PHY2054_02-10
... emf is traversed in the direction of the emf (from – to +), the change in the electric potential is +ε In (d), the source of emf is traversed in the direction opposite of the emf (from + to -), the change in the electric potential is -ε ...
... emf is traversed in the direction of the emf (from – to +), the change in the electric potential is +ε In (d), the source of emf is traversed in the direction opposite of the emf (from + to -), the change in the electric potential is -ε ...
SIMPLE DC CIRCUITS
... Choose the scale by turning the rotary switch to one of the settings in the DCV (direct-current volts) portion of its dial. A setting of, say, 20 means it can read potential differences as high as 20 volts. If you choose a scale smaller than values you’ll actually encounter, you may blow the meter. ...
... Choose the scale by turning the rotary switch to one of the settings in the DCV (direct-current volts) portion of its dial. A setting of, say, 20 means it can read potential differences as high as 20 volts. If you choose a scale smaller than values you’ll actually encounter, you may blow the meter. ...
ML Detection with Symbol Estimation for Nonlinear Distortion of OFDM Signals
... power efficiency, the HPA is usually operated near the saturation region and this introduces nonlinear distortion into over all system. Unfortunately, the OFDM signal is characterized by high peak-to-average power ratio (PARR) and a large dynamic variation of signal amplitude. A highly linear power ...
... power efficiency, the HPA is usually operated near the saturation region and this introduces nonlinear distortion into over all system. Unfortunately, the OFDM signal is characterized by high peak-to-average power ratio (PARR) and a large dynamic variation of signal amplitude. A highly linear power ...
Basic Concepts - Oakland University
... •The matrix G is symmetric, gkj = gjk and all of the off-diagonal terms are negative or zero. The gkk terms are the sum of all conductances connected to node k. The gkj terms are the negative sum of the conductances connected to BOTH node k and node j. ...
... •The matrix G is symmetric, gkj = gjk and all of the off-diagonal terms are negative or zero. The gkk terms are the sum of all conductances connected to node k. The gkj terms are the negative sum of the conductances connected to BOTH node k and node j. ...
Ch19_Circuits_part1_..
... Answer: Circuit A puts out more light. Argument I: In circuit A, each resistor has the full battery voltage V = 12V. In circuit B, each resistor has only half the battery voltage (by Kirchhoff's Voltage Law). Using P = V2 / R, we see that larger voltage with the same resistance means more power. Ar ...
... Answer: Circuit A puts out more light. Argument I: In circuit A, each resistor has the full battery voltage V = 12V. In circuit B, each resistor has only half the battery voltage (by Kirchhoff's Voltage Law). Using P = V2 / R, we see that larger voltage with the same resistance means more power. Ar ...
TAS5111A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The TAS5111A is a high-performance digital amplifier power stage designed to drive a 4-Ω speaker up to 70 W with 0.2% distortion plus noise. The device incorporates TI’s PurePath Digital technology and is used with a digital audio PWM processor (TAS50XX) and a simple passive demodulation filter to ...
... The TAS5111A is a high-performance digital amplifier power stage designed to drive a 4-Ω speaker up to 70 W with 0.2% distortion plus noise. The device incorporates TI’s PurePath Digital technology and is used with a digital audio PWM processor (TAS50XX) and a simple passive demodulation filter to ...
Experiment 4: Ohm`s Law and RC Circuits
... idea is that a capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a spacing, which may be filled with an insulating material (dielectric). One conductor has charge +Q and the other conductor has charge −Q . The conductor with positive charge is at a higher voltage then the conductor with negative cha ...
... idea is that a capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a spacing, which may be filled with an insulating material (dielectric). One conductor has charge +Q and the other conductor has charge −Q . The conductor with positive charge is at a higher voltage then the conductor with negative cha ...
Topic Constructing response curves: Introduction to the
... up the recorder only. 3.1 From the mechanical receiver to the final filter As defined in section 2, the amplitude response is constructed related to ground displacement. Multiplying all the units of our signal chain, we get the unit [V/m] for the ordinate axis. All elements, including mechanical rec ...
... up the recorder only. 3.1 From the mechanical receiver to the final filter As defined in section 2, the amplitude response is constructed related to ground displacement. Multiplying all the units of our signal chain, we get the unit [V/m] for the ordinate axis. All elements, including mechanical rec ...
