נספחים : דפי עזר לבחינה
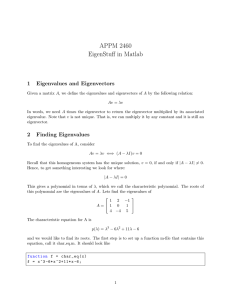
... S = char(A) converts the array A that contains nonnegative integers representing character codes into a MATLAB character array (the first codes are ASCII). The actual characters displayed depends on the 721 character encoding scheme for a given font. The result for any elements of A outside the rang ...
... S = char(A) converts the array A that contains nonnegative integers representing character codes into a MATLAB character array (the first codes are ASCII). The actual characters displayed depends on the 721 character encoding scheme for a given font. The result for any elements of A outside the rang ...
Algebra 2 Unit 2-2
... 20. Your teacher gives you a test worth 100 points with 35 questions. Each question is worth either 2 points or 4 points. Write a system of equations to determine the number of 2 point and 4 point questions on the test. ...
... 20. Your teacher gives you a test worth 100 points with 35 questions. Each question is worth either 2 points or 4 points. Write a system of equations to determine the number of 2 point and 4 point questions on the test. ...
Partial Derivatives
... If we want to find the maximum and minimum value of function f under condition(s) or constraint(s), then we can apply the method of Lagrange multipliers. Suppose we want to minimize the function f (x, y) under the constraint, function g (x, y) = k, then we define the Lagrange function as the followi ...
... If we want to find the maximum and minimum value of function f under condition(s) or constraint(s), then we can apply the method of Lagrange multipliers. Suppose we want to minimize the function f (x, y) under the constraint, function g (x, y) = k, then we define the Lagrange function as the followi ...
When divisors go bad… counterexamples with polynomial division
... x2 ≡ 1 (mod 8), so that means 1, 3, 5, 7 are four distinct roots of f (x) in Z8 . However, f only has degree 2. Another example is f (x) = 2x in Z4 [x]; this is a linear polynomial, but both 0 and 2 are roots in Z4 . This anomaly is quite related to our last one... 3. Roots of a product may not be r ...
... x2 ≡ 1 (mod 8), so that means 1, 3, 5, 7 are four distinct roots of f (x) in Z8 . However, f only has degree 2. Another example is f (x) = 2x in Z4 [x]; this is a linear polynomial, but both 0 and 2 are roots in Z4 . This anomaly is quite related to our last one... 3. Roots of a product may not be r ...
4.19.1. Theorem 4.20
... relative to the basis of unit coordinate vectors. Given x such that T x O , let X be the n 1 column matrix that corresponds to x. We have AX 0 , where 0 is the zero column matrix. Thus, B AX 0 for any n n matrix B. If B is a left inverse of A, then ...
... relative to the basis of unit coordinate vectors. Given x such that T x O , let X be the n 1 column matrix that corresponds to x. We have AX 0 , where 0 is the zero column matrix. Thus, B AX 0 for any n n matrix B. If B is a left inverse of A, then ...
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning vector spaces and linear mappings between such spaces. It includes the study of lines, planes, and subspaces, but is also concerned with properties common to all vector spaces.The set of points with coordinates that satisfy a linear equation forms a hyperplane in an n-dimensional space. The conditions under which a set of n hyperplanes intersect in a single point is an important focus of study in linear algebra. Such an investigation is initially motivated by a system of linear equations containing several unknowns. Such equations are naturally represented using the formalism of matrices and vectors.Linear algebra is central to both pure and applied mathematics. For instance, abstract algebra arises by relaxing the axioms of a vector space, leading to a number of generalizations. Functional analysis studies the infinite-dimensional version of the theory of vector spaces. Combined with calculus, linear algebra facilitates the solution of linear systems of differential equations.Techniques from linear algebra are also used in analytic geometry, engineering, physics, natural sciences, computer science, computer animation, and the social sciences (particularly in economics). Because linear algebra is such a well-developed theory, nonlinear mathematical models are sometimes approximated by linear models.