Optimality Theory and Human Sentence Processing: The
... (i.e., in case of ambiguity, attach the new node to the most recently processed constituent). According to this type of approach, structural preferences in processing are the result of general cognitive limitations, such as limitations on working memory or bounds on complexity. Another approach is t ...
... (i.e., in case of ambiguity, attach the new node to the most recently processed constituent). According to this type of approach, structural preferences in processing are the result of general cognitive limitations, such as limitations on working memory or bounds on complexity. Another approach is t ...
pdf file
... This implies in particular that to devise an appropriate approach to organisation modelling, both the structural aspects and the dynamic aspects and their relation have to be covered in an appropriate manner. Multi-agent or organisation modelling approaches have been developed in three manners. Firs ...
... This implies in particular that to devise an appropriate approach to organisation modelling, both the structural aspects and the dynamic aspects and their relation have to be covered in an appropriate manner. Multi-agent or organisation modelling approaches have been developed in three manners. Firs ...
Adding Consciousness to Cognitive Architectures
... 11.15Representation of a hierarchy of objectives. . . . . . . . . . . . 11.16Correspondence between the hierarchy of objectives and system organisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.17Objectives can be a) a certain state in the system’s ST-structure or b) a subprogram of it . ...
... 11.15Representation of a hierarchy of objectives. . . . . . . . . . . . 11.16Correspondence between the hierarchy of objectives and system organisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.17Objectives can be a) a certain state in the system’s ST-structure or b) a subprogram of it . ...
A Survey of the Eighth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence
... the 150 papers probe results. There are no mutually exclusive subsets of fields (although the answers to the question in each field are mutually exclusive), so each paper can contribute to the total for every field. ...
... the 150 papers probe results. There are no mutually exclusive subsets of fields (although the answers to the question in each field are mutually exclusive), so each paper can contribute to the total for every field. ...
Learning Where (Not) To Cache: A Cognitive Model for Corvids
... and very little else. This means a uniform setup is being used to study a diverse set of cognitive phenomena, making it possible to validate a single computational model across a large variety of experimental results. In this paper, we start the design of such a model by focusing on memory, for cach ...
... and very little else. This means a uniform setup is being used to study a diverse set of cognitive phenomena, making it possible to validate a single computational model across a large variety of experimental results. In this paper, we start the design of such a model by focusing on memory, for cach ...
Pardis, a Fuzzy Extension to Multi agent Simulation Systems
... The inference in such a system is an inference with words, and the knowledge is represented and stored as qualitative data, and not quantities. In the recent years, Zadeh has introduced a new concept that is called “Computing with Words” (CW) [4]. The main idea behind this concept, which he believes ...
... The inference in such a system is an inference with words, and the knowledge is represented and stored as qualitative data, and not quantities. In the recent years, Zadeh has introduced a new concept that is called “Computing with Words” (CW) [4]. The main idea behind this concept, which he believes ...
Multiagent Systems: Rational Decision Making and Negotiation
... Back to the Prisoner’s Dilemma • Unique Nash equilibrium: both agents confess: – if A changes strategy unilaterally, she will do worse – if B changes strategy unilaterally, she will also do worse • Discussion: Our analysis shows that it would be rational to confess. However, this seems counter-intui ...
... Back to the Prisoner’s Dilemma • Unique Nash equilibrium: both agents confess: – if A changes strategy unilaterally, she will do worse – if B changes strategy unilaterally, she will also do worse • Discussion: Our analysis shows that it would be rational to confess. However, this seems counter-intui ...
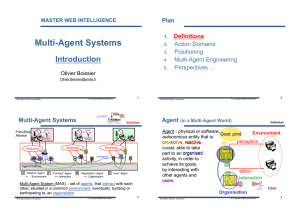
Multi-Agent Systems Introduction
... Autonomy: agents may exhibit activities that are not the one expected by the other agents in the system Delegation: agents may receive some control over their activities ...
