Step 2
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
Step 2 - The Grange School Blogs
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
... 46) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have A) different atomic numbers. B) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of protons. C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but diff ...
... 46) Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have A) different atomic numbers. B) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of protons. C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but diff ...
Measuring and Calculating
... atoms are held together by the sharing of a pair of electrons, which involves an overlap of the electron clouds and thus forms a strong bond and forms individual molecules. Occurs between nonmetal atoms. Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sh ...
... atoms are held together by the sharing of a pair of electrons, which involves an overlap of the electron clouds and thus forms a strong bond and forms individual molecules. Occurs between nonmetal atoms. Nonpolar covalent bond – very low electronegativity difference, results in a nearly equal sh ...
In organic chemistry, we studied a lot about the essential elements
... single corner of our life, chemistry is getting involved in. Even though in nature, chemistry is also taking an important role. For instant, how tree photosynthesize from inorganic substances (carbon dioxide and water) to organic substances like sugar carbohydrate and oxygen. How about the process o ...
... single corner of our life, chemistry is getting involved in. Even though in nature, chemistry is also taking an important role. For instant, how tree photosynthesize from inorganic substances (carbon dioxide and water) to organic substances like sugar carbohydrate and oxygen. How about the process o ...
Chemistry
... C4.10e Write the symbol for an isotope, X Z A , where Z is the atomic number, A is the mass number, and X is the symbol for the element. C5.2 Chemical Changes Chemical changes can occur when two substances, elements, or compounds interact and produce one or more different substances whose physical a ...
... C4.10e Write the symbol for an isotope, X Z A , where Z is the atomic number, A is the mass number, and X is the symbol for the element. C5.2 Chemical Changes Chemical changes can occur when two substances, elements, or compounds interact and produce one or more different substances whose physical a ...
Unit 6 – Chemical Reactions: Particles and Energy
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
Limiting Reactant WS with Answers
... 11) 1.000 g of vanadium (V) is mixed with 8.000 g of bromine (Br2). After the elements react, some bromine is left over, along with a single compound that contains the two elements. The excess bromine is removed and allowed to react with excess sodium sulfite and excess sodium hydroxide, producing a ...
... 11) 1.000 g of vanadium (V) is mixed with 8.000 g of bromine (Br2). After the elements react, some bromine is left over, along with a single compound that contains the two elements. The excess bromine is removed and allowed to react with excess sodium sulfite and excess sodium hydroxide, producing a ...
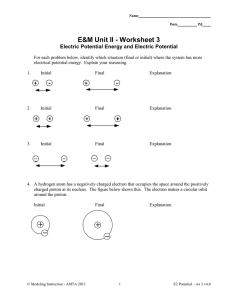
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... 4. A hydrogen atom has a negatively charged electron that occupies the space around the positively charged proton at its nucleus. The figure below shows this. The electron makes a circular orbit around the proton. ...
... 4. A hydrogen atom has a negatively charged electron that occupies the space around the positively charged proton at its nucleus. The figure below shows this. The electron makes a circular orbit around the proton. ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... An amount of an element or compound in moles can be converted to a mass in grams by multiplying by the appropriate molar mass. • example: ...
... An amount of an element or compound in moles can be converted to a mass in grams by multiplying by the appropriate molar mass. • example: ...
Balancing and Predicting Chemical Reactions:
... What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous calcium hydroxide and nitric acid? The products of this reaction are aqueous calcium nitrate and water. How does this net ionic equation compare to the net ionic equation shown on the earlier slide? ...
... What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous calcium hydroxide and nitric acid? The products of this reaction are aqueous calcium nitrate and water. How does this net ionic equation compare to the net ionic equation shown on the earlier slide? ...
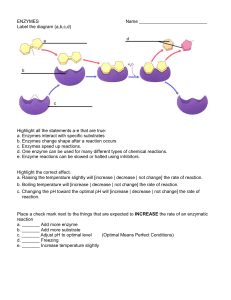
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Fall 2006
... 2. The potential in a region due to an Electric field is V 3xy 2 2 xz 2 5 , where x,y, and z are the coordinates and are measured in meters, and the potential is measured in Volts. a. Find the potential at the origin. ...
... 2. The potential in a region due to an Electric field is V 3xy 2 2 xz 2 5 , where x,y, and z are the coordinates and are measured in meters, and the potential is measured in Volts. a. Find the potential at the origin. ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
... Introduction: The equation H2 + O2 H2O is unbalanced because there are two oxygen atoms on the reactants side of the equation, and only one on the products side of the equation. To balance the equation, you cannot change the structure of any of the molecules, but you can change the number of molec ...
Document
... Seawater is essentially 0.438 M NaCl and 0.0512 M MgCl 2, together with several other minor solutes. What are the molarities of Na+, Mg2+, and Cl– in seawater? ...
... Seawater is essentially 0.438 M NaCl and 0.0512 M MgCl 2, together with several other minor solutes. What are the molarities of Na+, Mg2+, and Cl– in seawater? ...
Slide 1
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
FORMAL CHARGE AND OXIDATION NUMBER - IDC
... Although the total number of valence electrons in a molecule is easily calculated, there is not aways a simple and unambiguous way of determining how many reside in a particular bond or as non-bonding pairs on a particular atom. For example, one can write valid Lewis octet structures for carbon mono ...
... Although the total number of valence electrons in a molecule is easily calculated, there is not aways a simple and unambiguous way of determining how many reside in a particular bond or as non-bonding pairs on a particular atom. For example, one can write valid Lewis octet structures for carbon mono ...
CHEM 5142
... The course will focus primarily on the material in the text with additional assignments from the chemical literature. In addition, a list of other sources is given at the end of the syllabus. As a result of successfully completing this course you should be able to; 1. Understand the mechanisms invol ...
... The course will focus primarily on the material in the text with additional assignments from the chemical literature. In addition, a list of other sources is given at the end of the syllabus. As a result of successfully completing this course you should be able to; 1. Understand the mechanisms invol ...
1. What is a Chemical Reaction?
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
elements of chemistry unit
... OXIDATION NUMBER RULES For more complicated atoms, apply the following rules. OXIDATION NUMBER RULES Rule 1. As shown earlier, the oxidation number of atoms in a pure element is defined as zero: C(0) Fe(0) H2(0) OXIDATION NUMBER RULES Rule 2. A single atom is assigned an oxidation number equal to it ...
... OXIDATION NUMBER RULES For more complicated atoms, apply the following rules. OXIDATION NUMBER RULES Rule 1. As shown earlier, the oxidation number of atoms in a pure element is defined as zero: C(0) Fe(0) H2(0) OXIDATION NUMBER RULES Rule 2. A single atom is assigned an oxidation number equal to it ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.