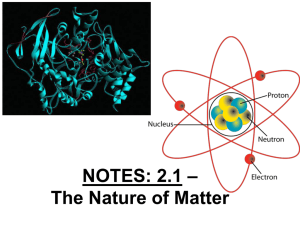
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... close together, a slight attraction can develop between the oppositely charged regions of ...
... close together, a slight attraction can develop between the oppositely charged regions of ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
document
... Part A: Match the letter of the correct definition to the Vocabulary term. 1. Octet Rule A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond element is willi ...
... Part A: Match the letter of the correct definition to the Vocabulary term. 1. Octet Rule A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond element is willi ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atoms to make new molecules, energy is released. The specific amount of energy that is needed to break a bond, or is releases when that same bond forms, is called bond energy. ...
... reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atoms to make new molecules, energy is released. The specific amount of energy that is needed to break a bond, or is releases when that same bond forms, is called bond energy. ...
CHEM 11 Practice Exam 2
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
Elements PPT
... the second can hold eight so it needs two more to be stable, that means that oxygen wants to combine with other elements or itself. ...
... the second can hold eight so it needs two more to be stable, that means that oxygen wants to combine with other elements or itself. ...
Chapter 2
... pH = relative concentration of H+ in a solution of water B. Acids - compounds which increase the concentration of H+ (pH = 1 to 6) C. Bases - compounds which decrease the concentration of H+ (pH = 8 to 14) D. Buffer - compound that prevents large changes in pH of a solution (pH “shock absorber”) ...
... pH = relative concentration of H+ in a solution of water B. Acids - compounds which increase the concentration of H+ (pH = 1 to 6) C. Bases - compounds which decrease the concentration of H+ (pH = 8 to 14) D. Buffer - compound that prevents large changes in pH of a solution (pH “shock absorber”) ...
bonding and geometry
... One of the elements is more electronegative than the other and therefore has a greater desire for the shared pair The MORE electronegative element tends to pull the electrons closer and thus has a slightly negative charge The LESS electronegative element has a slightly positive charge since th ...
... One of the elements is more electronegative than the other and therefore has a greater desire for the shared pair The MORE electronegative element tends to pull the electrons closer and thus has a slightly negative charge The LESS electronegative element has a slightly positive charge since th ...
Give reasons for the following: (i) Bond enthalpy of F2
... Fluorine being the most electronegative atom does not exhibit positive oxidation state because the electrons in fluorine are strongly attracted by the nuclear charge because of small size of fluorine atom and therefore, removal of an electron is not possible. ...
... Fluorine being the most electronegative atom does not exhibit positive oxidation state because the electrons in fluorine are strongly attracted by the nuclear charge because of small size of fluorine atom and therefore, removal of an electron is not possible. ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part A
... Forms of Energy • Chemical energy—stored in bonds of chemical substances • Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles • Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter • Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and ...
... Forms of Energy • Chemical energy—stored in bonds of chemical substances • Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles • Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter • Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... 8. Group 3A compounds are often electron deficient. How do the following compounds minimize the instability of their electron deficiencies? One sentence for each is enough. You can draw structures but you don't need to. Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer whe ...
... 8. Group 3A compounds are often electron deficient. How do the following compounds minimize the instability of their electron deficiencies? One sentence for each is enough. You can draw structures but you don't need to. Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer whe ...
Ch 5.1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... Polar Covalent Bond: In polar covalent bond, the e tend to be more towards the atom having a higher electro negativity. Ex. H2O Electro negativity difference and bonding: The difference in the electro negativity value of the two atoms will decide as to what kind of bond will be formed. Electro neg ...
... Polar Covalent Bond: In polar covalent bond, the e tend to be more towards the atom having a higher electro negativity. Ex. H2O Electro negativity difference and bonding: The difference in the electro negativity value of the two atoms will decide as to what kind of bond will be formed. Electro neg ...
atoms
... atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. ...
... atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms have one, and oxygen atoms have eight. The number of protons in an atom is referred to as the atomic number of that element. ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Valence shell not full Tend to gain, lose, or share electrons (form bonds) with other atoms to achieve stability ...
... Valence shell not full Tend to gain, lose, or share electrons (form bonds) with other atoms to achieve stability ...
Chemical Bonds - coellochemistry
... Triple bonds: three lines drawn and represents 6 valence electrons ...
... Triple bonds: three lines drawn and represents 6 valence electrons ...
Chapter 5
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
Review for second exam:
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
cell molecules
... when H+ or OH- is added to the solution. – Buffers accept hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donate hydrogen ions when they have been depleted. ...
... when H+ or OH- is added to the solution. – Buffers accept hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donate hydrogen ions when they have been depleted. ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. a. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchangi ...
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. a. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchangi ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
vsepr_lite_oct_2011 - chemistry11crescentsummer
... understand covalent bonding—polar and non-polar be able to draw Lewis structures for simple molecules and polyatomic ions, including molecules with double and triple bonds Introduction The premise of VSEPR theory: In a molecule or polyatomic ion, pairs of valence electrons on the central atom (c ...
... understand covalent bonding—polar and non-polar be able to draw Lewis structures for simple molecules and polyatomic ions, including molecules with double and triple bonds Introduction The premise of VSEPR theory: In a molecule or polyatomic ion, pairs of valence electrons on the central atom (c ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
... 2. Usually expressed as the energy needed to break one mole of bonds. 3. A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. 4. High dissociation energies tend to create very stable compounds that tend to be chemically unreactive. 5. Units are measured in kJ/mo1 6. A mol is a che ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... have full outside energy levels do not react with other elements ...
... have full outside energy levels do not react with other elements ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.