... Autonomy: agents may exhibit activities that are not the one expected by the other agents in the system Delegation: agents may receive some control over their activities ...
Game World Implementation of Artificial Recognition
... customer service on a web page that was one of many very primitive applications of artificial intelligence. Since John McCarthy had started to work on it, a huge group of tools have been used and developed in order to improve AI concept. Most of them are probabilistic methods due to AI problems are ...
... customer service on a web page that was one of many very primitive applications of artificial intelligence. Since John McCarthy had started to work on it, a huge group of tools have been used and developed in order to improve AI concept. Most of them are probabilistic methods due to AI problems are ...
Self-Motivating Computational System Cognitive Architecture
... The road to building artificial general intelligence (AGI) [9] is not just very complex but the most complex task computer scientists have tried to solve. While over the last 30+ years a great amount of work has been done, much of that work has been narrow from an application standpoint or has been ...
... The road to building artificial general intelligence (AGI) [9] is not just very complex but the most complex task computer scientists have tried to solve. While over the last 30+ years a great amount of work has been done, much of that work has been narrow from an application standpoint or has been ...
Analyzing Impact of AI Tools on Traditional Workflow Systems
... flexibility in unpredictable business environment. Artificial Intelligence, one of the emerging areas in computer science addresses different technical challenges of workflow system. Artificial Intelligence technologies can be incorporated with existing workflow systems to enhance their efficiency a ...
... flexibility in unpredictable business environment. Artificial Intelligence, one of the emerging areas in computer science addresses different technical challenges of workflow system. Artificial Intelligence technologies can be incorporated with existing workflow systems to enhance their efficiency a ...
Recent advances in computational models of natural argument
... Traditional symbolic AI models of reasoning are typically founded on firstorder predicate calculus or some subset thereof. Such first-order reasoning systems, however, are obliged to make a number of assumptions: that a given problem is fully specified ~such that the solution to a problem lies withi ...
... Traditional symbolic AI models of reasoning are typically founded on firstorder predicate calculus or some subset thereof. Such first-order reasoning systems, however, are obliged to make a number of assumptions: that a given problem is fully specified ~such that the solution to a problem lies withi ...
AMC - Queen Mary University of London
... In her seminal book The Creative Mind, Margaret Boden [2004] identifies three different types of creativity, relative to the notion of the conceptual space which contains all the concepts of a particular kind: combinatorial, exploratory, and transformational. Combinatorial creativity, similar in pri ...
... In her seminal book The Creative Mind, Margaret Boden [2004] identifies three different types of creativity, relative to the notion of the conceptual space which contains all the concepts of a particular kind: combinatorial, exploratory, and transformational. Combinatorial creativity, similar in pri ...
Application of Systemic Approach to Sophocles Global Specification
... The primary is a classical: in well foresight and defined situations a system (=agent) uses a fixed knowledge which is in the forms of algorithms or procedures, and it is organized in tree forms. It means, the objects of interventions, tools, and their attributes are initially established. The syste ...
... The primary is a classical: in well foresight and defined situations a system (=agent) uses a fixed knowledge which is in the forms of algorithms or procedures, and it is organized in tree forms. It means, the objects of interventions, tools, and their attributes are initially established. The syste ...
Grade 2 - MAFS - Florida Department Of Education
... Measure the length of an object to the nearest inch, foot, centimeter, or meter by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. Cognitive Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts Describe the inverse relationship between the ...
... Measure the length of an object to the nearest inch, foot, centimeter, or meter by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes. Cognitive Complexity: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts Describe the inverse relationship between the ...
The Role of analogy in cognitive science
... Analogy is an integral part of human understanding and problem solving, and thus becomes an interesting challenge for artificial intelligence[1]. The concept of analogy requires some ability to perceive likeness between dissimilar objects/abstractions in different domains and extrapolate a relations ...
... Analogy is an integral part of human understanding and problem solving, and thus becomes an interesting challenge for artificial intelligence[1]. The concept of analogy requires some ability to perceive likeness between dissimilar objects/abstractions in different domains and extrapolate a relations ...
