Instructor`s Notes Atomic Tiles: Play Your Way from Atoms to
... 3a. Students know the structure of the atom and know it is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know re ...
... 3a. Students know the structure of the atom and know it is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know re ...
MYP Chemistry: Final Review
... How are elements in the same group (column) related? How are the alkali metals all related? The noble gases? All have the same final electron configuration number; all have same number of valence electrons Alkali Metals: end in s1 configuration, have 1 valence electron Noble gases: end in s2p6, have ...
... How are elements in the same group (column) related? How are the alkali metals all related? The noble gases? All have the same final electron configuration number; all have same number of valence electrons Alkali Metals: end in s1 configuration, have 1 valence electron Noble gases: end in s2p6, have ...
Unit 1
... Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge difference from one end of the molecule to th ...
... Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge difference from one end of the molecule to th ...
Unit 1
... Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge difference from one end of the molecule to th ...
... Results from a covalent bond involving hydrogen Shared electron spends more time around the bigger nucleus of the Oxygen atom This leaves the hydrogen end with a net positive charge & the Oxygen end with a net negative. A polar molecule due to the charge difference from one end of the molecule to th ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shared equally Electronegativity Differences Bond Type ...
... 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shared equally Electronegativity Differences Bond Type ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 3. How are bonds different in ionic and covalent compounds. Ionic bonds – transfer of electrons ...
... 3. How are bonds different in ionic and covalent compounds. Ionic bonds – transfer of electrons ...
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Inter-atomic Bonding
... We begin with the basic vocabulary of the individual atom. element – Fundamental chemical species, represented in the periodic table. All materials are made of elements or combinations of these elements. atom – The smallest building block of an element, consisting of a central nucleus of protons and ...
... We begin with the basic vocabulary of the individual atom. element – Fundamental chemical species, represented in the periodic table. All materials are made of elements or combinations of these elements. atom – The smallest building block of an element, consisting of a central nucleus of protons and ...
Success of classical free electron theory
... The electron theory explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. It explains the binding in solids, behaviour of conductors and insulators, ferromagnetism, electrical and thermal conductivities of solids, elasticity, cohesive and repulsive forces in solids etc. ...
... The electron theory explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. It explains the binding in solids, behaviour of conductors and insulators, ferromagnetism, electrical and thermal conductivities of solids, elasticity, cohesive and repulsive forces in solids etc. ...
Column A
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
Alkaline earth metals
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled shell contains 8 electrons (octet) Except for ...
... D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled shell contains 8 electrons (octet) Except for ...
Safety - Wando High School
... 2. What happens with the electrons in an ionic and covalent bond? 3. Why do atoms bond? 4. In a chemical formula what do the symbols and numbers represent? 5. What is a molecule? Is CO2 a molecule? Is NaCl a molecule? 6. What is an elements oxidation number(s)? 7. What rule does bonding (typically) ...
... 2. What happens with the electrons in an ionic and covalent bond? 3. Why do atoms bond? 4. In a chemical formula what do the symbols and numbers represent? 5. What is a molecule? Is CO2 a molecule? Is NaCl a molecule? 6. What is an elements oxidation number(s)? 7. What rule does bonding (typically) ...
Units 3 and 4 Revision
... These elements have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level – this gives them similar properties. Q10. Chlorine atoms exists as two different isotopes 35Cl and 37Cl. ...
... These elements have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level – this gives them similar properties. Q10. Chlorine atoms exists as two different isotopes 35Cl and 37Cl. ...
Chapter 2 Practice Questions
... E) All of these statements are true according to modern atomic theory. 4. Avogadro's hypothesis states that: A) Each atom of oxygen is 16 times more massive than an atom of hydrogen. B) A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. C) When two elements form a seri ...
... E) All of these statements are true according to modern atomic theory. 4. Avogadro's hypothesis states that: A) Each atom of oxygen is 16 times more massive than an atom of hydrogen. B) A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. C) When two elements form a seri ...
Main Group Notes 1
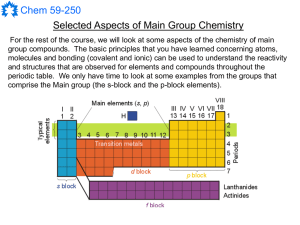
... Selected Aspects of Main Group Chemistry For the rest of the course, we will look at some aspects of the chemistry of main group compounds. The basic principles that you have learned concerning atoms, molecules and bonding (covalent and ionic) can be used to understand the reactivity and structures ...
... Selected Aspects of Main Group Chemistry For the rest of the course, we will look at some aspects of the chemistry of main group compounds. The basic principles that you have learned concerning atoms, molecules and bonding (covalent and ionic) can be used to understand the reactivity and structures ...
Review - Final Exam
... elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across the second period and use these to predict the combining number for each element. 24. What happens to the ...
... elements and down a group? What information is gained from the valence electrons? Why do chemical families have similar properties? 23. Draw Lewis (Electron Dot) symbols for the elements across the second period and use these to predict the combining number for each element. 24. What happens to the ...
Chemistry Terms
... ionic bond A bond between atoms in which an electron from one atom leaves and resides in the other shell of the other atom, giving both atoms a net electric charge such that they attract each other and stick together. metallic bond The kind of bond holding atoms together in metals. The bonding elect ...
... ionic bond A bond between atoms in which an electron from one atom leaves and resides in the other shell of the other atom, giving both atoms a net electric charge such that they attract each other and stick together. metallic bond The kind of bond holding atoms together in metals. The bonding elect ...
Exam Review
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
... _P,As,Sb,Bi__8. Name of another element in the same family with Nitrogen _Li,Be,B,C,O,F,Ne____9. Name of another element in the same period with Nitrogen ...
Chemistry Study Guide What is matter made of? Matter is anything
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
... properties that are the same or very similar. The elements in each group also have the same number of electrons in their outer shell. The horizontal rows are called periods. The elements in each period are arranged by atomic number and have the same number of electron shells around the nucleus. Eac ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
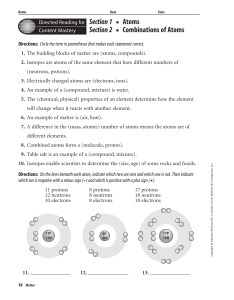
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...