TEP Earth`s magnetic field with Cobra4 Mobile
... slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle α of the magnetic needle is measured from its resting posit ...
... slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle α of the magnetic needle is measured from its resting posit ...
Welcome to Faraday`s Electromagnetic Lab! To begin, search
... Once you are in the simulation, click on the “Pickup Coil” tab above. You should see the screen shown to the right. Take a minute to familiarize yourself with the controls and parts of the simulation, and then begin the following activity. ...
... Once you are in the simulation, click on the “Pickup Coil” tab above. You should see the screen shown to the right. Take a minute to familiarize yourself with the controls and parts of the simulation, and then begin the following activity. ...
Unit 14: Electric Charge
... o The fundamental quantity in electrostatics is electric charge. There are two kinds of charge, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to ...
... o The fundamental quantity in electrostatics is electric charge. There are two kinds of charge, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to ...
230007 - EM - Electromagnetism
... Learning objectives of the subject To learn the main principles and laws of Electromagnetism, and to adquire the ability of solving fundamental problems related to its main topics either in vacuum or in material media. Formulation of the laws in integral and differential form (Maxwell equations) . D ...
... Learning objectives of the subject To learn the main principles and laws of Electromagnetism, and to adquire the ability of solving fundamental problems related to its main topics either in vacuum or in material media. Formulation of the laws in integral and differential form (Maxwell equations) . D ...
Department of Natural Sciences
... c. Will sometimes repel and sometimes attract each other. d. Will neither repel nor attract each other. 3. A negative charge moves inside a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the charge? a. Toward the top of the page. b. Toward the bottom of the pa ...
... c. Will sometimes repel and sometimes attract each other. d. Will neither repel nor attract each other. 3. A negative charge moves inside a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the charge? a. Toward the top of the page. b. Toward the bottom of the pa ...
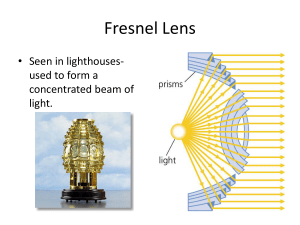
Fresnel Lens
... • But now, a behavior of light was observed that fit Planck’s energy packet idea. • So electromagnetic radiation appears to behave as if it is both a wave and a particle. • In fact, you can think of light as discrete wave packets-packets of waves which, depending upon the measurement you make, somet ...
... • But now, a behavior of light was observed that fit Planck’s energy packet idea. • So electromagnetic radiation appears to behave as if it is both a wave and a particle. • In fact, you can think of light as discrete wave packets-packets of waves which, depending upon the measurement you make, somet ...
Document
... The electric and magnetic fields are mutually orthogonal. The magnetic field strength B is equal to E/C. ...
... The electric and magnetic fields are mutually orthogonal. The magnetic field strength B is equal to E/C. ...
PHY2054_f11-10
... currents in the same direction. The currents are out of the page in the figure. (a) What is the direction of the magnetic field at P on the x-axis set up by the two wires? (b) Find an expression for the magnitude of the field at P. (c) From (b), determine the field midway between the two wires. ...
... currents in the same direction. The currents are out of the page in the figure. (a) What is the direction of the magnetic field at P on the x-axis set up by the two wires? (b) Find an expression for the magnitude of the field at P. (c) From (b), determine the field midway between the two wires. ...
Coverage - Smart Science
... Recognise magnetism as a property and know some magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between ...
... Recognise magnetism as a property and know some magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Know that magnets come with two poles – north and south. Describe simple interactions of magnets and correctly use the terms apply, repel. MOST students should (levels 5–6): Understand the difference between ...
Click here for Final Jeopardy Circuits Magnets Definitions 10 Point
... rod, what can you do to produce an electrical current? a. Place the wire near the north pole of the magnet b. Move the permanent magnet rapidly over the ...
... rod, what can you do to produce an electrical current? a. Place the wire near the north pole of the magnet b. Move the permanent magnet rapidly over the ...
713 Analyze
... r Charges of opposite sign attract one another, and charges of the same sign repel one another. r system is conserved. 714 The total charge Chapterin23an isolated Electric Fields r Charge is quantized. Coulomb’s law states that the electric force exerted by a point charge q 1 on a second point charg ...
... r Charges of opposite sign attract one another, and charges of the same sign repel one another. r system is conserved. 714 The total charge Chapterin23an isolated Electric Fields r Charge is quantized. Coulomb’s law states that the electric force exerted by a point charge q 1 on a second point charg ...
Booklet #6 - Science 9 Homework Page
... Faraday constructed the first motor. By coiling (copper) wire around a (iron) metal core a strong electromagnet can be made. When attached to an electrical source it will produce a strong magnetic field. To keep this electromagnet spinning in a magnetic field, the direction that the current is trave ...
... Faraday constructed the first motor. By coiling (copper) wire around a (iron) metal core a strong electromagnet can be made. When attached to an electrical source it will produce a strong magnetic field. To keep this electromagnet spinning in a magnetic field, the direction that the current is trave ...
Lab I - Electromagnet
... We want to make a motor using a regular battery, a heart-shaped wire and a small magnet. • Take a 15 cm piece of tin wire and straighten it out, as shown in figure 5a. Make a small bump on the middle of the wire. • Bend the wire so that it is parallel to itself (Figure 5b). • Attach a pack of neodym ...
... We want to make a motor using a regular battery, a heart-shaped wire and a small magnet. • Take a 15 cm piece of tin wire and straighten it out, as shown in figure 5a. Make a small bump on the middle of the wire. • Bend the wire so that it is parallel to itself (Figure 5b). • Attach a pack of neodym ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
... This course, aiming at students in Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Science and Technology programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws of electricity and magnetism, and applications of electromagnetism in modern science and technology. This course consists of five parts: electrost ...
04-01VoltageandElectricField
... A gravitational field exerts a force of 126. N on a 13.0 kg mass away from point B and toward point A that is vertically displaced from B a distance of 12.0 m. What is the field strength? In what direction? What is the change in gravitational potential if you go from B to A? ...
... A gravitational field exerts a force of 126. N on a 13.0 kg mass away from point B and toward point A that is vertically displaced from B a distance of 12.0 m. What is the field strength? In what direction? What is the change in gravitational potential if you go from B to A? ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.