DIRAC`S DREAM: THE MYSTERY OF THE MAGNETIC MONOPOLE
... with charge q and with strength falling off with the squared of the distance. We would then expect a magnetic monopole to produce a “hedgehog” magnetic field B = rg2 r̂. A bar magnet looks like two such monopoles put together. However, bar magnets are secretly the magnetic fields generated by the sp ...
... with charge q and with strength falling off with the squared of the distance. We would then expect a magnetic monopole to produce a “hedgehog” magnetic field B = rg2 r̂. A bar magnet looks like two such monopoles put together. However, bar magnets are secretly the magnetic fields generated by the sp ...
What is a Magnet?
... Test it and see: YES / NO Is the coil of wire connected to the battery magnetic? Test it, and see: YES / NO How many paper clips are you able to pick up? _______________ Is the nail wrapped in a coil of wire and connected to the battery magnetic? Test it, and see: YES / NO How many pap ...
... Test it and see: YES / NO Is the coil of wire connected to the battery magnetic? Test it, and see: YES / NO How many paper clips are you able to pick up? _______________ Is the nail wrapped in a coil of wire and connected to the battery magnetic? Test it, and see: YES / NO How many pap ...
expansion phase
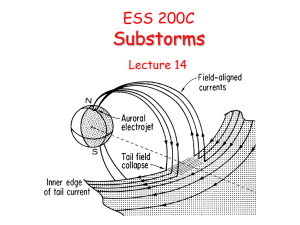
... X-line begins to move tailward. • Earthward of the X-line the plasma sheet thickens and strong earthward flows are observed. • As the X-line moves toward its distant location, the currents and aurora begin to die at the lower edge of the auroral bulge. This is the beginning of the recovery phase. • ...
... X-line begins to move tailward. • Earthward of the X-line the plasma sheet thickens and strong earthward flows are observed. • As the X-line moves toward its distant location, the currents and aurora begin to die at the lower edge of the auroral bulge. This is the beginning of the recovery phase. • ...
Ch 32 Maxwell`s Equations Magnetism of Matter
... transmitters and receivers (發射與接收器), telephones, fax machines, radar, and microwave ovens. Maxwell’s equations are the basis from which many of the equations can be derived. They are also the basis of many of the equations you will see in Ch33-36 ...
... transmitters and receivers (發射與接收器), telephones, fax machines, radar, and microwave ovens. Maxwell’s equations are the basis from which many of the equations can be derived. They are also the basis of many of the equations you will see in Ch33-36 ...
magnetic field
... • magnitude: F = qvBsinθ – q: charge in Coulombs – v: speed in meters/second – B: magnetic field in Tesla – θ: angle between v and B • direction: Right Hand Rule • FB = q v x B (This is a “vector cross product”) ...
... • magnitude: F = qvBsinθ – q: charge in Coulombs – v: speed in meters/second – B: magnetic field in Tesla – θ: angle between v and B • direction: Right Hand Rule • FB = q v x B (This is a “vector cross product”) ...
Lenz` Law, Motional emf, Induced emf and Electric Field Script Lenz
... Consider a loop of wire, radius r, in a magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field changes with time by Faraday’s law and emf would be induced in the loop of wire so the emf = - change in flux/ change in time which causes a flow of current. The induction of the curren ...
... Consider a loop of wire, radius r, in a magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic field changes with time by Faraday’s law and emf would be induced in the loop of wire so the emf = - change in flux/ change in time which causes a flow of current. The induction of the curren ...
t299-1-03f
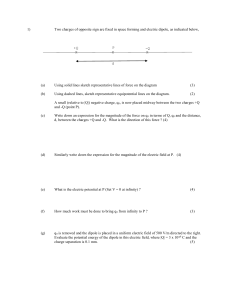
... the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. (a) ...
... the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. (a) ...
P3 Revision - the Redhill Academy
... coil back in. Diaphragm vibrates so much sound waves are produced Watch a video ...
... coil back in. Diaphragm vibrates so much sound waves are produced Watch a video ...
Magnetism - Cabrillo College
... only charged particles can exert them or feel them. But magnetic forces, unlike electric forces, act on charges only when they are moving, and rather than attracting or repelling them, they push them sideways. The magnetic force on a moving charge is always at right angles to the motion of the charg ...
... only charged particles can exert them or feel them. But magnetic forces, unlike electric forces, act on charges only when they are moving, and rather than attracting or repelling them, they push them sideways. The magnetic force on a moving charge is always at right angles to the motion of the charg ...
Lesson 2 Magnetism File
... not attract all metal objects. • Only a few metals, such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, are attracted to magnets or can be made into permanent magnets. • What makes these elements magnetic? Remember that every atom contains electrons. ...
... not attract all metal objects. • Only a few metals, such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, are attracted to magnets or can be made into permanent magnets. • What makes these elements magnetic? Remember that every atom contains electrons. ...
Hall effect

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879.The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current.