Errors and Limitations of the Magnetic Compass
... There is no practical way of eliminating the effects of the local field. If the points at which the measurements have been made are 50 miles apart, and declination values are averaged over groups of about nine stations (three by three) the effects of the local field are uncorrelated at neighbouring ...
... There is no practical way of eliminating the effects of the local field. If the points at which the measurements have been made are 50 miles apart, and declination values are averaged over groups of about nine stations (three by three) the effects of the local field are uncorrelated at neighbouring ...
Poster_IAEA 2000 - Helically Symmetric eXperiment
... Abstract HSX is a toroidal quasihelically-symmetric stellarator with negligibly small toroidal curvature. Vacuum magnetic surfaces at 1 kG are measured using low-energy electron beams that strike a fluorescent mesh. The images are recorded with a CCD camera and show no observable evidence of island ...
... Abstract HSX is a toroidal quasihelically-symmetric stellarator with negligibly small toroidal curvature. Vacuum magnetic surfaces at 1 kG are measured using low-energy electron beams that strike a fluorescent mesh. The images are recorded with a CCD camera and show no observable evidence of island ...
What is Beneath the Sunspots? Home Page ____________________________________________
... Sunspots are the dark spots seen on sun’s surface [5], they are regions where strong magnetic fields emerge from solar interior and where major eruptive events occurs [6], it was studied individually as a phenomenon with strong magnetic field [5]. Until now, sunspots are conceived as a magnetic flu ...
... Sunspots are the dark spots seen on sun’s surface [5], they are regions where strong magnetic fields emerge from solar interior and where major eruptive events occurs [6], it was studied individually as a phenomenon with strong magnetic field [5]. Until now, sunspots are conceived as a magnetic flu ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: An Introduction
... The magnetic moment of the nucleus forces the nucleus to behave as a tiny bar magnet. In the absence of an external magnetic field, each magnet is randomly oriented. During the NMR experiment the sample is placed in an external magnetic field, B , which forces the bar magnets to align with (low ener ...
... The magnetic moment of the nucleus forces the nucleus to behave as a tiny bar magnet. In the absence of an external magnetic field, each magnet is randomly oriented. During the NMR experiment the sample is placed in an external magnetic field, B , which forces the bar magnets to align with (low ener ...
Understanding Our Home Star FDP: Full Disk Patrol Telescope ISS
... VSM, FDP, and ISS installed atop the Vacuum Tower at Kitt Peak, Arizona, southwest of Tucson. Seismic images of magnetic activitiy on the farside of the Sun that cannot directly be seen from Earth. The images show sound wave travel time variations, with locations of shorter travel times appearing da ...
... VSM, FDP, and ISS installed atop the Vacuum Tower at Kitt Peak, Arizona, southwest of Tucson. Seismic images of magnetic activitiy on the farside of the Sun that cannot directly be seen from Earth. The images show sound wave travel time variations, with locations of shorter travel times appearing da ...
B - Purdue Physics
... electric fields and objects get squished when they move, and also that time runs differently for a moving observer. • Let’s do a simple example to see how this can create magnetism. • In reality, electric and magnetic fields are two parts of a single relativistic object called the Faraday tensor (do ...
... electric fields and objects get squished when they move, and also that time runs differently for a moving observer. • Let’s do a simple example to see how this can create magnetism. • In reality, electric and magnetic fields are two parts of a single relativistic object called the Faraday tensor (do ...
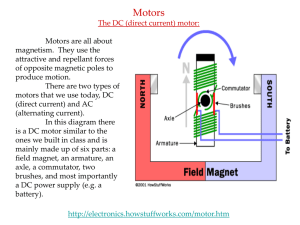
5-Motors
... can only continue the rotational movement if we change the direction of the flow of electrons by reversing the battery connections. This “flips” the electric field of the electromagnet causing another repulsion and attraction between the poles of the two magnets, pushing the nail around again to com ...
... can only continue the rotational movement if we change the direction of the flow of electrons by reversing the battery connections. This “flips” the electric field of the electromagnet causing another repulsion and attraction between the poles of the two magnets, pushing the nail around again to com ...
