AN-1329 APPLICATION NOTE
... Some LDOs allow the use of an external capacitor to filter the reference. In fact, many ultralow noise LDOs require the use of an external noise reduction capacitor, usually denoted as CBYP in the application schematic, to achieve their low noise specifications. The drawback of only filtering the re ...
... Some LDOs allow the use of an external capacitor to filter the reference. In fact, many ultralow noise LDOs require the use of an external noise reduction capacitor, usually denoted as CBYP in the application schematic, to achieve their low noise specifications. The drawback of only filtering the re ...
AN11127 - NXP Semiconductors
... There are many I/O standards that have different voltage level requirements for the input voltage (VIH or VIL) and output voltage (VOH or VOL) typically based on the device operating voltage. The different technologies available in circuit design determine the input voltage threshold and output volt ...
... There are many I/O standards that have different voltage level requirements for the input voltage (VIH or VIL) and output voltage (VOH or VOL) typically based on the device operating voltage. The different technologies available in circuit design determine the input voltage threshold and output volt ...
Universal Transducer Interface (UTI)
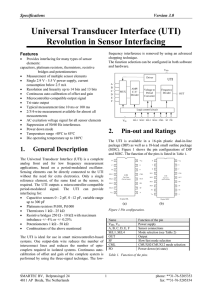
... The sequences of all phases are referred to the first one (phase 1). In this phase, the constant part (or offset) is measured. This phase also contains the synchronization for the microcontroller, since the output frequency in this phase is doubled. During the described measurements, an Intel 87C51F ...
... The sequences of all phases are referred to the first one (phase 1). In this phase, the constant part (or offset) is measured. This phase also contains the synchronization for the microcontroller, since the output frequency in this phase is doubled. During the described measurements, an Intel 87C51F ...
DN355 - Op Amp Selection Guide for Optimum Noise Performance
... noise sources presented externally. The equation for the input referred RMS sum of all the noise sources, VN(TOTAL) is also shown. It is this voltage noise density, multiplied by the noise gain of the circuit (NG = 1 + R1/R2) that appears at the output. , LTC and LT are registered trademarks of Line ...
... noise sources presented externally. The equation for the input referred RMS sum of all the noise sources, VN(TOTAL) is also shown. It is this voltage noise density, multiplied by the noise gain of the circuit (NG = 1 + R1/R2) that appears at the output. , LTC and LT are registered trademarks of Line ...
LTC2421/LTC2422 - 1-/2-Channel 20-Bit
... Through a single pin, the LTC2421/LTC2422 can be configured for better than 110dB rejection at 50Hz or 60Hz ±2%, or can be driven by an external oscillator for a user defined rejection frequency in the range 1Hz to 120Hz. The internal oscillator requires no external frequency setting components. The ...
... Through a single pin, the LTC2421/LTC2422 can be configured for better than 110dB rejection at 50Hz or 60Hz ±2%, or can be driven by an external oscillator for a user defined rejection frequency in the range 1Hz to 120Hz. The internal oscillator requires no external frequency setting components. The ...
BSNL JTO Exam Paper 2005
... b) Each of them decreases c) Copper increases and germanium decreases d) Copper decreases and germanium increases Answer: d) When a signal of 10 mV at 75 MHz is to be measured then which of the following instrument can be used a) VTVM b) Cathode ray oscilloscope c) Moving iron voltmeter d) Digital m ...
... b) Each of them decreases c) Copper increases and germanium decreases d) Copper decreases and germanium increases Answer: d) When a signal of 10 mV at 75 MHz is to be measured then which of the following instrument can be used a) VTVM b) Cathode ray oscilloscope c) Moving iron voltmeter d) Digital m ...
chap04, Chapter 04 - Faculty Website Listing
... 20. True or False? Boolean algebra allows us to apply provable mathematical principles to the design of circuits. 21. True or False? DeMorgan's law states that inverting the output of an AND gate is equivalent to inverting the individual input signals and then passing them through an OR gate. 22. Tr ...
