PHY 112 Master Syllabus
... • a broad view of the physics of electromagnetism, which is the combination of electric and magnetic phenomena, the basis of the natural world. • a knowledge of electric and magnetic quantities and physical laws associated with them. • a knowledge of the related mathematics required to manipulate th ...
... • a broad view of the physics of electromagnetism, which is the combination of electric and magnetic phenomena, the basis of the natural world. • a knowledge of electric and magnetic quantities and physical laws associated with them. • a knowledge of the related mathematics required to manipulate th ...
PHY 114 Master Syllabus
... include electric and magnetic fields, electric and magnetic flux, electric and magnetic dipoles, electric potential, and elementary circuits consisting of batteries, resistors, capacitors and inductors. Also studied are the physical laws associated with electromagnetic phenomena including Coulomb's ...
... include electric and magnetic fields, electric and magnetic flux, electric and magnetic dipoles, electric potential, and elementary circuits consisting of batteries, resistors, capacitors and inductors. Also studied are the physical laws associated with electromagnetic phenomena including Coulomb's ...
Presentation
... It is the task of the receiver electronics to measure the very small signal from the eddy currents in the presence of the much larger signal arising from the primary magnetic field. To facilitate this measurement an internally generated signal is used to cancel or "null" the large primary signal so ...
... It is the task of the receiver electronics to measure the very small signal from the eddy currents in the presence of the much larger signal arising from the primary magnetic field. To facilitate this measurement an internally generated signal is used to cancel or "null" the large primary signal so ...
PPT
... Parallel Plate: C = e0A/d Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1+C2 Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1+1/C2 Batteries provide fixed potential difference ...
... Parallel Plate: C = e0A/d Capacitors in parallel: Ceq = C1+C2 Capacitors in series: 1/Ceq = 1/C1+1/C2 Batteries provide fixed potential difference ...
ppt - plutonium
... terms of the electric field near the surface? How do we apply Gauss’s Law to determine the total charge on a surface in terms of the electric field near the surface? How do we prove and apply the relationship between the surface charge density on a conductor and the electric field strength near ...
... terms of the electric field near the surface? How do we apply Gauss’s Law to determine the total charge on a surface in terms of the electric field near the surface? How do we prove and apply the relationship between the surface charge density on a conductor and the electric field strength near ...
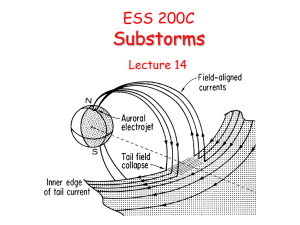
expansion phase
... • The currents responsible for the diurnal variation. – Two cells of current circulate around foci located at about 300 magnetic latitude. – At the equator the currents flow from dawn to dusk.This is called the equatorial electrojet. ...
... • The currents responsible for the diurnal variation. – Two cells of current circulate around foci located at about 300 magnetic latitude. – At the equator the currents flow from dawn to dusk.This is called the equatorial electrojet. ...
Gravitation, Electrostatics, and the Electron-Positron
... to have an effect on acceleration in relation to electrostatic forces, but not in relation to gravitational forces. The latter point is not so. This is a misconception based on Galileo’s famous experiment at the Leaning Tower of Pisa. When the mutual acceleration that two gravitating bodies induce o ...
... to have an effect on acceleration in relation to electrostatic forces, but not in relation to gravitational forces. The latter point is not so. This is a misconception based on Galileo’s famous experiment at the Leaning Tower of Pisa. When the mutual acceleration that two gravitating bodies induce o ...
Homebrew Piezoelectric Crystal
... How to make Piezoelectric Ceramics All ceramics are man-made and are forced to become piezoelectric through a process of polarization The process of “poling” exposes ceramic material to a high-intensity electric field which aligns the the electric dipoles and causes the ceramic to become piezoelect ...
... How to make Piezoelectric Ceramics All ceramics are man-made and are forced to become piezoelectric through a process of polarization The process of “poling” exposes ceramic material to a high-intensity electric field which aligns the the electric dipoles and causes the ceramic to become piezoelect ...
Lecture 6
... (2) Magnitude: surface must be chosen such that E has the same value at all points on the surface when E is perpendicular to the surface. ...
... (2) Magnitude: surface must be chosen such that E has the same value at all points on the surface when E is perpendicular to the surface. ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.