Nonlinear Device Noise Models: Thermodynamic Requirements RLE Technical Report No. 616
... The aptly-named fluctuation-dissipation theorem [Pathria, Sect. 13.7; Callen and Welton] governs the conversion of thermal energy to noisy fluctuations in macroscopic variables. It generalizes Johnson’s and Nyquist’s resistor noise model to mechanical, chemical, hydraulic, and other domains. But the ...
... The aptly-named fluctuation-dissipation theorem [Pathria, Sect. 13.7; Callen and Welton] governs the conversion of thermal energy to noisy fluctuations in macroscopic variables. It generalizes Johnson’s and Nyquist’s resistor noise model to mechanical, chemical, hydraulic, and other domains. But the ...
LT1812 - 3mA, 100MHz, 750V/µs Operational Amplifier with Shutdown
... Note 8: The LT1812C is guaranteed to meet specified performance from 0°C to 70°C. The LT1812C is designed, characterized and expected to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C but is not tested or QA sampled at these temperatures. The LT1812I is guaranteed to meet specified performance from –40° ...
... Note 8: The LT1812C is guaranteed to meet specified performance from 0°C to 70°C. The LT1812C is designed, characterized and expected to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C but is not tested or QA sampled at these temperatures. The LT1812I is guaranteed to meet specified performance from –40° ...
AD8311 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AD8311 provides a voltage output, VAPC, which has the voltage range and current drive to directly connect to the gain control pin of most handset power amplifiers. VAPC can swing from 300 mV above ground to within 200 mV below the supply voltage. Load currents of up to 6 mA can be supported. ...
... The AD8311 provides a voltage output, VAPC, which has the voltage range and current drive to directly connect to the gain control pin of most handset power amplifiers. VAPC can swing from 300 mV above ground to within 200 mV below the supply voltage. Load currents of up to 6 mA can be supported. ...
Experiment 6_revised
... The middle pin (2) is connected to the wiper. – The resistance between pins 1 and 2 is x Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. – The resistance between pins 2 and 3 is (1 – x) Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. – There may be a n ...
... The middle pin (2) is connected to the wiper. – The resistance between pins 1 and 2 is x Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. – The resistance between pins 2 and 3 is (1 – x) Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. – There may be a n ...
Simulation of Silicon Photomultiplier Signals
... photodiodes (GM-APDs) are connected in parallel so as to combine the photon counting capabilities of each of these so-called microcells into a proportional light sensor. The discharge of a single microcell is relatively well understood and electronic models exist to simulate this process. In this pa ...
... photodiodes (GM-APDs) are connected in parallel so as to combine the photon counting capabilities of each of these so-called microcells into a proportional light sensor. The discharge of a single microcell is relatively well understood and electronic models exist to simulate this process. In this pa ...
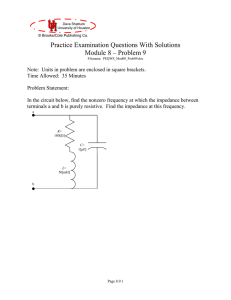
PEQWS_Mod08_Prob09_v06
... In many problems we would go ahead and substitute in the values for R, L, and C. However, in this kind of problem, where we may have to perform some complex algebra, we prefer to wait and substitute in near the end, to keep the notation simple and clear. Now, the goal is to find a frequency, , wher ...
... In many problems we would go ahead and substitute in the values for R, L, and C. However, in this kind of problem, where we may have to perform some complex algebra, we prefer to wait and substitute in near the end, to keep the notation simple and clear. Now, the goal is to find a frequency, , wher ...
low-pass, high-pass, band-pass VARIABLE
... Sinusoidal Frequency Analysis Bode plots to display frequency response data Resonant Circuits The resonance phenomenon and its characterization Scaling Impedance and frequency scaling Filter Networks Networks with frequency selective characteristics: low-pass, high-pass, band-pass ...
... Sinusoidal Frequency Analysis Bode plots to display frequency response data Resonant Circuits The resonance phenomenon and its characterization Scaling Impedance and frequency scaling Filter Networks Networks with frequency selective characteristics: low-pass, high-pass, band-pass ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistance, and the application of ohm’s law using series and parallel circuits via a computer simulation. TIME ALLOWANCE: This activity should take no more than 60 minutes. ASSESSMENT: Individual completion of this worksheet f ...
... To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistance, and the application of ohm’s law using series and parallel circuits via a computer simulation. TIME ALLOWANCE: This activity should take no more than 60 minutes. ASSESSMENT: Individual completion of this worksheet f ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.