Single Output , 0.8-3.3V 10 Amp DC/DC’s in SMT Packages
... DATEL's LSM D5 Series for SMT (surface-mount) are non-isolated DC/DC converters that accept a 5V input (4.5V to 5.5V input range) and deliver 0.8V, 1V, 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2V, 2.5V, or 3.3V outputs at 10 Amps. LSM D5 SMT's are designed to take on-board 5V power and convert it, with the highest efficie ...
... DATEL's LSM D5 Series for SMT (surface-mount) are non-isolated DC/DC converters that accept a 5V input (4.5V to 5.5V input range) and deliver 0.8V, 1V, 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2V, 2.5V, or 3.3V outputs at 10 Amps. LSM D5 SMT's are designed to take on-board 5V power and convert it, with the highest efficie ...
MAX710/MAX711 3.3V/5V or Adjustable, Step-Up/Down DC
... With N/E connected to PS, when the IC is boosting, the linear regulator operates with VFV forward voltage (typically 0.5V at 5V VOUT) for optimum noise rejection. Linear regulation occurs when VIN > VOUT + VFV. The VFV voltage differential results in boost efficiency typically 10% lower than with th ...
... With N/E connected to PS, when the IC is boosting, the linear regulator operates with VFV forward voltage (typically 0.5V at 5V VOUT) for optimum noise rejection. Linear regulation occurs when VIN > VOUT + VFV. The VFV voltage differential results in boost efficiency typically 10% lower than with th ...
a Ultralow Noise, High Speed, BiFET Op Amp AD745
... Figure 8. Graph of Resistance vs. Input Bias Current Where the Equivalent Noise 兹4 kT/R, Equals the Noise of the Bias Current I B 2qI B ...
... Figure 8. Graph of Resistance vs. Input Bias Current Where the Equivalent Noise 兹4 kT/R, Equals the Noise of the Bias Current I B 2qI B ...
Chapter 28
... When two or more resistors are connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series. For a series combination of resistors, the currents are the same in all the resistors because the amount of charge that passes through one resistor must also pass through the other resistors in the same time interval ...
... When two or more resistors are connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series. For a series combination of resistors, the currents are the same in all the resistors because the amount of charge that passes through one resistor must also pass through the other resistors in the same time interval ...
Automatic engine RPM control circuit description 3
... The short output pulse from TIMER 2 is the valid trigger which SET the F/F and starts the voltage sweep. (linear ramp) While the trigger pulse from the microphone amplifier is connected to both timers, only TIMER 1 will trigger on the first ‘firing’ sound since TIMER 2 has no power yet. When the se ...
... The short output pulse from TIMER 2 is the valid trigger which SET the F/F and starts the voltage sweep. (linear ramp) While the trigger pulse from the microphone amplifier is connected to both timers, only TIMER 1 will trigger on the first ‘firing’ sound since TIMER 2 has no power yet. When the se ...
LT4256-1/LT4256-2 - Positive High Voltage Hot Swap
... When the voltage on FB is lower than the high-to-low threshold of 3.99V, PWRGD is pulled low and released when FB is pulled above the 4.45V low-to-high threshold. The voltage present on FB affects foldback current limit (see Figure 7 and related discussion). PWRGD (Pin 3): Power Good Output. PWRGD i ...
... When the voltage on FB is lower than the high-to-low threshold of 3.99V, PWRGD is pulled low and released when FB is pulled above the 4.45V low-to-high threshold. The voltage present on FB affects foldback current limit (see Figure 7 and related discussion). PWRGD (Pin 3): Power Good Output. PWRGD i ...
LM5111 Dual 5A Compound Gate Driver (Rev. G)
... connected. The drive current capability in parallel operation is precisely 2× the drive of an individual channel. Small differences in switching speed between the driver channels will produce a transient current (shoot-through) in the output stage when two output pins are connected to drive a single ...
... connected. The drive current capability in parallel operation is precisely 2× the drive of an individual channel. Small differences in switching speed between the driver channels will produce a transient current (shoot-through) in the output stage when two output pins are connected to drive a single ...
Optoelectronics for Mouse and Shaft Encoder Applications
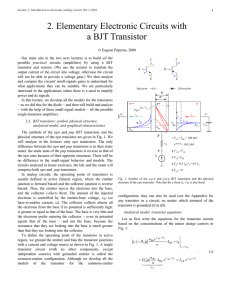
... RS = 180 Ohm, and RL = 1K Ohm. In this example, the IRED forward current will be approximately 20mA. The current in the detector should be sufficient to saturate it. The output voltage in the low (clear optical path) condition will be less than 0.2V. The lower limit on VO is the saturation voltage o ...
... RS = 180 Ohm, and RL = 1K Ohm. In this example, the IRED forward current will be approximately 20mA. The current in the detector should be sufficient to saturate it. The output voltage in the low (clear optical path) condition will be less than 0.2V. The lower limit on VO is the saturation voltage o ...
LP2950/LP2951 Series of Adjustable Micropower Voltage Regulators Series General Description
... this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tantalum or aluminum electrolytics work fine here; even film types work but are not recommended for reasons of cost. Many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes that freeze at about −30˚C, so solid tantalums are recommended for operation below ...
... this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tantalum or aluminum electrolytics work fine here; even film types work but are not recommended for reasons of cost. Many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes that freeze at about −30˚C, so solid tantalums are recommended for operation below ...
The Tube Rectifier Sag Mod
... Before installation I biased my stock Hot Rod to 68mV and measured 422VDC plate voltage. I then installed a 100 ohm power resistor—the most typical value used for this mod. My power tubes were instantly rebiased to 54mV at the bias test point. After rebiasing to 68mV I found that my 100 ohm resisto ...
... Before installation I biased my stock Hot Rod to 68mV and measured 422VDC plate voltage. I then installed a 100 ohm power resistor—the most typical value used for this mod. My power tubes were instantly rebiased to 54mV at the bias test point. After rebiasing to 68mV I found that my 100 ohm resisto ...
2W Constant Output Power Class-D Audio Amplifier with Adaptive
... The built-in boost converter operates from a battery supply voltage and generates a higher output voltage PVDD at 5.75 V that drives the supply voltage of the Class-D amplifier. This provides a louder audio output than a stand-alone amplifier directly connected to the battery. The battery tracking A ...
... The built-in boost converter operates from a battery supply voltage and generates a higher output voltage PVDD at 5.75 V that drives the supply voltage of the Class-D amplifier. This provides a louder audio output than a stand-alone amplifier directly connected to the battery. The battery tracking A ...
TDA7100 434 MHz ASK/FSK Transmitter in 10-pin Package Wireless Control
... The crystal frequency is divided by 16. The resulting 847.5 kHz are available at the clock output CLKOUT (pin1) to drive the clock input of a micro controller. To achieve FSK transmission, the oscillator frequency can be detuned by a fixed amount by switching an external capacitor via FSKOUT (pin 4) ...
... The crystal frequency is divided by 16. The resulting 847.5 kHz are available at the clock output CLKOUT (pin1) to drive the clock input of a micro controller. To achieve FSK transmission, the oscillator frequency can be detuned by a fixed amount by switching an external capacitor via FSKOUT (pin 4) ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.