is deflected when brought near a wire through which the electric current flows. At last, during a lecture he adjusted, by chance, the wire parallel ...
NEW METHOD OF ELECTROSTATIC ACCELERATING AND
... a very low energy (63.0 keV in the centre-of-mass frame). Head-on-tail collisions at equal orbital moments are considered. In this case atomic ions of deuterium and tritium need correspondingly 0.90 and 0.63 MeV of energy. The physical cost of one neutron is 1.5 MeV, which essential smaller than tha ...
... a very low energy (63.0 keV in the centre-of-mass frame). Head-on-tail collisions at equal orbital moments are considered. In this case atomic ions of deuterium and tritium need correspondingly 0.90 and 0.63 MeV of energy. The physical cost of one neutron is 1.5 MeV, which essential smaller than tha ...
PHYSICS E06 11
... 1. Balloons and Static Electricity – Use this lab to help students understand electric charges: ...
... 1. Balloons and Static Electricity – Use this lab to help students understand electric charges: ...
P6 Revision Questions Motors and Generators
... How is electricity generated at a power station? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. A bar magnet rotates inside coils of wire. An electromagnet rotates around a permanent magnet. ...
... How is electricity generated at a power station? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to the correct answer. A bar magnet rotates inside coils of wire. An electromagnet rotates around a permanent magnet. ...
Physics 417G : Solutions for Problem set 2
... |~x − ~x0 |3 where ~x − ~x0 is the vector from ~x, point of source charge, to the integration volume d3 x0 . b) The right side of the expression (1) can be found from Gauss’s law for the uniformly charged solid sphere, which can be written in terms of the dipole moment of q. c) Use the superposition ...
... |~x − ~x0 |3 where ~x − ~x0 is the vector from ~x, point of source charge, to the integration volume d3 x0 . b) The right side of the expression (1) can be found from Gauss’s law for the uniformly charged solid sphere, which can be written in terms of the dipole moment of q. c) Use the superposition ...
Draft - NYU Steinhardt
... metals are good conductors, especially copper. Electric current does not pass easily through other materials. These materials are insulators. Air, rubber, glass, and plastic are insulators. Take a look at an electric cord. The metal wire inside conducts—or carries—the current into an appliance. The ...
... metals are good conductors, especially copper. Electric current does not pass easily through other materials. These materials are insulators. Air, rubber, glass, and plastic are insulators. Take a look at an electric cord. The metal wire inside conducts—or carries—the current into an appliance. The ...
Electric Charge and Static Electricity Reading
... Name ___________________________________ Date ____________ Period ___________ ...
... Name ___________________________________ Date ____________ Period ___________ ...
The History of Electricity – A Timeline
... hollow charged vessels contain no charge on the inside and based on his knowledge that hollow shells of mass have no gravity inside correctly deduces that the electric force law is inverse square. ca 1775 - Henry Cavendish invents the idea of capacitance and resistance (the latter without any way of ...
... hollow charged vessels contain no charge on the inside and based on his knowledge that hollow shells of mass have no gravity inside correctly deduces that the electric force law is inverse square. ca 1775 - Henry Cavendish invents the idea of capacitance and resistance (the latter without any way of ...
General Physics II: Oscillations, Waves, Electromagnetism
... NOTE: Neither charge can interact with its own field. ...
... NOTE: Neither charge can interact with its own field. ...
Energy TEST-Light, Sound, Electricity (and magnetism)
... **Remember…..ALL of this, Light, Sound, Waves, Thermal Energy, and Electricity…..ALL can be explained within the realm of the LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: Energy cannot be created NOR destroyed, only changed or converted. THINK: A Battery (chemical energy) sent current through the wires of a circu ...
... **Remember…..ALL of this, Light, Sound, Waves, Thermal Energy, and Electricity…..ALL can be explained within the realm of the LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: Energy cannot be created NOR destroyed, only changed or converted. THINK: A Battery (chemical energy) sent current through the wires of a circu ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.