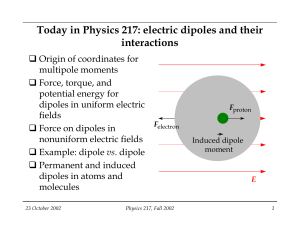
Living near High- Voltage Installations
... quence of attraction or repulsion of a certain electrical charge by another electrical charge. When a light bulb is plugged into a power outlet and connected to the electricity grid, it creates an electrical field, even when the light switch is switched off. In short, anywhere where there are electr ...
... quence of attraction or repulsion of a certain electrical charge by another electrical charge. When a light bulb is plugged into a power outlet and connected to the electricity grid, it creates an electrical field, even when the light switch is switched off. In short, anywhere where there are electr ...
Document
... It is important for you to come to class prepared, i.e. be familiar with the material to be presented. To test your preparedness, a simple five-minute quiz, testing your qualitative familiarity with the material to be discussed in class, will be given at the beginning of some of the classes. No make ...
... It is important for you to come to class prepared, i.e. be familiar with the material to be presented. To test your preparedness, a simple five-minute quiz, testing your qualitative familiarity with the material to be discussed in class, will be given at the beginning of some of the classes. No make ...
Electric motors Electric motors are everywhere! In your house
... and repel one another. The key to an electric motor is to then go one step further so that, at the moment that this half-turn of motion completes, the field of the electromagnet flips. The flip causes the electromagnet to complete another half-turn of motion. You flip the magnetic field just by chan ...
... and repel one another. The key to an electric motor is to then go one step further so that, at the moment that this half-turn of motion completes, the field of the electromagnet flips. The flip causes the electromagnet to complete another half-turn of motion. You flip the magnetic field just by chan ...
Physics 202, Lecture 16 Lenz`s Law (Reminder)
... Lenz’s Law (Reminder) "!The emf due to change of magnetic flux tends to created a current which produces a magnetic field to compensate the change of original magnetic flux. ...
... Lenz’s Law (Reminder) "!The emf due to change of magnetic flux tends to created a current which produces a magnetic field to compensate the change of original magnetic flux. ...
Maxwell`s Equations
... •But there are also many other types of EM waves •The constant c is one of the most important fundamental constants of the universe ...
... •But there are also many other types of EM waves •The constant c is one of the most important fundamental constants of the universe ...
CHAPTER 29: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION • So far we have
... higher potential – “uphill”). This increase in energy is then dissipated in the form of heat (due to resistance) as it moves from a to b. Since we are talking about a nonconservative force, the mechanical energy is not conserved but, as is always true, the total energy is conserved. Since the area ...
... higher potential – “uphill”). This increase in energy is then dissipated in the form of heat (due to resistance) as it moves from a to b. Since we are talking about a nonconservative force, the mechanical energy is not conserved but, as is always true, the total energy is conserved. Since the area ...
3D Finite Element Analysis for Arcing Chamber Optimization
... chamber In Fig.2 is presented the construction plan of the current path which includes the output terminals A, B, the conducting bars 1,2, the brake contacts 3 (lasting contacts) and 4 (arc brake contacts), the slopes 5, 6 placed in the arcing chamber CS. Within the arcing chamber there are the ferr ...
... chamber In Fig.2 is presented the construction plan of the current path which includes the output terminals A, B, the conducting bars 1,2, the brake contacts 3 (lasting contacts) and 4 (arc brake contacts), the slopes 5, 6 placed in the arcing chamber CS. Within the arcing chamber there are the ferr ...
Ch36 - Southwest High School
... A galvanometer and a motor are similar in that they both employ coils positioned in magnetic fields. When current passes through the coils, forces on the wires rotate the coils. The fundamental difference is that the maximum rotation of the coil in a galvanometer is one half turn, whereas in a motor ...
... A galvanometer and a motor are similar in that they both employ coils positioned in magnetic fields. When current passes through the coils, forces on the wires rotate the coils. The fundamental difference is that the maximum rotation of the coil in a galvanometer is one half turn, whereas in a motor ...
36 Magnetism - KaiserScience
... A galvanometer and a motor are similar in that they both employ coils positioned in magnetic fields. When current passes through the coils, forces on the wires rotate the coils. The fundamental difference is that the maximum rotation of the coil in a galvanometer is one half turn, whereas in a motor ...
... A galvanometer and a motor are similar in that they both employ coils positioned in magnetic fields. When current passes through the coils, forces on the wires rotate the coils. The fundamental difference is that the maximum rotation of the coil in a galvanometer is one half turn, whereas in a motor ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.