Rocket observation of energetic electrons in the low-altitude auroral
... board the sounding rocket S-310-35, which was launched from Andøya Rocket Range, Norway, at 0033:00 UT on 13 December 2004 during the DELTA campaign. The APD was designed to measure energy spectra of energetic electrons in the range of 3.5 to 65 keV every 10 ms using avalanche photodiodes. The measu ...
... board the sounding rocket S-310-35, which was launched from Andøya Rocket Range, Norway, at 0033:00 UT on 13 December 2004 during the DELTA campaign. The APD was designed to measure energy spectra of energetic electrons in the range of 3.5 to 65 keV every 10 ms using avalanche photodiodes. The measu ...
PDF 3
... states lie below EF while the empty states lie above EF . The broad peak below EF corresponds to the filled 3d states. Adapted from http://www.personal.psu.edu/ams751/VASP-Cu/ small that they can be considered to be continuous. Density of states (DOS) is defined as the number of available energy sta ...
... states lie below EF while the empty states lie above EF . The broad peak below EF corresponds to the filled 3d states. Adapted from http://www.personal.psu.edu/ams751/VASP-Cu/ small that they can be considered to be continuous. Density of states (DOS) is defined as the number of available energy sta ...
Chapter 4 (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple
... As an example consider infinite well potential describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trap ...
... As an example consider infinite well potential describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trap ...
Lone pairs
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
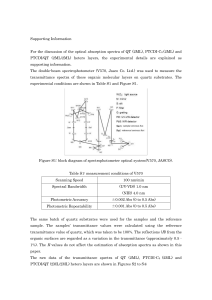
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
... In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT HOMO level drops to a lower level or the optical band-gap expands after exposure to air. In an ...
Name_______________________________________________
... 3. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable that those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
... 3. Noble-gas atoms are able to exist independently in nature because a. they are exceptions to the octet rule. b. their bond energies are low compared to their bond lengths. c. their electron configurations are more stable that those of other atoms. d. they share electrons in overlapping orbitals wi ...
Balancing Chemical Equation Practice.docx
... atoms, as in H2O2, this gives us a chemical entirely different from water. H2O2 is actually hydrogen peroxide, a chemical applied to externally to cuts to prevent bacterial infection. ...
... atoms, as in H2O2, this gives us a chemical entirely different from water. H2O2 is actually hydrogen peroxide, a chemical applied to externally to cuts to prevent bacterial infection. ...
Spontaneous Particle-Hole Symmetry Breaking in the $\ nu= 5/2
... Hamiltonian H 3 and, naturally, the Pf is its ground state. Importantly, when normal ordered, H 3 contains a three-body term exactly the minus of H3 plus a twobody term, a one-body term (the chemical potential), and a constant [18]. Adding H3 and H 3 simply eliminates the three-body interaction and ...
... Hamiltonian H 3 and, naturally, the Pf is its ground state. Importantly, when normal ordered, H 3 contains a three-body term exactly the minus of H3 plus a twobody term, a one-body term (the chemical potential), and a constant [18]. Adding H3 and H 3 simply eliminates the three-body interaction and ...
File
... cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts of excited and ground state of electrons in atoms (electromagnetic radiation is given off as photons), emission spectrum ...
... cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts of excited and ground state of electrons in atoms (electromagnetic radiation is given off as photons), emission spectrum ...
Fine structure of the hydrogen atom
... emerges from a slit to be bombarded by electrons which bring about one atom in a hundred million atoms to the metastable state. After a small recoil deflection, the excited atoms move on to a metal surface from which they can eject electrons and so be detected. Between bombarder and detector, the at ...
... emerges from a slit to be bombarded by electrons which bring about one atom in a hundred million atoms to the metastable state. After a small recoil deflection, the excited atoms move on to a metal surface from which they can eject electrons and so be detected. Between bombarder and detector, the at ...
final exam review packet
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...
... C-Matter-201. I can explain what physical and chemical properties are, and list examples. C-Matter-202. I can describe how density relates to mass and volume for matter. C-Matter-203. I can calculate density given the mass and volume, or calculate relationships between density, mass and volume C-Mat ...
Chapter 2: Atoms and Electrons
... natural phenomena, relating these observations to previously established theory, and finally establishing a physical model for the observations. For example, we can explain the behavior of a spring-supported weight moving up and down periodically after an initial displacement, because the differenti ...
... natural phenomena, relating these observations to previously established theory, and finally establishing a physical model for the observations. For example, we can explain the behavior of a spring-supported weight moving up and down periodically after an initial displacement, because the differenti ...
Electron Spin I - Rutgers Physics
... The z in the upper left corner indicates that the magnetic field gradient is oriented in the negative z-direction. This splits the electrons into two beams in z with the upper beam corresponding to electrons with spin-up in the z-direction and the lower beam to electrons with spin-down in the z-dire ...
... The z in the upper left corner indicates that the magnetic field gradient is oriented in the negative z-direction. This splits the electrons into two beams in z with the upper beam corresponding to electrons with spin-up in the z-direction and the lower beam to electrons with spin-down in the z-dire ...
This Week Final Exam Marks on the Web
... • The electrons suffer centripetal acceleration in their orbits. • Any accelerated charge should radiate electromagnetic energy. ⇒ The electrons should lose energy and spiral into the nucleus in very little time. ⇒ A planetary atom should not be stable! ⇒ Classical theory does not explain the st ...
... • The electrons suffer centripetal acceleration in their orbits. • Any accelerated charge should radiate electromagnetic energy. ⇒ The electrons should lose energy and spiral into the nucleus in very little time. ⇒ A planetary atom should not be stable! ⇒ Classical theory does not explain the st ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.