Nervous System Communication
... • Stimuli cause movements of ions through membrane • Threshold potential – Sufficient stimulation to depolarize membrane ...
... • Stimuli cause movements of ions through membrane • Threshold potential – Sufficient stimulation to depolarize membrane ...
Sensory play research project
... “we now know that the human brain is made up of billions of cells called neurons. These remain at rest until a stimulus occurs when an electrical signal passes from one neuron to another, relaying information about everything we can see, hear, taste, touch and smell.” (Wartik and Carlson-Finnerty, 1 ...
... “we now know that the human brain is made up of billions of cells called neurons. These remain at rest until a stimulus occurs when an electrical signal passes from one neuron to another, relaying information about everything we can see, hear, taste, touch and smell.” (Wartik and Carlson-Finnerty, 1 ...
Learning and Memory, Part I: Brain Regions Involved in Two Types
... cortex, and tastes are consolidated in the insular cortex. Although the hippocampus is required for the consolidation of these declarative memories, it is thought that they are broken down into separate sensory components before their long-term storage in relevant cortical areas. Second, why were on ...
... cortex, and tastes are consolidated in the insular cortex. Although the hippocampus is required for the consolidation of these declarative memories, it is thought that they are broken down into separate sensory components before their long-term storage in relevant cortical areas. Second, why were on ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
Control Coordination
... and restores your energy. It directs blood to your digestive tract and makes sure you actively digest food. It also maintains your blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate at a low level. That's why it is sometimes called your 'rest and digest' system. ...
... and restores your energy. It directs blood to your digestive tract and makes sure you actively digest food. It also maintains your blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate at a low level. That's why it is sometimes called your 'rest and digest' system. ...
Turning neurons into a nervous system
... multiple climbing fibers that contact the immature Purkinje cell. Only one climbing fiber will innervate the mature neuron. If climbing fibers are inefficiently removed in mouse mutants, or if they are synchronously activated, the multiplanar tree is not remodeled. Dendritic trees form under two bro ...
... multiple climbing fibers that contact the immature Purkinje cell. Only one climbing fiber will innervate the mature neuron. If climbing fibers are inefficiently removed in mouse mutants, or if they are synchronously activated, the multiplanar tree is not remodeled. Dendritic trees form under two bro ...
Nervous System ch 11
... •Oligodendrocytes – branched cells that wrap CNS nerve fibers; produce myelin sheath •Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) – surround fibers of the PNS; produce myelin sheath •Satellite cells - surround neuron cell bodies with ganglia Neurons (Nerve Cells) •Structural units of the nervous system –Compose ...
... •Oligodendrocytes – branched cells that wrap CNS nerve fibers; produce myelin sheath •Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) – surround fibers of the PNS; produce myelin sheath •Satellite cells - surround neuron cell bodies with ganglia Neurons (Nerve Cells) •Structural units of the nervous system –Compose ...
PDF
... liberty to explore and discuss a mathematical approach to the following three questions: (1) What is the architectural abstraction principle for evolution to build the brain?; (2) How do neural networks give rise to intelligence that is capable of dealing with uncertainties and infinite possibilitie ...
... liberty to explore and discuss a mathematical approach to the following three questions: (1) What is the architectural abstraction principle for evolution to build the brain?; (2) How do neural networks give rise to intelligence that is capable of dealing with uncertainties and infinite possibilitie ...
Chapter 13 - Las Positas College
... - Explain the organization of the white matter and gray matter of the brain stem and compare it to that of the matter in the cerebrum and cerebellum. - Explain the ventricles of the brain as adult neural canal regions, including specific locations. - Describe the gross anatomy of the cerebral hemisp ...
... - Explain the organization of the white matter and gray matter of the brain stem and compare it to that of the matter in the cerebrum and cerebellum. - Explain the ventricles of the brain as adult neural canal regions, including specific locations. - Describe the gross anatomy of the cerebral hemisp ...
