Direct and Alternating Voltages, the Oscilloscope
... 6. Set the function generator to make a high-frequency (1.5 MHz) square wave and use the scope to measure the rise time. This is the time it takes the wave to go from 10% to 90% of its maximum amplitude. Measure also the corresponding fall time. 7. What is the use of the alternate and chop options? ...
... 6. Set the function generator to make a high-frequency (1.5 MHz) square wave and use the scope to measure the rise time. This is the time it takes the wave to go from 10% to 90% of its maximum amplitude. Measure also the corresponding fall time. 7. What is the use of the alternate and chop options? ...
Low voltage CMOS single 2-input or gate with 5V tolerant input
... silicon gate and double-layer metal wiring C2MOS technology. It is ideal for 1.65 to 5.5 VCC operations and low power and low noise applications. The internal circuit is composed of 3 stages including buffer ...
... silicon gate and double-layer metal wiring C2MOS technology. It is ideal for 1.65 to 5.5 VCC operations and low power and low noise applications. The internal circuit is composed of 3 stages including buffer ...
Goal: To understand what Electric Fields are
... In DC vs AC • In Direct current you get some small direct flow of charge. • In AC though, the charges go back and forth – sort of like a compression wave, or waves on an ocean, or the springs we saw in class. • This gives us our back and forth nature of the current. • So, when you pay for electric, ...
... In DC vs AC • In Direct current you get some small direct flow of charge. • In AC though, the charges go back and forth – sort of like a compression wave, or waves on an ocean, or the springs we saw in class. • This gives us our back and forth nature of the current. • So, when you pay for electric, ...
Introduction to Electricity
... side of the battery. This was the convention established when electricity was first discovered, but it is incorrect! Electron Flow is what actually happens. The electrons flow out of the negative side of the battery, through the circuit, and back to the positive side of the battery. ...
... side of the battery. This was the convention established when electricity was first discovered, but it is incorrect! Electron Flow is what actually happens. The electrons flow out of the negative side of the battery, through the circuit, and back to the positive side of the battery. ...
C41032125
... components that are employed in all or most architectures: a variable gain amplifier, a peak signal detector and a gain control voltage generation circuit. The AGC core cell is the variable gain amplifier. This cell determines the main properties of the complete AGC, such as the frequency response, ...
... components that are employed in all or most architectures: a variable gain amplifier, a peak signal detector and a gain control voltage generation circuit. The AGC core cell is the variable gain amplifier. This cell determines the main properties of the complete AGC, such as the frequency response, ...
lm4880.pdf
... Selection of external components when using integrated power amplifiers is critical to optimize device and system performance. While the LM4880 is tolerant of external component combinations, care must be exercised when choosing component values. The LM4880 is unity-gain stable which gives a designe ...
... Selection of external components when using integrated power amplifiers is critical to optimize device and system performance. While the LM4880 is tolerant of external component combinations, care must be exercised when choosing component values. The LM4880 is unity-gain stable which gives a designe ...
Trip Circuit Supervision for M
... 1. Under I/O Configuration, the Input #1 setting must be configured as “General Input”. ...
... 1. Under I/O Configuration, the Input #1 setting must be configured as “General Input”. ...
78ET-2
... star, (b) in mesh, to a three-phase, 50 Hz supply, the line voltage being 500 volts. Calculate for each case the line current and the total power absorbed. What is meant by 'reverse current' and 'reverse power'? Describe a relay that will operate under these conditions. (a) Why is plain overload pro ...
... star, (b) in mesh, to a three-phase, 50 Hz supply, the line voltage being 500 volts. Calculate for each case the line current and the total power absorbed. What is meant by 'reverse current' and 'reverse power'? Describe a relay that will operate under these conditions. (a) Why is plain overload pro ...
Chap. 3 Conceptual Modules Fishbane
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
80K-40 High Voltage Probe
... extend the voltage measuring capability of an ac/dc voltmeter up to 40,000 volts Overvoltage Category I. This means the probe can only be used to make measurements on energy limited circuits within equipment. Examples include high voltage within televisions or photo copy machines. DO NOT use this pr ...
... extend the voltage measuring capability of an ac/dc voltmeter up to 40,000 volts Overvoltage Category I. This means the probe can only be used to make measurements on energy limited circuits within equipment. Examples include high voltage within televisions or photo copy machines. DO NOT use this pr ...
Series Circuits
... load is a fraction of the voltage supplied by the source. The sum of the voltage across each bulb is equal to the voltage supplied by the source. The intensity of the bulbs decreased as more lights were added. The power supplied by the battery is the sum of the power supplied to each of the bulbs. I ...
... load is a fraction of the voltage supplied by the source. The sum of the voltage across each bulb is equal to the voltage supplied by the source. The intensity of the bulbs decreased as more lights were added. The power supplied by the battery is the sum of the power supplied to each of the bulbs. I ...
HIGH-VOLTAGE, HIGH SLEW RATE, WIDEBAND FET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER THS4631 FEATURES
... The THS4631 is a high-speed, FET-input operational amplifier designed for applications requiring wideband operation, high-input impedance, and high-power supply voltages. By providing a 210-MHz gain bandwidth product, ±15-V supply operation, and 100-pA input bias current, the THS4631 is capable of s ...
... The THS4631 is a high-speed, FET-input operational amplifier designed for applications requiring wideband operation, high-input impedance, and high-power supply voltages. By providing a 210-MHz gain bandwidth product, ±15-V supply operation, and 100-pA input bias current, the THS4631 is capable of s ...
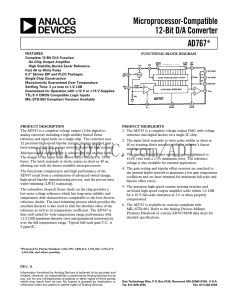
AD767: Microprocessor-Compatible 12-Bit D/A Converter Data Sheet (Rev A, 04/1988)
... STEP I … ZERO ADJUST Turn all bits OFF and adjust zero trimmer R1, until the output reads 0.000 volts (1 LSB = 2.44 mV). In most cases this trim is not needed, and Pin 4 should be connected to Pin 5. ...
... STEP I … ZERO ADJUST Turn all bits OFF and adjust zero trimmer R1, until the output reads 0.000 volts (1 LSB = 2.44 mV). In most cases this trim is not needed, and Pin 4 should be connected to Pin 5. ...
15-A, 48-V INPUT, 5-V OUTPUT, ISOLATED, 1/8th BRICK DC/DC
... VO Adjust: Allows the output voltage to be trimmed by up or down between +10% and –20% of its nominal value. The adjustment method uses a single external resistor. Connecting the resistor between VO Adjust and –VO adjusts the output voltage lower, and placing it between VO Adjust and +VO adjusts the ...
... VO Adjust: Allows the output voltage to be trimmed by up or down between +10% and –20% of its nominal value. The adjustment method uses a single external resistor. Connecting the resistor between VO Adjust and –VO adjusts the output voltage lower, and placing it between VO Adjust and +VO adjusts the ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).