Chapter16
... • The opposition that a circuit element presents to current is impedance, Z – Z = V/I, is in units of ohms – Z in phasor form is Z – is the phase difference between voltage and current ...
... • The opposition that a circuit element presents to current is impedance, Z – Z = V/I, is in units of ohms – Z in phasor form is Z – is the phase difference between voltage and current ...
Presentation Memristorx
... that has moved through each one. The wires in this image are 50 nm wide, or about 150 atoms in total width. ...
... that has moved through each one. The wires in this image are 50 nm wide, or about 150 atoms in total width. ...
General Licensing Class
... A. Output is high when either or both inputs are low. B. Output is high only when both inputs are high. C. Output is low when either or both inputs are high. ...
... A. Output is high when either or both inputs are low. B. Output is high only when both inputs are high. C. Output is low when either or both inputs are high. ...
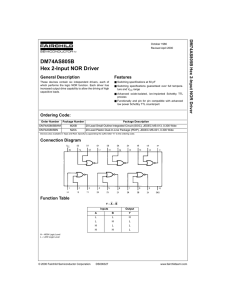
Test Procedure for the NCV8853GEVB Evaluation Board
... 2. Connect a load between VOUT and GND 3. Connect a dc enable voltage, within the 2.0 V to 5.5 V range, between EN/SYNC and GND 4. Optionally, for external clock synchronization, connect a pulse source between EN/SYNC and GND. The high state level should be within the 2.0 V to 5.5 V range, and the l ...
... 2. Connect a load between VOUT and GND 3. Connect a dc enable voltage, within the 2.0 V to 5.5 V range, between EN/SYNC and GND 4. Optionally, for external clock synchronization, connect a pulse source between EN/SYNC and GND. The high state level should be within the 2.0 V to 5.5 V range, and the l ...
Capacitor Self
... A half-wave rectifier is often used as a power supply in inexpensive, low-power circuits. Its output is unregulated DC with a quasi-sawtooth ripple voltage proportional to the load current. The single diode can be damaged by excessive reverse voltage, often due to a transient on the power line, or i ...
... A half-wave rectifier is often used as a power supply in inexpensive, low-power circuits. Its output is unregulated DC with a quasi-sawtooth ripple voltage proportional to the load current. The single diode can be damaged by excessive reverse voltage, often due to a transient on the power line, or i ...
Electric Circuit Lab
... Procedure for Series Lab: Connect the given resistors in series. One 100 , one 250 . Measure the voltage across each resistor and the current in the circuit. Use a 6 V battery as your power source. Before connecting the battery make sure to show your circuit to the teacher for approval. Circuit ...
... Procedure for Series Lab: Connect the given resistors in series. One 100 , one 250 . Measure the voltage across each resistor and the current in the circuit. Use a 6 V battery as your power source. Before connecting the battery make sure to show your circuit to the teacher for approval. Circuit ...
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
... • Series: Two or more elements are in series if they are cascaded or connected sequentially and consequently carry the same current. • The equivalent resistance of any number of resistors connected in a series is the sum of the ...
... • Series: Two or more elements are in series if they are cascaded or connected sequentially and consequently carry the same current. • The equivalent resistance of any number of resistors connected in a series is the sum of the ...
ideal voltage and current sources
... For example, an ideal 5 V source has a voltage of 5 V across its terminals, for currents of 1 mA, 1 A or 1000 A. This behaviour contrasts with a real source, in which the terminal voltage reduces as the current drawn increases. The current drawn from an ideal voltage source depends only on the circu ...
... For example, an ideal 5 V source has a voltage of 5 V across its terminals, for currents of 1 mA, 1 A or 1000 A. This behaviour contrasts with a real source, in which the terminal voltage reduces as the current drawn increases. The current drawn from an ideal voltage source depends only on the circu ...
Electrical energy flows around a path called a “circuit”
... The energy is carried by an electric “current” measured in units called “Amps” or smaller units called “milliAmps”. Current is measured using a device called an “Ammeter”. ...
... The energy is carried by an electric “current” measured in units called “Amps” or smaller units called “milliAmps”. Current is measured using a device called an “Ammeter”. ...
Linear Technology Chronicle
... shutdown state. Quiescent current is well controlled for these devices; it does not rise in dropout—when the input to output voltage differential is below the dropout rating—as is the case with many other regulators. The LT1762 and LT1763 regulators feature low noise operation. With the addition of ...
... shutdown state. Quiescent current is well controlled for these devices; it does not rise in dropout—when the input to output voltage differential is below the dropout rating—as is the case with many other regulators. The LT1762 and LT1763 regulators feature low noise operation. With the addition of ...
... using the single differential pair employing the dynamic level shifting technique has been designed in 0.18µm technology.The Operational amplifier has been designed to achieve high speed by employing extra bias circuitry for high slew rate. This amplifier has been used successfully as a unity gain b ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).