Slide 1
... rarely in the course of human events have so many starting equations been given in so little time ...
... rarely in the course of human events have so many starting equations been given in so little time ...
DEVICE TOPIC THEORETICAL Lenz’s Law Demonstration
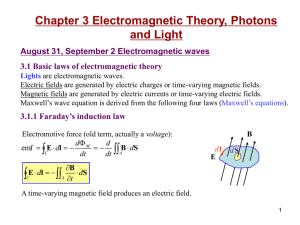
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
Electric Potential Difference
... Use >, <, and = signs to compare the electric potential (V) at the four points of the circuit. VA ...
... Use >, <, and = signs to compare the electric potential (V) at the four points of the circuit. VA ...
Name ______ period __
... energy to ___________________ energy to cause motion. Stereo speakers – magnetic ______________cause motion that produce ________________ waves 14.Faraday’s Law - An _________________ current can be produced in a circuit by a _________________________ magnetic field. Electromagnetic _______________ ...
... energy to ___________________ energy to cause motion. Stereo speakers – magnetic ______________cause motion that produce ________________ waves 14.Faraday’s Law - An _________________ current can be produced in a circuit by a _________________________ magnetic field. Electromagnetic _______________ ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... What causes magnetism? How is magnetism linked to electric charges? • Magnetic fields come from moving charges • a moving charge around an atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move ( ...
... What causes magnetism? How is magnetism linked to electric charges? • Magnetic fields come from moving charges • a moving charge around an atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move ( ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism.pptx
... What causes magnetism? How is magnetism linked to electric charges? • Magnetic fields come from moving charges • a moving charge around an atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to mo ...
... What causes magnetism? How is magnetism linked to electric charges? • Magnetic fields come from moving charges • a moving charge around an atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to mo ...
Slide 1
... All matter is composed of atoms, which are composed of negative electrons and positive protons. These opposite charges attract each other and require a force to separate. Rubbing your feet on the carpet, combing your hair (both “charge by friction”), or passing a wire through a magnetic field can pr ...
... All matter is composed of atoms, which are composed of negative electrons and positive protons. These opposite charges attract each other and require a force to separate. Rubbing your feet on the carpet, combing your hair (both “charge by friction”), or passing a wire through a magnetic field can pr ...
Lecture 1.2 : Electric Force and Electric Field
... What do we already know about the qualities of this new Electric force we are looking for?! ‣ Oppositely charged objects attract, like charged objects repel.! ‣ The more vigorously we charge an object, the stronger it interacts with other charged objects.! ...
... What do we already know about the qualities of this new Electric force we are looking for?! ‣ Oppositely charged objects attract, like charged objects repel.! ‣ The more vigorously we charge an object, the stronger it interacts with other charged objects.! ...
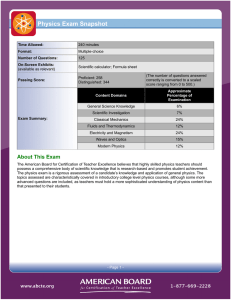
Physics Exam Snapshot - American Board for Certification of
... Electric field and its relation to force and charge ...
... Electric field and its relation to force and charge ...
Sections 2 - Columbia Physics
... 5. A static magnetic monopole (i.e., a point magnetic charge giving rise to a Coulomb magnetic field) is located at the origin and a static electric charge is located on the z-axis at (0, 0, a). (a) Write expression for the magnetic and electric fields in terms of the magnetic charge g and electric ...
... 5. A static magnetic monopole (i.e., a point magnetic charge giving rise to a Coulomb magnetic field) is located at the origin and a static electric charge is located on the z-axis at (0, 0, a). (a) Write expression for the magnetic and electric fields in terms of the magnetic charge g and electric ...
lesson 5 review with answers
... Before You Read Lesson 5 Read each statement below. Place a check mark in the circle to indicate whether you agree or disagree with the statement. 1. All electric currents provide the same amount of energy. 2. Magnets can be used to produce electricity. 3. Electricity powers generators. 4. In a gene ...
... Before You Read Lesson 5 Read each statement below. Place a check mark in the circle to indicate whether you agree or disagree with the statement. 1. All electric currents provide the same amount of energy. 2. Magnets can be used to produce electricity. 3. Electricity powers generators. 4. In a gene ...
Electricity - School Links Programme
... Other alternative energy sources being used today are geothermal and biomass ...
... Other alternative energy sources being used today are geothermal and biomass ...
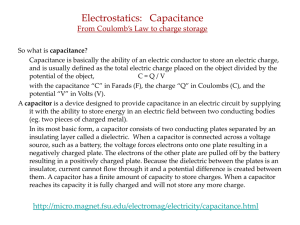
Coulomb`s Law
... equation because the charges q1 and q2 can be either positive or negative While the force F will always remain positive When the both charges q1 and q2 have the same sign either positive or negative the forces are repulsive When the both charges q1 and q2 have the opposite sign positive and ne ...
... equation because the charges q1 and q2 can be either positive or negative While the force F will always remain positive When the both charges q1 and q2 have the same sign either positive or negative the forces are repulsive When the both charges q1 and q2 have the opposite sign positive and ne ...
Vol. 19, No 4, Nov 2016
... In 1600, the English scientist William Gilbert coined the New Latin word electricus from ἤλεκτρον (ēlektron), the Greek word for amber, which soon gave rise to the English words "electric" and "electricity”. In 1660 Otto von Guericke invented the first primitive electrostatic generator consisting of ...
... In 1600, the English scientist William Gilbert coined the New Latin word electricus from ἤλεκτρον (ēlektron), the Greek word for amber, which soon gave rise to the English words "electric" and "electricity”. In 1660 Otto von Guericke invented the first primitive electrostatic generator consisting of ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.