Chapter 14 Enzyme Characteristics
... curve where t = 0. Many things can influence the catalytic ability of an enzyme, including the accumulation of products as well as denaturation of the protein itself. It is only at the initiation of the reaction that one is sure of the amount of active enzyme present and the other conditions of subs ...
... curve where t = 0. Many things can influence the catalytic ability of an enzyme, including the accumulation of products as well as denaturation of the protein itself. It is only at the initiation of the reaction that one is sure of the amount of active enzyme present and the other conditions of subs ...
Document
... carboxyl group and splits off a molecule of water to create the cyclic ester. The rate constant here is about 10-6. Very slow because it is just wandering around. Let’s then put some methyl groups on this molecule and methyl groups on one of the methylene linkage to the carboxylic acid. And, let’s i ...
... carboxyl group and splits off a molecule of water to create the cyclic ester. The rate constant here is about 10-6. Very slow because it is just wandering around. Let’s then put some methyl groups on this molecule and methyl groups on one of the methylene linkage to the carboxylic acid. And, let’s i ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... Reaction A: Reactants are at a higher energy level than products. 100 kJ of energy are required for activation and 100kJ are released. The reaction is exothermic Reaction B: Products are at a higher energy content than reactants. 250 kJ are required to activate the reaction. A total of 100 kJ are ab ...
... Reaction A: Reactants are at a higher energy level than products. 100 kJ of energy are required for activation and 100kJ are released. The reaction is exothermic Reaction B: Products are at a higher energy content than reactants. 250 kJ are required to activate the reaction. A total of 100 kJ are ab ...
Energetic
... Heat of neutralization for weak acids and alkalis The heats of neutralization for reactions involving weak acids or weak alkalis are either _________ or _________ than -57.3 kJ mol-1. ...
... Heat of neutralization for weak acids and alkalis The heats of neutralization for reactions involving weak acids or weak alkalis are either _________ or _________ than -57.3 kJ mol-1. ...
AP Chemistry
... I have taught AP Chemistry for 10 years and am very excited about next year. AP Chemistry is designed to prepare you to be successful in college chemistry as well as to pass the AP Chemistry test. Attached is the summer work placket to prepare you. Expect a test on this material the second day of sc ...
... I have taught AP Chemistry for 10 years and am very excited about next year. AP Chemistry is designed to prepare you to be successful in college chemistry as well as to pass the AP Chemistry test. Attached is the summer work placket to prepare you. Expect a test on this material the second day of sc ...
Unit 8 Note Packet
... 2. Balance a chemical equation based upon the law of conservation of matter. 3. Analyze or draw a graph for the energy change of a chemical reaction. 4. Calculate the heat of solution for a given compound. We are looking for: 1a. Given the word equation/sentence, translate it into a formula chemical ...
... 2. Balance a chemical equation based upon the law of conservation of matter. 3. Analyze or draw a graph for the energy change of a chemical reaction. 4. Calculate the heat of solution for a given compound. We are looking for: 1a. Given the word equation/sentence, translate it into a formula chemical ...
Big Idea #3
... • Cell notation also applies when the metal(s) is not part of the reaction and an inert (non-reactive) electrode is used) Ex: Pt(s)l H2(g) lH+(aq) ll Ag+(aq)l Ag(s) ...
... • Cell notation also applies when the metal(s) is not part of the reaction and an inert (non-reactive) electrode is used) Ex: Pt(s)l H2(g) lH+(aq) ll Ag+(aq)l Ag(s) ...
Document
... H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(g) What do we do to avoid violating the law of conservation of matter? (As written we’ve lost an oxygen atom somewhere.) ...
... H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(g) What do we do to avoid violating the law of conservation of matter? (As written we’ve lost an oxygen atom somewhere.) ...
2007 - SolPass
... solid changing to a liquid phase solid changing to a gaseous phase gas filling the space in its container liquid taking the shape of its container ...
... solid changing to a liquid phase solid changing to a gaseous phase gas filling the space in its container liquid taking the shape of its container ...
Document
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
nomenclature review
... ________ Magnesium chloride is dissolved in water. ________ Hydrochloric acid neutralizes sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. 13. Why are phase changes considered only physical changes? 14. Sketch an example of the following at the molecular level: a. a gaseous compound b. a mixture ...
... ________ Magnesium chloride is dissolved in water. ________ Hydrochloric acid neutralizes sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. 13. Why are phase changes considered only physical changes? 14. Sketch an example of the following at the molecular level: a. a gaseous compound b. a mixture ...
PowerPoint - Science Geek
... reason backward. This is a very useful accomplishment, and a very easy one, but people do not practice it much.” Sherlock Holmes, in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s A Study in Scarlet ...
... reason backward. This is a very useful accomplishment, and a very easy one, but people do not practice it much.” Sherlock Holmes, in Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s A Study in Scarlet ...
Every reaction is reversible: A chemical reaction is in equilibrium
... Increasing the temperature increases the energy E forcing the equilibrium to move to the left. This would reduce [C2H6] and increase [C2H2] and [H2]. This would therefore reduce the value of K. Increasing the pressure forces the equilibrium to move to the right increasing [C2H6] and reducing [C2H2] ...
... Increasing the temperature increases the energy E forcing the equilibrium to move to the left. This would reduce [C2H6] and increase [C2H2] and [H2]. This would therefore reduce the value of K. Increasing the pressure forces the equilibrium to move to the right increasing [C2H6] and reducing [C2H2] ...
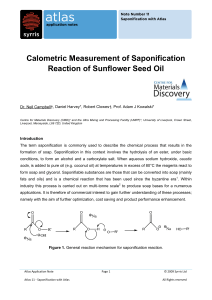
Calometric Measurement of Saponification Reaction
... The enthalpy of formation of the soap product is calculated using Power Compensation Calorimetery (PCC). This is achieved through the control and online monitoring of the power applied through the compensation heating rod (which is inserted directly into the reaction-content) and control of the temp ...
... The enthalpy of formation of the soap product is calculated using Power Compensation Calorimetery (PCC). This is achieved through the control and online monitoring of the power applied through the compensation heating rod (which is inserted directly into the reaction-content) and control of the temp ...
No Slide Title
... Chemical Equilibrium • Chemical Equilibrium: A state in which the tendency of the reactants to form products is balanced by the tendency of the products to form reactants. • Could also be defined as a system in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are the same. No observable chang ...
... Chemical Equilibrium • Chemical Equilibrium: A state in which the tendency of the reactants to form products is balanced by the tendency of the products to form reactants. • Could also be defined as a system in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are the same. No observable chang ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.