Introduction - Greetings from Eng. Nkumbwa
... basic models of the dynamic physical systems are differential equations obtained by the application of the appropriate laws of nature. These equations may be linear or nonlinear depending on the phenomena being modeled. The differential equations are inconvenient for the analysis and design mani ...
... basic models of the dynamic physical systems are differential equations obtained by the application of the appropriate laws of nature. These equations may be linear or nonlinear depending on the phenomena being modeled. The differential equations are inconvenient for the analysis and design mani ...
Magnetism
... What causes magnetism? • Just as electricity is caused by • This still doesn’t make a magnet the movement of electrons, so is because the atoms’ poles are all magnetism. pointing in different directions. • Electrons moved from place to • If the atoms can be shifted so that place causes electricity. ...
... What causes magnetism? • Just as electricity is caused by • This still doesn’t make a magnet the movement of electrons, so is because the atoms’ poles are all magnetism. pointing in different directions. • Electrons moved from place to • If the atoms can be shifted so that place causes electricity. ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... 1948 the Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves and in 1849 he published the first results obtained by his method for determining the speed of light (Fizeau-Foucault apparatus), Fizeau’s experiment of 1849 measured the value to be about 3×108 m/s. (Fizeau' s value for light' s speed was about 5% t ...
... 1948 the Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves and in 1849 he published the first results obtained by his method for determining the speed of light (Fizeau-Foucault apparatus), Fizeau’s experiment of 1849 measured the value to be about 3×108 m/s. (Fizeau' s value for light' s speed was about 5% t ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... God said, “Let there be lights in the firmament of the heaven to divide the day from the night” (Genesis 1:14). This light is the original source of earth’s energy. Today the growing and active population of the earth is searching for new ways to get energy for the machines of our civilization. Our ...
... God said, “Let there be lights in the firmament of the heaven to divide the day from the night” (Genesis 1:14). This light is the original source of earth’s energy. Today the growing and active population of the earth is searching for new ways to get energy for the machines of our civilization. Our ...
Click here for Final Jeopardy Circuits Magnets Definitions 10 Point
... rod, what can you do to produce an electrical current? a. Place the wire near the north pole of the magnet b. Move the permanent magnet rapidly over the ...
... rod, what can you do to produce an electrical current? a. Place the wire near the north pole of the magnet b. Move the permanent magnet rapidly over the ...
Kinematics of fluid motion
... The mapping equation (1) specifies the path of particle P initially at α; on the other hand, for fixed t equation (1) determines a transformation of the region initially occupied by the fluid into its position at time t. We assume that initially distinct points remains distinct throughout the entire ...
... The mapping equation (1) specifies the path of particle P initially at α; on the other hand, for fixed t equation (1) determines a transformation of the region initially occupied by the fluid into its position at time t. We assume that initially distinct points remains distinct throughout the entire ...
doc
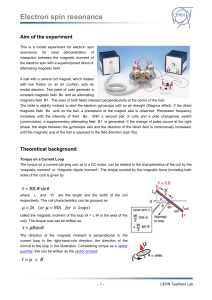
... be induced between spin states by applying a magnetic field and then supplying electromagnetic energy, usually in the microwave range of frequencies. The resulting absorption spectra are described as electron spin resonance (ESR) or electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). ESR was first observed in Ka ...
... be induced between spin states by applying a magnetic field and then supplying electromagnetic energy, usually in the microwave range of frequencies. The resulting absorption spectra are described as electron spin resonance (ESR) or electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). ESR was first observed in Ka ...
Rooney AP Physics Ch 20
... Motional emf • As the negative charges accumulate at the base, a net positive charge exists at the upper end of the conductor. • As a result of this charge separation, an electric field is produced in the conductor. • Charges build up at the ends of the conductor until the downward magnetic force i ...
... Motional emf • As the negative charges accumulate at the base, a net positive charge exists at the upper end of the conductor. • As a result of this charge separation, an electric field is produced in the conductor. • Charges build up at the ends of the conductor until the downward magnetic force i ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.