... 20. True or False? Boolean algebra allows us to apply provable mathematical principles to the design of circuits. 21. True or False? DeMorgan's law states that inverting the output of an AND gate is equivalent to inverting the individual input signals and then passing them through an OR gate. 22. Tr ...
Microsoft Powerpoint File
... of equipment grounding conductors, bonding jumpers or bonding conductors, approved metallic raceways, connectors and couplings, approved metallic sheathed cable and cable fittings, and other approved devices. A ground fault path is effective when it will safely carry the maximum ground fault current ...
... of equipment grounding conductors, bonding jumpers or bonding conductors, approved metallic raceways, connectors and couplings, approved metallic sheathed cable and cable fittings, and other approved devices. A ground fault path is effective when it will safely carry the maximum ground fault current ...
Impedance - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... ‣ If I put random fluctuations of pressure into a pipe, some modes will grow and some modes won’t ...
... ‣ If I put random fluctuations of pressure into a pipe, some modes will grow and some modes won’t ...
PC8349/E [Preliminary]
... – Data bus width options: – Dual 32-bit data PCI interfaces operating at up to 66 MHz – Single 64-bit data PCI interface operating at up to 66 MHz – PCI 3.3-V compatible – PCI host bridge capabilities on both interfaces – PCI agent mode on PCI1 interface – PCI-to-memory and memory-to-PCI streaming – ...
... – Data bus width options: – Dual 32-bit data PCI interfaces operating at up to 66 MHz – Single 64-bit data PCI interface operating at up to 66 MHz – PCI 3.3-V compatible – PCI host bridge capabilities on both interfaces – PCI agent mode on PCI1 interface – PCI-to-memory and memory-to-PCI streaming – ...
Fuse Technology Tech Note
... DC current. The characteristics represented on most published graphs usually indicate a fuse’s average melting time when subjected to a certain level of current. The curves will typically demonstrate the ability to carry 100% of rated current. They also represent the fuse’s ability to open within th ...
... DC current. The characteristics represented on most published graphs usually indicate a fuse’s average melting time when subjected to a certain level of current. The curves will typically demonstrate the ability to carry 100% of rated current. They also represent the fuse’s ability to open within th ...
ltc1694.pdf
... drivers with resistive or current source pull-ups. This protocol allows multiple devices to drive and monitor the bus without bus contention. The simplicity of resistive or fixed current source pull-ups is offset by the slow rise times they afford when bus capacitance is high. Rise times can be impr ...
... drivers with resistive or current source pull-ups. This protocol allows multiple devices to drive and monitor the bus without bus contention. The simplicity of resistive or fixed current source pull-ups is offset by the slow rise times they afford when bus capacitance is high. Rise times can be impr ...
SPECIAL PROTECTION SCHEME
... Modern numerical relays are often designed to be able to operate correctly even when the CT saturates after a very short time. The required minimum time to saturation for these relays is often very short. Sometimes the required time to saturation can be even less than 2 ms. To get the benefit of the ...
... Modern numerical relays are often designed to be able to operate correctly even when the CT saturates after a very short time. The required minimum time to saturation for these relays is often very short. Sometimes the required time to saturation can be even less than 2 ms. To get the benefit of the ...
file (7.8 MB, pdf)
... • It is one of the applications of opamp (Figure 17.34). • Peak detector circuit produces a voltage at the output equal to peak amplitude of the input signal. • Essentially, it is a clipper-circuit with a parallel resistor-capacitor connected at its output. • Here is how it works: The clipper repr ...
... • It is one of the applications of opamp (Figure 17.34). • Peak detector circuit produces a voltage at the output equal to peak amplitude of the input signal. • Essentially, it is a clipper-circuit with a parallel resistor-capacitor connected at its output. • Here is how it works: The clipper repr ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).










![PC8349/E [Preliminary]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000076051_1-052fc2cccce23cc32c18f48f9f811182-300x300.png)