Pre- AP & NET IONIC EQUATIONS
... Net ionic equations for single and double replacement (taught with solutions) Solubility rules ...
... Net ionic equations for single and double replacement (taught with solutions) Solubility rules ...
+ H 2 (g)
... crystalline. (g) if: any “big 7” , CO2, CO. (aq) if: all acids, dissolved in water, solution. electric if electricity is added. *If substance does not fit above criteria, do not put any state of matter. ...
... crystalline. (g) if: any “big 7” , CO2, CO. (aq) if: all acids, dissolved in water, solution. electric if electricity is added. *If substance does not fit above criteria, do not put any state of matter. ...
Monte Carlo Simulation of Water Radiolysis for
... lose energy primarily through collisions with bound electrons. Ionization cross sections for the projectile and secondary electron energies are needed to follow the history of an incident particle and its products, covering all ranges of energy transfers in individual collisions. For fast ions, the ...
... lose energy primarily through collisions with bound electrons. Ionization cross sections for the projectile and secondary electron energies are needed to follow the history of an incident particle and its products, covering all ranges of energy transfers in individual collisions. For fast ions, the ...
File - Varsity Field
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
Pure substances
... Chemistry majors sometimes get holes in the cotton jeans they wear to lab because of acid spills ...
... Chemistry majors sometimes get holes in the cotton jeans they wear to lab because of acid spills ...
Unit (1)
... (3) Write the scientific term: 1- The ability of the Earth to attract an object to its center. 2- An instrument used to change electric energy into magnetic energy. 3- The force that accompanies the massive amount of energy and it is stored in the nucleus. 4- Property of an object has to resist the ...
... (3) Write the scientific term: 1- The ability of the Earth to attract an object to its center. 2- An instrument used to change electric energy into magnetic energy. 3- The force that accompanies the massive amount of energy and it is stored in the nucleus. 4- Property of an object has to resist the ...
CHEM1001 2012-J-2 June 2012 22/01(a) • Complete the following
... foil. Most of the particles passed straight through or were slightly deflected, but the occasional one was reflected back towards the source. The conclusion drawn was that atoms consist of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. ...
... foil. Most of the particles passed straight through or were slightly deflected, but the occasional one was reflected back towards the source. The conclusion drawn was that atoms consist of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. ...
AP Chemistry - Oak Park Unified School District
... Write the number next to the word that fits the paragraph. Measurement in Chemistry Science knowledge is advanced by observing patterns, (1), and constructing explanations, (2); which are supported by repeatable (3) evidence. Measurements are made using the metric system, where the standard units ar ...
... Write the number next to the word that fits the paragraph. Measurement in Chemistry Science knowledge is advanced by observing patterns, (1), and constructing explanations, (2); which are supported by repeatable (3) evidence. Measurements are made using the metric system, where the standard units ar ...
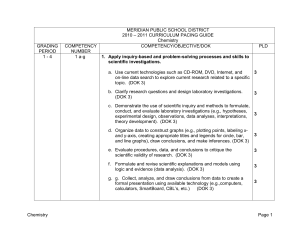
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... composition, mass, charge, penetrating power) The concept of half-life for a radioactive isotope (e.g., carbon-14 dating) based on the principle that the decay of any individual atom is a random process Page 4 ...
... composition, mass, charge, penetrating power) The concept of half-life for a radioactive isotope (e.g., carbon-14 dating) based on the principle that the decay of any individual atom is a random process Page 4 ...
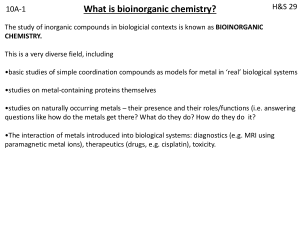
bioinorganic 1
... usually coupled to bond making-breaking). Few naturally occurring organic substrates can do this. Transition metals are excellent for electron transfer because they can adopt more than one oxidation state. Iron is particularly adept at this because the redox potential can be controlled by its enviro ...
... usually coupled to bond making-breaking). Few naturally occurring organic substrates can do this. Transition metals are excellent for electron transfer because they can adopt more than one oxidation state. Iron is particularly adept at this because the redox potential can be controlled by its enviro ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... For the two samples described above and the experiment you described in part (c), what data would be the same (within experimental error) and what data would be different? Can you say (at least qualitatively) how they would differ? In other words, what data would be larger/smaller for what sample? [ ...
... For the two samples described above and the experiment you described in part (c), what data would be the same (within experimental error) and what data would be different? Can you say (at least qualitatively) how they would differ? In other words, what data would be larger/smaller for what sample? [ ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... Development of new effective solvents for different industrial and technological applications is one of the important tasks of modern chemical science. These solvents should possess such properties like low volatility, low to no toxicity, non-flammable, as well as high thermal stability, all in accor ...
... Development of new effective solvents for different industrial and technological applications is one of the important tasks of modern chemical science. These solvents should possess such properties like low volatility, low to no toxicity, non-flammable, as well as high thermal stability, all in accor ...
