Application Note No. 066
... For some LED applications, including fixed or “architectural” displays, voltages greater than the 18 V maximum rating (pin 3) of the BCR402R may be encountered. For example +24 V is frequently used in so-called architectural display. This section describes the advantages of using BCR402R in such sys ...
... For some LED applications, including fixed or “architectural” displays, voltages greater than the 18 V maximum rating (pin 3) of the BCR402R may be encountered. For example +24 V is frequently used in so-called architectural display. This section describes the advantages of using BCR402R in such sys ...
Application Note AN-9052 Design Guide for Selection of Bootstrap Components www.fairchildsemi.com
... and Cbs. When the load is connected and forms the charge path in the bootstrap circuit, the initial charging time is defined by Cbs and the relationship between Rbs, Rvs, and the load impedance RL. Most designs, the value of Cbs is picked with some margins, which leads to longer star-up time. If nod ...
... and Cbs. When the load is connected and forms the charge path in the bootstrap circuit, the initial charging time is defined by Cbs and the relationship between Rbs, Rvs, and the load impedance RL. Most designs, the value of Cbs is picked with some margins, which leads to longer star-up time. If nod ...
SE-330, SE-330HV SERIES Protection Relays & Controls Neutral-Grounding-Resistor Monitoring Description
... continuous monitoring of the neutral-to-ground path to verify that the neutral-grounding resistor (NGR) is intact. This is of utmost importance—an open NGR renders current-sensing ground-fault protection inoperative and could result in a false belief that the system is functioning properly. The SE-3 ...
... continuous monitoring of the neutral-to-ground path to verify that the neutral-grounding resistor (NGR) is intact. This is of utmost importance—an open NGR renders current-sensing ground-fault protection inoperative and could result in a false belief that the system is functioning properly. The SE-3 ...
HW025 Dual Positive Output-Series
... Another SELV reliability test is conducted on the whole system (combination of supply source and subject module), as required by the safety agencies, to verify that under a single fault, hazardous voltages do not appear at the module’s output. ...
... Another SELV reliability test is conducted on the whole system (combination of supply source and subject module), as required by the safety agencies, to verify that under a single fault, hazardous voltages do not appear at the module’s output. ...
Introduction to Electricity (EEM 104)
... 11 Describe the effect of an inductor in a DC and in a AC circuit. 12 Describe the effect of a capacitor in a DC and AC circuits. 13 Define the function and operation of a transformer. 14 Describe how to calculate the output voltage and current load for a transformer. ...
... 11 Describe the effect of an inductor in a DC and in a AC circuit. 12 Describe the effect of a capacitor in a DC and AC circuits. 13 Define the function and operation of a transformer. 14 Describe how to calculate the output voltage and current load for a transformer. ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSRJCE) ISSN: 2278-0661, ISBN: 2278-8727
... greater than cladding. High transmission efficiency could be achieved using traditional waveguide but it can't be fabricated by modern Ultra Large Scale Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor process (CMOS). Instead of using Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) it uses silicon substrate widely as materials a ...
... greater than cladding. High transmission efficiency could be achieved using traditional waveguide but it can't be fabricated by modern Ultra Large Scale Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor process (CMOS). Instead of using Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) it uses silicon substrate widely as materials a ...
MAX5875 16-Bit, 200Msps, High-Dynamic-Performance, Dual DAC with CMOS Inputs General Description
... applications found in wireless base stations and other communications applications. Operating from 3.3V and 1.8V supplies, this dual DAC offers exceptional dynamic performance such as 78dBc spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) at fOUT = 16MHz and supports update rates of 200Msps, with a power dissipat ...
... applications found in wireless base stations and other communications applications. Operating from 3.3V and 1.8V supplies, this dual DAC offers exceptional dynamic performance such as 78dBc spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) at fOUT = 16MHz and supports update rates of 200Msps, with a power dissipat ...
Understand Low-Dropout Regulator (LDO)
... Efficiency = IOUT/(IOUT + IGND) × VOUT/VIN × 100% For high efficiency, the headroom voltage and ground current must be minimized. In addition, the voltage difference between input and output must be minimized. The input-tooutput voltage difference is an intrinsic factor in determining the efficiency ...
... Efficiency = IOUT/(IOUT + IGND) × VOUT/VIN × 100% For high efficiency, the headroom voltage and ground current must be minimized. In addition, the voltage difference between input and output must be minimized. The input-tooutput voltage difference is an intrinsic factor in determining the efficiency ...
RF3855 数据资料DataSheet下载
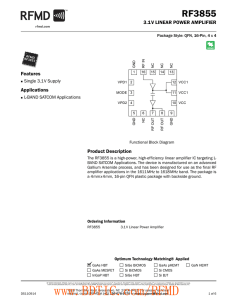
... Connect to ground plane via 15nH inductor. DC return for the second stage bias circuit. This pin has no internal bonding; therefore, this pin can be connected to output pin 7, connected to the ground plane, or not connected. Slight tuning of the output match may be required due to stray capacitance ...
