Final review free response ch 1-4
... Proton versus Neutrons versus Electrons Percent abundance, and mass spectrometry Periodic trends (diatomic, metals, nonmetals, metalloids, cations versus anions) Ionic (transferring of electrons) versus covalent (shared electrons) Naming: ionic, covalent, ions (oxy-ions), acids (binary and ...
... Proton versus Neutrons versus Electrons Percent abundance, and mass spectrometry Periodic trends (diatomic, metals, nonmetals, metalloids, cations versus anions) Ionic (transferring of electrons) versus covalent (shared electrons) Naming: ionic, covalent, ions (oxy-ions), acids (binary and ...
Physical Chemistry - School of Chemistry, University of Leeds
... water pumped through the jacket from a thermostatted water bath. The conductivity cell is a pair of platinum black electrodes with electrical connections and an integrated thermometer. Instructions for the use of the conductivity meters and computer data acquisition units are provided with the appar ...
... water pumped through the jacket from a thermostatted water bath. The conductivity cell is a pair of platinum black electrodes with electrical connections and an integrated thermometer. Instructions for the use of the conductivity meters and computer data acquisition units are provided with the appar ...
Smith-D
... For adiabatic systems, the amount of work required to change the internal energy of the system is independent of how the work is performed The system is dependent on its initial and final states but independent of how it got there Hence the internal energy is a state function (or potential) ...
... For adiabatic systems, the amount of work required to change the internal energy of the system is independent of how the work is performed The system is dependent on its initial and final states but independent of how it got there Hence the internal energy is a state function (or potential) ...
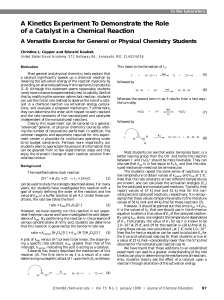
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely have a chance to experimentally test its validity. We fin ...
... a catalyst significantly speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (typically by providing an alternate pathway from reactants to products) (1–3). Although this statement seems reasonable, students rarely have a chance to experimentally test its validity. We fin ...
Chemical Equations
... • AgNO3 + NaCl ---> AgCl + NaNO3 A precipitate is formed Use solubility table to see if a precipitate will form ...
... • AgNO3 + NaCl ---> AgCl + NaNO3 A precipitate is formed Use solubility table to see if a precipitate will form ...
*6th Grade Science-Chapter 5 Study Guide Lesson 5.1: Observing
... A precipitate is a solid that forms from liquids that undergo chemical changes in a chemical reaction. A gas can form from a solid or liquid as a result of chemical changes. A color change can occur as a result of chemical changes. Exothermic reaction- net energy is released from a chemical reaction ...
... A precipitate is a solid that forms from liquids that undergo chemical changes in a chemical reaction. A gas can form from a solid or liquid as a result of chemical changes. A color change can occur as a result of chemical changes. Exothermic reaction- net energy is released from a chemical reaction ...
Ch. 18 Class PowerPoint
... • This principle is true for all dynamic equilibria, chemical as well as physical. ...
... • This principle is true for all dynamic equilibria, chemical as well as physical. ...
50 Forgotten Facts
... b) Adding a catalyst will _________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps from the reaction pathway (mechanism). c) Adding an inhibitor will __________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps to the reaction pathway. ...
... b) Adding a catalyst will _________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps from the reaction pathway (mechanism). c) Adding an inhibitor will __________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps to the reaction pathway. ...
Second Year Chemistry
... G = H – TS; H = U + pV; dU = dq + dw For an infinitesimal change in G: G + dG = H + dH – (T + dT)(S + dS) = H + dH – TS – TdS – SdT – dTdS dG = dH – TdS – SdT Also can write: dH = dU + pdV + Vdp dU = TdS – pdV (dS = dqrev/T and dw = -pdV) ...
... G = H – TS; H = U + pV; dU = dq + dw For an infinitesimal change in G: G + dG = H + dH – (T + dT)(S + dS) = H + dH – TS – TdS – SdT – dTdS dG = dH – TdS – SdT Also can write: dH = dU + pdV + Vdp dU = TdS – pdV (dS = dqrev/T and dw = -pdV) ...
pdfCfE Higher - Unit 3 - Pupil Booklet 2 MB
... Catalysts increase the rate at which an equilibrium is formed but do not affect the equilibrium position. The Position of Equilibrium The position of equilibrium means the extent to which the reaction has taken place. The equilibrium in this case lies well to the right hand side. There is 80% conver ...
... Catalysts increase the rate at which an equilibrium is formed but do not affect the equilibrium position. The Position of Equilibrium The position of equilibrium means the extent to which the reaction has taken place. The equilibrium in this case lies well to the right hand side. There is 80% conver ...
6-1 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
... someone take note of the initial temperature. SLOWLY add ACID TO WATER. Take temperature again. Typical temperature change will be from around 22o C to 93o C. The equation for this reaction is: H2O (l) + H2SO4 (aq) = H2O (l) + H2SO4 (aq) (diluted) The amount of heat in Joules can be calculated as fo ...
... someone take note of the initial temperature. SLOWLY add ACID TO WATER. Take temperature again. Typical temperature change will be from around 22o C to 93o C. The equation for this reaction is: H2O (l) + H2SO4 (aq) = H2O (l) + H2SO4 (aq) (diluted) The amount of heat in Joules can be calculated as fo ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.