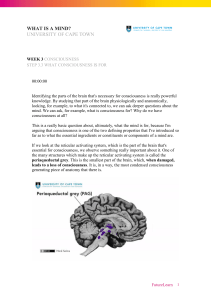
what is a mind? university of cape town
... part is stimulated, exquisitely, delicious, delightful, orgasmic sensations of consciousness are generated. When you stimulate this part of the animal, it really likes you and wants you to carry on. These are the sorts of predictions that one makes. In humans, we know that it does this. It causes fe ...
... part is stimulated, exquisitely, delicious, delightful, orgasmic sensations of consciousness are generated. When you stimulate this part of the animal, it really likes you and wants you to carry on. These are the sorts of predictions that one makes. In humans, we know that it does this. It causes fe ...
Ch. 9 - Quia
... hypnotist to help the victim of abuse better recall repressed memories. You inform the inspector that: • A) he should only use a highly trained ...
... hypnotist to help the victim of abuse better recall repressed memories. You inform the inspector that: • A) he should only use a highly trained ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... Our senses • Cells called receptors detect stimuli (changes) in our environment. • Our receptors can be found: • Eyes – sensitive to light • Ears – sensitive to sound • Nose – sensitive to smell • Skin – sensitive to touch, pressure, and temperature • Mouth – sensitive to chemicals in food. ...
... Our senses • Cells called receptors detect stimuli (changes) in our environment. • Our receptors can be found: • Eyes – sensitive to light • Ears – sensitive to sound • Nose – sensitive to smell • Skin – sensitive to touch, pressure, and temperature • Mouth – sensitive to chemicals in food. ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... fifth of the size, citing Charles Darwin six times – whereas The God Delusion cites Charles Darwin's name thirty four times. Donda and Heilman's introduction rejects Descartes idea that the pineal part of our brains is where our souls originate from. This perhaps oversimplifies Descartes, as his sou ...
... fifth of the size, citing Charles Darwin six times – whereas The God Delusion cites Charles Darwin's name thirty four times. Donda and Heilman's introduction rejects Descartes idea that the pineal part of our brains is where our souls originate from. This perhaps oversimplifies Descartes, as his sou ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
Syllabus P140C (68530) Cognitive Science
... • Need converging evidence from different perspectives to really understand cognitive processes ...
... • Need converging evidence from different perspectives to really understand cognitive processes ...
Test.
... • This talk describes work by Richard Andersen’s Laboratory at Caltech. Figures copied from the lab’s webpage. ...
... • This talk describes work by Richard Andersen’s Laboratory at Caltech. Figures copied from the lab’s webpage. ...
Chapter 14 Autonomic nervous system
... A. Cutaneous Sensations 1. Cutaneous sensations include tactile sensations (touch, pressure, vibration), thermoreceptive sensations (cold and heat), and pain. a. The receptors for these sensations are located in the skin, in connective tissue under the skin, in mucous membranes, and at the ends of t ...
... A. Cutaneous Sensations 1. Cutaneous sensations include tactile sensations (touch, pressure, vibration), thermoreceptive sensations (cold and heat), and pain. a. The receptors for these sensations are located in the skin, in connective tissue under the skin, in mucous membranes, and at the ends of t ...
The Nervous System
... Convergent circuits = messages from several neurons come together at a single neuron; permits integration of information from several sources Divergent circuits = messages from a single neuron spreads out to several neurons; permits transmission of information from several sources Reverberatin ...
... Convergent circuits = messages from several neurons come together at a single neuron; permits integration of information from several sources Divergent circuits = messages from a single neuron spreads out to several neurons; permits transmission of information from several sources Reverberatin ...
chapter 4 part 3
... messages through the thalamus • Pathways from olfactory bulb sends information on for further processing in several brain regions – Including frontal lobe and amygdala ...
... messages through the thalamus • Pathways from olfactory bulb sends information on for further processing in several brain regions – Including frontal lobe and amygdala ...
Chapter 10 Slides
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...