Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
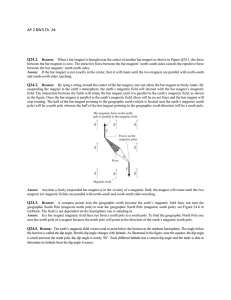
... wires are along the radial direction from the center C of the circular portion. Find the magnetic field at point C. ...
... wires are along the radial direction from the center C of the circular portion. Find the magnetic field at point C. ...
Magnetic_lesson - (EU
... From the discussion of the science of magnetism, we have learned that individual atoms, in a magnetic material like iron, act as tiny magnets with north and south poles. Initially, because the atoms are organized in random orientations, they cancel one another and the iron is not magnetic, However, ...
... From the discussion of the science of magnetism, we have learned that individual atoms, in a magnetic material like iron, act as tiny magnets with north and south poles. Initially, because the atoms are organized in random orientations, they cancel one another and the iron is not magnetic, However, ...
1 Early observations of and knowledge on air electricity and
... nature of thunderclouds was confirmed. Without knowledge of this experiment H. de Romas independently performed a similar experiment in Europe in 1753 with a kite at a 170 m long wire and came to the same conclusion. • The permanent air electrical field was discovered by le Monnier in St. Germain, F ...
... nature of thunderclouds was confirmed. Without knowledge of this experiment H. de Romas independently performed a similar experiment in Europe in 1753 with a kite at a 170 m long wire and came to the same conclusion. • The permanent air electrical field was discovered by le Monnier in St. Germain, F ...
Magnetic Field Strength H
... They suggest that the effect of external magnetic fields is to cause the domain boundaries to shift in favor of those domains which are parallel to the applied field. It is not clear how this applies to bulk magnetic materials which are polycrystalline. Keep in mind the fact that the internal magnet ...
... They suggest that the effect of external magnetic fields is to cause the domain boundaries to shift in favor of those domains which are parallel to the applied field. It is not clear how this applies to bulk magnetic materials which are polycrystalline. Keep in mind the fact that the internal magnet ...
Ch7 sec1
... placed near the north pole of a second magnet, the two magnets repel. This can be summarized by stating that “like poles repel.” In contrast, you found that when the north pole of one magnet is placed near the south pole of a second magnet, the two magnets attract. This can be summarized by stating ...
... placed near the north pole of a second magnet, the two magnets repel. This can be summarized by stating that “like poles repel.” In contrast, you found that when the north pole of one magnet is placed near the south pole of a second magnet, the two magnets attract. This can be summarized by stating ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.