Activity 1: Resistors Quiz
... where the resistance values, R1 and R2 are known, as is the applied voltage, V0 . Use Kirchoff’s Laws to determine 1. The Current through R1 . 2. The Current through R2 . 3. The Voltage across R1 . 4. The Voltage across R2 . 5. The Power Delivered by V0 . 6. The Power absorbed by R1 . 7. The Power a ...
... where the resistance values, R1 and R2 are known, as is the applied voltage, V0 . Use Kirchoff’s Laws to determine 1. The Current through R1 . 2. The Current through R2 . 3. The Voltage across R1 . 4. The Voltage across R2 . 5. The Power Delivered by V0 . 6. The Power absorbed by R1 . 7. The Power a ...
BDTIC C o o l S E T -Q1
... The PWM controller during normal operation consists of a digital signal processing circuit including an up/ down counter, a zero-crossing counter (ZC counter) and a comparator, and an analog circuit including a current measurement unit and a comparator. The switch-on and -off time points are each de ...
... The PWM controller during normal operation consists of a digital signal processing circuit including an up/ down counter, a zero-crossing counter (ZC counter) and a comparator, and an analog circuit including a current measurement unit and a comparator. The switch-on and -off time points are each de ...
STEVAL-ILD005V1: Trailing edge phase control rotary wall dimmer
... switch which opens the circuit at the minimum setting. Control of the board is achieved with a triple 3input NOR gate (pin-to-pin compatible with ST's HCF4025BE 14-lead dual in-line CMOS gate logic device in a plastic SO-14 micropackage), which acts as a gate driving voltage signal source and perfor ...
... switch which opens the circuit at the minimum setting. Control of the board is achieved with a triple 3input NOR gate (pin-to-pin compatible with ST's HCF4025BE 14-lead dual in-line CMOS gate logic device in a plastic SO-14 micropackage), which acts as a gate driving voltage signal source and perfor ...
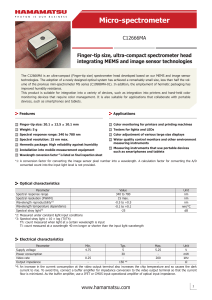
Micro-spectrometer - Hamamatsu Photonics
... Information described in this material is current as of February, 2016. Product specifications are subject to change without prior notice due to improvements or other reasons. This document has been carefully prepared and the information contained is believed to be accurate. In rare cases, however, ...
... Information described in this material is current as of February, 2016. Product specifications are subject to change without prior notice due to improvements or other reasons. This document has been carefully prepared and the information contained is believed to be accurate. In rare cases, however, ...
CHAPTER 2
... Most AC electrical power systems supply loads that are both resistive and reactive. Power source delivers real power to the resistive component of the load and this real power is converted into the useful work. ...
... Most AC electrical power systems supply loads that are both resistive and reactive. Power source delivers real power to the resistive component of the load and this real power is converted into the useful work. ...
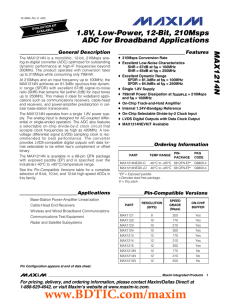
MAX1214N 1.8V, Low-Power, 12-Bit, 210Msps ADC for Broadband Applications General Description
... The MAX1214N is a monolithic, 12-bit, 210Msps analog-to-digital converter (ADC) optimized for outstanding dynamic performance at high-IF frequencies beyond 300MHz. The product operates with conversion rates up to 210Msps while consuming only 799mW. At 210Msps and an input frequency up to 100MHz, the ...
... The MAX1214N is a monolithic, 12-bit, 210Msps analog-to-digital converter (ADC) optimized for outstanding dynamic performance at high-IF frequencies beyond 300MHz. The product operates with conversion rates up to 210Msps while consuming only 799mW. At 210Msps and an input frequency up to 100MHz, the ...
Alternating Current - Sakshieducation.com
... inductance and the other contains only a capacitor. If the frequency of the emf of AC is increased, the effect on the value of the current will be a) Increases in the first circuit and decreases in the other b) Increases in both the circuits c) Decreases in both the circuits d) Decreases in the firs ...
... inductance and the other contains only a capacitor. If the frequency of the emf of AC is increased, the effect on the value of the current will be a) Increases in the first circuit and decreases in the other b) Increases in both the circuits c) Decreases in both the circuits d) Decreases in the firs ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).