... Connect to ground plane via 15nH inductor. DC return for the second stage bias circuit. This pin has no internal bonding; therefore, this pin can be connected to output pin 7, connected to the ground plane, or not connected. Slight tuning of the output match may be required due to stray capacitance ...
74LCX16245 Low Voltage 16-Bit Bidirectional Transceiver with 5V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... Note 4: The Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. The device should not be operated at these limits. The parametric values defined in the Electrical Characteristics tables are not guaranteed at the Absolute Maximum Ratings. The “Recomme ...
... Note 4: The Absolute Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. The device should not be operated at these limits. The parametric values defined in the Electrical Characteristics tables are not guaranteed at the Absolute Maximum Ratings. The “Recomme ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Electronics
... • An electronic circuit generally contains both the passive and active components. Therefore a dc power supply is essential for the operation of its active components. An electronic processing or amplifier devices also need different power source than its DC operating power source called input signa ...
... • An electronic circuit generally contains both the passive and active components. Therefore a dc power supply is essential for the operation of its active components. An electronic processing or amplifier devices also need different power source than its DC operating power source called input signa ...
S and C Band over 100W GaN HEMT 1-Chip High
... A schematic of high power amplifier with the cell division configuration is shown in Fig.1. It consists of one multi-cell transistor chip (8 cells for this case) and matching circuits. Unlike a conventional multi-cell chip, whose cells share one large drain electrode pad, 8 transistor cells are divi ...
... A schematic of high power amplifier with the cell division configuration is shown in Fig.1. It consists of one multi-cell transistor chip (8 cells for this case) and matching circuits. Unlike a conventional multi-cell chip, whose cells share one large drain electrode pad, 8 transistor cells are divi ...
Basic Electrical Understanding
... The unit of resistance to current flow An ohm is the amount of resistance that allows 1 amp of current to flow when the applied voltage is 1 volt Like a reducer in a water pipe or rough pipe vs smooth pipe – restricts flow ...
... The unit of resistance to current flow An ohm is the amount of resistance that allows 1 amp of current to flow when the applied voltage is 1 volt Like a reducer in a water pipe or rough pipe vs smooth pipe – restricts flow ...
MAX882/MAX883/MAX884 5V/3.3V or Adjustable, Low-Dropout, Low I , 200mA Linear Regulators
... 1, they consist of a 1.20V reference, error amplifier, MOSFET driver, P-channel pass transistor, dual-mode comparator, and feedback voltage-divider. The 1.20V reference is connected to the error amplifier’s inverting input. The error amplifier compares this reference with the selected feedback volta ...
... 1, they consist of a 1.20V reference, error amplifier, MOSFET driver, P-channel pass transistor, dual-mode comparator, and feedback voltage-divider. The 1.20V reference is connected to the error amplifier’s inverting input. The error amplifier compares this reference with the selected feedback volta ...
electrical technology (ee‐103‐f)
... ammeters & voltmeters operate. These instruments can be used only in AC system while dynamometer type wattmeter can be used in AC as well as DC system. ...
... ammeters & voltmeters operate. These instruments can be used only in AC system while dynamometer type wattmeter can be used in AC as well as DC system. ...
lab proceedures (word format) - Rose
... copy the cif files from my public directory into your cadence directory (cif files are the format many fabrication facilities use to create the masks for the chip) • go into your cadence directory • copy the file: cp /Users/faculty/hudson/Public/circuitA.cif . • repeat for circuitB.cif make a new li ...
... copy the cif files from my public directory into your cadence directory (cif files are the format many fabrication facilities use to create the masks for the chip) • go into your cadence directory • copy the file: cp /Users/faculty/hudson/Public/circuitA.cif . • repeat for circuitB.cif make a new li ...
Banana Switch - T3 Nederland
... A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a device that changes the conductivity of a circuit based on the voltage applied to the device. An FET has three legs named the gate, the source, and the drain. The two legs called the source and drain can be inserted into a circuit to act similarly to a switch con ...
... A Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a device that changes the conductivity of a circuit based on the voltage applied to the device. An FET has three legs named the gate, the source, and the drain. The two legs called the source and drain can be inserted into a circuit to act similarly to a switch con ...
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS IN THEORY AND PRACTICE INTRODUCTION
... From Figure 2 it is seen that avalanche occurs at a lower value of VDS when the gate is reverse biased than for the zero-bias condition. This is caused by the fact that the reverse-bias gate voltage adds to the drain voltage, thereby increasing the effective voltage across the junction. The maximum ...
... From Figure 2 it is seen that avalanche occurs at a lower value of VDS when the gate is reverse biased than for the zero-bias condition. This is caused by the fact that the reverse-bias gate voltage adds to the drain voltage, thereby increasing the effective voltage across the junction. The maximum ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.