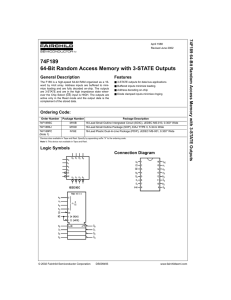
74F189 64-Bit Random Access Memory with 3
... 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N16E ...
... 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N16E ...
The transistor amplifier
... input voltages (from a microphone or other amplifier stage etc.) to change Vb up and down, but only around the steady bias voltage already determined by R1 and R2. Note that these changes will typically be measured in a small number of millivolts, they are not large changes. At most, the signal volt ...
... input voltages (from a microphone or other amplifier stage etc.) to change Vb up and down, but only around the steady bias voltage already determined by R1 and R2. Note that these changes will typically be measured in a small number of millivolts, they are not large changes. At most, the signal volt ...
Slide 1
... In a bridge circuit the voltage difference between the two parallel branches is used to indicate the potential difference between the two points. ...
... In a bridge circuit the voltage difference between the two parallel branches is used to indicate the potential difference between the two points. ...
Lecture 1
... • Determine input-output relationship (gain, phase) => point out that this is only good for 2 rad/sec frequency sinusoids ...
... • Determine input-output relationship (gain, phase) => point out that this is only good for 2 rad/sec frequency sinusoids ...
AN-7733 FL7732 设计工具流程(升降压式) Enter Input/Output Spec. Transformer Design
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
... VOUT condition. The switching frequency should be <65kHz. Enter Np over Np.min. If Np is too big to fit in transformer window, reduce Max. Duty. Pulse-by-pulse current limit is 0.67V. If VCS.MAX is too close to 0.67V, increase Max. Duty. t DIS means secondary diode conduction time at peak input volt ...
Review Test #6: Electric Circuits
... 3. A circuit in your home has a 15 A circuit breaker. How many 60 W incandescent bulbs can be operated at the same time using 120 V? ...
... 3. A circuit in your home has a 15 A circuit breaker. How many 60 W incandescent bulbs can be operated at the same time using 120 V? ...
Theoretical Background of a Series RLC Circuit
... The RLC Circuit and Experiments The RLC series circuit is simply – a resistor Rs of about 10 in series with an inductor of 10 mH (having an internal coil resistance of RL of about 66 ) in series with a capacitor C. We currently are using two different capacitor C values, one value is 1 nF that g ...
... The RLC Circuit and Experiments The RLC series circuit is simply – a resistor Rs of about 10 in series with an inductor of 10 mH (having an internal coil resistance of RL of about 66 ) in series with a capacitor C. We currently are using two different capacitor C values, one value is 1 nF that g ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... A simulated filter example is shown in Figure 3 with a third-order elliptical filter with a 3 dB frequency of 3 MHz. Matching input and output impedances makes the filter design easier, so the shunt resistor chosen is 100 Ω, producing an ac swing of 1 V p-p differential for a 0 mA to 20 mA DAC full- ...
... A simulated filter example is shown in Figure 3 with a third-order elliptical filter with a 3 dB frequency of 3 MHz. Matching input and output impedances makes the filter design easier, so the shunt resistor chosen is 100 Ω, producing an ac swing of 1 V p-p differential for a 0 mA to 20 mA DAC full- ...
Source Conversions Proof
... For any realistic voltage source comprised of an ideal voltage source with series internal resistance there exists an equivalent current source consisting of an ideal current source with parallel internal resistance. The converse is also true. By equivalent we mean that both sources will produce the ...
... For any realistic voltage source comprised of an ideal voltage source with series internal resistance there exists an equivalent current source consisting of an ideal current source with parallel internal resistance. The converse is also true. By equivalent we mean that both sources will produce the ...
HP Agilent 8116A
... The fully programmable HP 8116A features pulse as well as function generator capabilities in one small unit. A broad 1 mHz-50 MHz band for all waveforms and a wide choice of operating and modulating modes assure high flexibility. These factors, plus good repeatability, make the HP 8116A a sound, lon ...
... The fully programmable HP 8116A features pulse as well as function generator capabilities in one small unit. A broad 1 mHz-50 MHz band for all waveforms and a wide choice of operating and modulating modes assure high flexibility. These factors, plus good repeatability, make the HP 8116A a sound, lon ...
File
... The IC 555 is a highly stable device for generating accurate time delays or oscillation. It is a timer and it can be used to construct timing circuits in two modes such as an Astable and Monostable multivibrators. Additional terminals are provided for triggering or resetting. In the time delay mode ...
... The IC 555 is a highly stable device for generating accurate time delays or oscillation. It is a timer and it can be used to construct timing circuits in two modes such as an Astable and Monostable multivibrators. Additional terminals are provided for triggering or resetting. In the time delay mode ...
+/-200V Common-Mode Voltage Difference
... be summed directly into the amplifier’s output signal, this technique can be used to null the amplifier’s input offset voltage. Figure 2 shows an optional circuit for trimming the offset voltage. To maintain high common-mode rejection (CMR), the source impedance of any signal applied to the Ref term ...
... be summed directly into the amplifier’s output signal, this technique can be used to null the amplifier’s input offset voltage. Figure 2 shows an optional circuit for trimming the offset voltage. To maintain high common-mode rejection (CMR), the source impedance of any signal applied to the Ref term ...
Photodiode Amplifiers
... Photodiode Amplifier Types: The Photovoltaic Mode: No voltage across diode means no current though the big resistor ~ • No dark current. ...
... Photodiode Amplifier Types: The Photovoltaic Mode: No voltage across diode means no current though the big resistor ~ • No dark current. ...
ECE1250F14_HW2_2p1soln
... All of the statements are true. The equivalent resistance statement does depend on Kirchhoff's laws for its proof, but the key ingredient is the linearity of Ohm's law. That is, doubling the applied voltage will double the current everywhere in the resistor network. To prove the statement about curr ...
... All of the statements are true. The equivalent resistance statement does depend on Kirchhoff's laws for its proof, but the key ingredient is the linearity of Ohm's law. That is, doubling the applied voltage will double the current everywhere in the resistor network. To prove the statement about curr ...
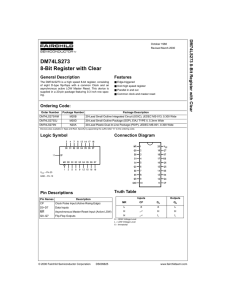
DM74LS273 8-Bit Register with Clear
... 20-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N20A ...
... 20-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N20A ...
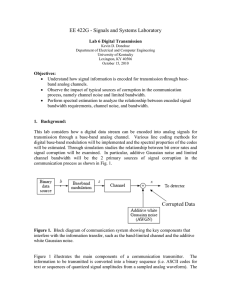
Electronics and photonics
... capacity of a communication medium, device or network. It is determined by the highest frequency that can be practically transmitted. For a 1-km long typical copper telecommunication cable, due to the skin effect, the bandwidth is only around 500kHz. The skin effect does not exist for light signals ...
... capacity of a communication medium, device or network. It is determined by the highest frequency that can be practically transmitted. For a 1-km long typical copper telecommunication cable, due to the skin effect, the bandwidth is only around 500kHz. The skin effect does not exist for light signals ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.