Mind Design II : Philosophy, Psychology, Artificial Intelligence
... perception and action. Yet these turn out to be extraordinarily difficult to achieve artificially at any plausible level of sophistication. And, what may be worse, ignoring real-time environmental interaction distorts a system designer's assumptions about how intelligent systems are related to the w ...
... perception and action. Yet these turn out to be extraordinarily difficult to achieve artificially at any plausible level of sophistication. And, what may be worse, ignoring real-time environmental interaction distorts a system designer's assumptions about how intelligent systems are related to the w ...
Mind Design II : Philosophy, Psychology, Artificial Intelligence
... perception and action. Yet these turn out to be extraordinarily difficult to achieve artificially at any plausible level of sophistication. And, what may be worse, ignoring real-time environmental interaction distorts a system designer's assumptions about how intelligent systems are related to the w ...
... perception and action. Yet these turn out to be extraordinarily difficult to achieve artificially at any plausible level of sophistication. And, what may be worse, ignoring real-time environmental interaction distorts a system designer's assumptions about how intelligent systems are related to the w ...
Document
... The difference between propositional and first order logic is in the ontological commitment. It assumes about the nature of reality. 4. Define Epistemological commitment. The logic that allows the possible states of knowledge with respect to each fact. 5. Define domain and domain elements. The set o ...
... The difference between propositional and first order logic is in the ontological commitment. It assumes about the nature of reality. 4. Define Epistemological commitment. The logic that allows the possible states of knowledge with respect to each fact. 5. Define domain and domain elements. The set o ...
Tarek R. Besold, Kai
... calculus are shown in Figure 2. DC EC ∗ syntax includes a system of sorts S, a signature f , a grammar for terms t, and a grammar for sentences φ; these are shown on the left half of the figure. The proof calculus is based on natural deduction [Jaśkowski, 1934], and includes all the standard introd ...
... calculus are shown in Figure 2. DC EC ∗ syntax includes a system of sorts S, a signature f , a grammar for terms t, and a grammar for sentences φ; these are shown on the left half of the figure. The proof calculus is based on natural deduction [Jaśkowski, 1934], and includes all the standard introd ...
Back Propagation Weight Update Rule
... Equations 21 and 22 show that the weights change is an input signal multiplied by a local gradient. This gives a direction that also has magnitude dependent on the magnitude of the error. If the direction is taken with no magnitude then all changes will be of equal size which will depend on the lea ...
... Equations 21 and 22 show that the weights change is an input signal multiplied by a local gradient. This gives a direction that also has magnitude dependent on the magnitude of the error. If the direction is taken with no magnitude then all changes will be of equal size which will depend on the lea ...
Intelligent Agents - Department of Computer Science, Oxford
... itself, autonomy is a somewhat tricky concept to tie down precisely, but I mean it in the sense that agents are able to act without the intervention of humans or other systems: they have control both over their own internal state, and over their behaviour. In section 1.2.3, we will contrast agents w ...
... itself, autonomy is a somewhat tricky concept to tie down precisely, but I mean it in the sense that agents are able to act without the intervention of humans or other systems: they have control both over their own internal state, and over their behaviour. In section 1.2.3, we will contrast agents w ...
Intelligent Agents: Theory and Practice
... repair or improve it. It is perhaps never logically required even for humans, but expressing reasonably briefly what is actually known about the state of the machine in a particular situation may require mental qualities or qualities isomorphic to them. Theories of belief, knowledge and wanting can ...
... repair or improve it. It is perhaps never logically required even for humans, but expressing reasonably briefly what is actually known about the state of the machine in a particular situation may require mental qualities or qualities isomorphic to them. Theories of belief, knowledge and wanting can ...
Document
... Learning Algorithm Rosenblatt (1958) devised a learning algorithm for artificial neurons ...
... Learning Algorithm Rosenblatt (1958) devised a learning algorithm for artificial neurons ...