Chapter 6A Chemical Reactions CHAPTER OUTLINE
... K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. K2CrO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq) ...
... K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. K2CrO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2 (aq) ...
Document
... Simple chemical reactions Chemical reactions In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are ...
... Simple chemical reactions Chemical reactions In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... (solid, liquid, aqueous, or gas). If no reaction occurs write the words "no reaction" (or NR) instead of the products in your balanced equation and indicate why your think there was no reaction. Unless otherwise indicated, dispose of all waste in the waste container, or a beaker that you pour into t ...
... (solid, liquid, aqueous, or gas). If no reaction occurs write the words "no reaction" (or NR) instead of the products in your balanced equation and indicate why your think there was no reaction. Unless otherwise indicated, dispose of all waste in the waste container, or a beaker that you pour into t ...
6-1 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
... q = specific heat of water x grams of water x change in temperature specific heat of water = 4.18 J /(g oC) grams of water = 50. change in temperature = final temperature - initial temperature There are 4.184 Joules in one calorie. Clean Up: Barium is a toxic metal and must be disposed of by EH&S. C ...
... q = specific heat of water x grams of water x change in temperature specific heat of water = 4.18 J /(g oC) grams of water = 50. change in temperature = final temperature - initial temperature There are 4.184 Joules in one calorie. Clean Up: Barium is a toxic metal and must be disposed of by EH&S. C ...
classification of chemical reactions
... ____________________________________________________________ energy is needed to keep the reaction going energy is shown on________________________________________ Reactants + heat energy products ...
... ____________________________________________________________ energy is needed to keep the reaction going energy is shown on________________________________________ Reactants + heat energy products ...
final exam review packet
... A. The solution’s ___________________ point is higher. (when you cook pasta) B. The solution’s ___________________ point is lower. (when you add salt to roads in winter) C. These properties are called __________________properties because they depend on the concentration of solute but not the nature ...
... A. The solution’s ___________________ point is higher. (when you cook pasta) B. The solution’s ___________________ point is lower. (when you add salt to roads in winter) C. These properties are called __________________properties because they depend on the concentration of solute but not the nature ...
Types of Chemical Reactions Name_________________________
... An Introduction to Types of Chemical Reactions The purpose of this Internet assignment is to provide you with an independent learning opportunity to learn about the different types of chemical reactions. The website address for this assignment is www.ric.edu/ptiskus/reactions. On the website you wil ...
... An Introduction to Types of Chemical Reactions The purpose of this Internet assignment is to provide you with an independent learning opportunity to learn about the different types of chemical reactions. The website address for this assignment is www.ric.edu/ptiskus/reactions. On the website you wil ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... 19. A 11.6-g sample of iron ore, containing Fe3O4 (232 g/mol), is reacted with carbon to form purified iron. The other product of the reaction is carbon dioxide gas. 2.10 g of iron is recovered from one such trial. ...
... 19. A 11.6-g sample of iron ore, containing Fe3O4 (232 g/mol), is reacted with carbon to form purified iron. The other product of the reaction is carbon dioxide gas. 2.10 g of iron is recovered from one such trial. ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... (a) Compare non transition and transition elements on the basis of their (i) Variability of oxidation states (ii) stability of oxidation states. (b) Give chemical reactions for the following observations: (i) Potassium dichromate is a good oxidising agent in acidic medium. (ii) Inter convertibility ...
... (a) Compare non transition and transition elements on the basis of their (i) Variability of oxidation states (ii) stability of oxidation states. (b) Give chemical reactions for the following observations: (i) Potassium dichromate is a good oxidising agent in acidic medium. (ii) Inter convertibility ...
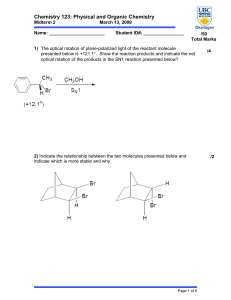
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... 14) Which of the following would have the greater ΔS? (A) C(s) (B) C(g) (C) CO(g) (D) CO2(g) 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; ...
... 14) Which of the following would have the greater ΔS? (A) C(s) (B) C(g) (C) CO(g) (D) CO2(g) 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; ...
Word Equations • a summary
... Use molecular building kits to look at the reaction of: Methane + CH4 ...
... Use molecular building kits to look at the reaction of: Methane + CH4 ...
Thermochemistry: The Heat of Neutralization
... Energy is defined as the ability to do work. One form of energy is heat, defined as thermal energy flowing from an object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature. For example, a piece of molten iron placed in water will lose (give off) heat while the water will gain (absorb) heat ...
... Energy is defined as the ability to do work. One form of energy is heat, defined as thermal energy flowing from an object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature. For example, a piece of molten iron placed in water will lose (give off) heat while the water will gain (absorb) heat ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
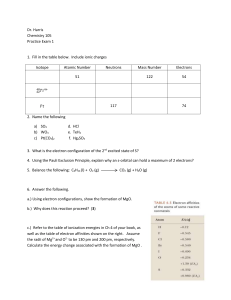
1 Types of Chemical Reactions
... and chemical properties are formed. Chemical reactions can be grouped into categories depending on the nature of the chemical reaction. For example during a decomposition reaction a single substance can break apart into several different substances. ...
... and chemical properties are formed. Chemical reactions can be grouped into categories depending on the nature of the chemical reaction. For example during a decomposition reaction a single substance can break apart into several different substances. ...
Chapter 8powerp point for chemical reactions
... Solid iron(III)oxide and carbon monoxide gas produces solid iron and carbon dioxide gas. ...
... Solid iron(III)oxide and carbon monoxide gas produces solid iron and carbon dioxide gas. ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-II Chemistry (Theory) Class-XII
... Neetu and Asha look organic compound synthesis as their chemistry project. They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again a ...
... Neetu and Asha look organic compound synthesis as their chemistry project. They prepare benzene diazonium chloride and stored it at room temperature. Due to holiday, they start preparing azodye but it cannot be prepared. Then their friend Reena told them to prepare benzene diazonium chloride again a ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.