State Standard - SchoolNotes.com
... C-4.2 Predict the products of acid-base neutralization and combustion reactions. C-4.3 Analyze the energy changes (endothermic or exothermic) associated with chemical reactions. C-4.4 Apply the concept of moles to determine the number of particles of a substance in a chemical reaction, the percent c ...
... C-4.2 Predict the products of acid-base neutralization and combustion reactions. C-4.3 Analyze the energy changes (endothermic or exothermic) associated with chemical reactions. C-4.4 Apply the concept of moles to determine the number of particles of a substance in a chemical reaction, the percent c ...
syllabus details - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effective nuclear charge are not required. Ionization energy is defined as the minimum energy required to remove one electron from an isolated gaseous atom. ...
... balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effective nuclear charge are not required. Ionization energy is defined as the minimum energy required to remove one electron from an isolated gaseous atom. ...
Course Pack3 Phase Diagrams
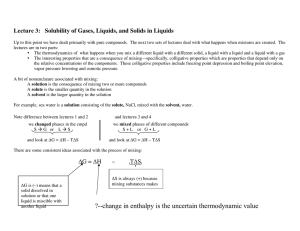
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
... ∆Hsoln is (+) for NaCl in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for Na2SO4 in H2O ∆Hsoln is (–) for O2 in H2O Consider the case that ∆Hmix is negative: since ∆Smix is positive then ∆Gsoln will have to be negative and the reaction happens. Now consider the case that ∆Hmix is positive: in this case the spontaneity of the ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hy ...
... oxidation state. The melting point is 29.8º C and therefore melts by increasing room temperature by a little. Gallium is important because it forms gallium arsenide (GaAs), which can convert light directly into electricity. Also due to thermite reaction, aluminum can extract oxygen from water and hy ...
College Chemistry 1 Note Guide(free download)
... 6. give a brief description of how a basic mass spectrometer works. 7. give a general overview of the periodic table and point out where types of elements and families/groups of elements are found. 8. introduce the concept of the mole roadmap and demonstrate how to use this concept in chemical calcu ...
... 6. give a brief description of how a basic mass spectrometer works. 7. give a general overview of the periodic table and point out where types of elements and families/groups of elements are found. 8. introduce the concept of the mole roadmap and demonstrate how to use this concept in chemical calcu ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
Openstax - Chemistry - Answer Key
... 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always have the same ratio. 5. Dalton originally thought that all atoms of a particular element had identical properties, including mass. Thus, the concept of i ...
... 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always have the same ratio. 5. Dalton originally thought that all atoms of a particular element had identical properties, including mass. Thus, the concept of i ...
- Deans Community High School
... current through the molten substance results in electrolysis. What type of structure is presenting the substance? A. ionic B. metallic C. covalent molecular D. covalent network 6. In which of the substances, in the solid state, would Van der Waals’ attractions be a significant “intermolecular force” ...
... current through the molten substance results in electrolysis. What type of structure is presenting the substance? A. ionic B. metallic C. covalent molecular D. covalent network 6. In which of the substances, in the solid state, would Van der Waals’ attractions be a significant “intermolecular force” ...
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND
... ionic solid, molecules for molecular solids) under standard conditions is called lattice enthalpy (∆lHo). The lattice enthalpy is a positive quantity. ELECTRO VALENCY: The number of electrons lost or gain by an atom of an element is called as electrovalency. The element which give up electrons to fo ...
... ionic solid, molecules for molecular solids) under standard conditions is called lattice enthalpy (∆lHo). The lattice enthalpy is a positive quantity. ELECTRO VALENCY: The number of electrons lost or gain by an atom of an element is called as electrovalency. The element which give up electrons to fo ...
Electron - CoolHub
... used interchangeably as if they are the same thing. Explain to students that an atom is the smallest particle or “building block” of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same type of atom. For instance, a piece of pure carbon is made up of only carbon atoms. This piece of pure c ...
... used interchangeably as if they are the same thing. Explain to students that an atom is the smallest particle or “building block” of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same type of atom. For instance, a piece of pure carbon is made up of only carbon atoms. This piece of pure c ...
File
... A reaction in which a species is both oxidized and reduced is called disproportionation. It may occur when a substance can act as both an oxidizing agent and as a reducing agent. ...
... A reaction in which a species is both oxidized and reduced is called disproportionation. It may occur when a substance can act as both an oxidizing agent and as a reducing agent. ...
chemistry-2nd-edition-julia-burdge-solution
... Rubidium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation. The polyatomic ion nitrite, NO 2 , has a 1 charge. Because the charges on the cation and anion are numerically equal, the ions combine in a oneto-one ratio. The correct formula is RbNO2. Potassium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation ...
... Rubidium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation. The polyatomic ion nitrite, NO 2 , has a 1 charge. Because the charges on the cation and anion are numerically equal, the ions combine in a oneto-one ratio. The correct formula is RbNO2. Potassium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation ...