The hippocampal–striatal axis in learning, prediction and
... association between an organism’s state or action and its outcome is cached (i.e. stored, captured) in a scalar signal summarizing its long-term value, without specifying the nature or features of the outcome. This class contrasts with model-based approaches, in which state or action associations wi ...
... association between an organism’s state or action and its outcome is cached (i.e. stored, captured) in a scalar signal summarizing its long-term value, without specifying the nature or features of the outcome. This class contrasts with model-based approaches, in which state or action associations wi ...
Associative memory properties of multiple cortical modules
... as inputs to each of the modules A and B, which are therefore denoted as input modules, C is a convergent module which receives paired inputs. Its patterns of sustained activity (due to its attractor network properties) are associated by Hebb-like modifiable synapses to the corresponding sustained a ...
... as inputs to each of the modules A and B, which are therefore denoted as input modules, C is a convergent module which receives paired inputs. Its patterns of sustained activity (due to its attractor network properties) are associated by Hebb-like modifiable synapses to the corresponding sustained a ...
the iterative reprocessing model
... Building on recent advances in cognitive and affective neuroscience, we present a preliminary neural model of the networks involved in evaluation (see Cunningham & Zelazo, 2007; Zelazo & Cunningham, 2007 for more details). The IR Model of evaluation is predicated on the interaction between different ...
... Building on recent advances in cognitive and affective neuroscience, we present a preliminary neural model of the networks involved in evaluation (see Cunningham & Zelazo, 2007; Zelazo & Cunningham, 2007 for more details). The IR Model of evaluation is predicated on the interaction between different ...
ACT-R and fMRI 1 Using the ACT-R Cognitive Architecture in
... requirements were independently manipulated in an associative recognition task. Figure 2a shows the basic procedure. A trial started with a 2 second fixation screen, followed by a 6 second study presentation of a paired-associate. Subjects were asked to memorize the paired-associate that was present ...
... requirements were independently manipulated in an associative recognition task. Figure 2a shows the basic procedure. A trial started with a 2 second fixation screen, followed by a 6 second study presentation of a paired-associate. Subjects were asked to memorize the paired-associate that was present ...
Spring 2002
... electrical activity of the brain. The recorded impulses are known as the electroencephalogram (EEG). The impulses come from the change in electrical currents ...
... electrical activity of the brain. The recorded impulses are known as the electroencephalogram (EEG). The impulses come from the change in electrical currents ...
Figure 4.8 The human brain stem This composite structure extends
... – Right above the medulla-SC junction, most of these fibers cross-over (decussate). ...
... – Right above the medulla-SC junction, most of these fibers cross-over (decussate). ...
The mind`s mirror
... "You might pick up a teacup because you want to take a sip, or because you're clearing the table," says Marco Iacoboni. "The question is whether mirror neurons can tell the difference." In a recent study published in PLOS Biology (Vol. 3, No. 3, pages 529–535), he and his colleagues found some evide ...
... "You might pick up a teacup because you want to take a sip, or because you're clearing the table," says Marco Iacoboni. "The question is whether mirror neurons can tell the difference." In a recent study published in PLOS Biology (Vol. 3, No. 3, pages 529–535), he and his colleagues found some evide ...
Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition
... Higher visual cortical processing can be roughly divided into areas that are concerned with the analysis of objects (form, colour, etc.), and areas that are concerned with their spatial location and movement. The former appears to be mediated by a ventral stream, and the latter by a dorsal stream (U ...
... Higher visual cortical processing can be roughly divided into areas that are concerned with the analysis of objects (form, colour, etc.), and areas that are concerned with their spatial location and movement. The former appears to be mediated by a ventral stream, and the latter by a dorsal stream (U ...
Spike-Timing Theory of Working Memory
... of one representation spreads to others, resulting in uncontrollable epileptic-like ‘‘runaway excitation’’. The narrow memory content is at odds with experimental findings that neurons participate in many different neural circuits (see e.g. [16–18]) and, therefore, are part of many distinct represen ...
... of one representation spreads to others, resulting in uncontrollable epileptic-like ‘‘runaway excitation’’. The narrow memory content is at odds with experimental findings that neurons participate in many different neural circuits (see e.g. [16–18]) and, therefore, are part of many distinct represen ...
The Functional Organization of Perception and Movement
... exit the spinal cord and innervate skeletal muscles. Unlike the sensory nuclei, the motor nuclei form columns that run the length of the spinal cord. Interneurons of various types in the gray matter inhibit the output of the spinal cord neurons. These inhibitory interneurons thus modulate both senso ...
... exit the spinal cord and innervate skeletal muscles. Unlike the sensory nuclei, the motor nuclei form columns that run the length of the spinal cord. Interneurons of various types in the gray matter inhibit the output of the spinal cord neurons. These inhibitory interneurons thus modulate both senso ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
Responses of the Human Brain to Mild Dehydration and
... MATERIALS AND METHODS: Serial T1-weighted and 1H-MR spectroscopy data were acquired in 15 healthy individuals at normohydration, on 12 hours of dehydration, and during 1 hour of oral rehydration. Osmotic challenges were monitored by serum measures, including osmolality and hematocrit. MR imaging dat ...
... MATERIALS AND METHODS: Serial T1-weighted and 1H-MR spectroscopy data were acquired in 15 healthy individuals at normohydration, on 12 hours of dehydration, and during 1 hour of oral rehydration. Osmotic challenges were monitored by serum measures, including osmolality and hematocrit. MR imaging dat ...
Questions and Answers From Episode 27
... 3) How are the senses of smell and appetite linked and if you lose the sense of smell, why would this decrease the ability to taste? Answer: Input from olfactory (smell) receptors and taste receptors are sent to the brain and processed individually in sensory receiving areas and in association with ...
... 3) How are the senses of smell and appetite linked and if you lose the sense of smell, why would this decrease the ability to taste? Answer: Input from olfactory (smell) receptors and taste receptors are sent to the brain and processed individually in sensory receiving areas and in association with ...
SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 3
... It also secretes hormones which control the activity of the other endocrine glands, e.g. thyroid stimulationg hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland. Thyroid gland: When stimulated by TSH from the pituitary, the thyroid gland secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates an individual's metabol ...
... It also secretes hormones which control the activity of the other endocrine glands, e.g. thyroid stimulationg hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland. Thyroid gland: When stimulated by TSH from the pituitary, the thyroid gland secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates an individual's metabol ...
Neural Network Dynamics
... Understanding how neural circuitry generates complex patterns of activity is challenging, and it is even more difficult to build models of this type that remain sensitive to sensory input. In mathematical terms, we need to understand how a system can reconcile a rich internal state structure with a h ...
... Understanding how neural circuitry generates complex patterns of activity is challenging, and it is even more difficult to build models of this type that remain sensitive to sensory input. In mathematical terms, we need to understand how a system can reconcile a rich internal state structure with a h ...
Direct and Indirect Activation of Cortical Neurons by Electrical
... doi:10.1152/jn.00126.2006. Electrical microstimulation has been used to elucidate cortical function. This review discusses neuronal excitability and effective current spread estimated by using three different methods: 1) single-cell recording, 2) behavioral methods, and 3) functional magnetic resona ...
... doi:10.1152/jn.00126.2006. Electrical microstimulation has been used to elucidate cortical function. This review discusses neuronal excitability and effective current spread estimated by using three different methods: 1) single-cell recording, 2) behavioral methods, and 3) functional magnetic resona ...
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation - Cirrie
... techniques of compensatory strategies for memory disorders are effective in individuals with minor traumatic brain injuries (Gordon et al. 2006). In moderately or severely injured individuals, the most effective interventions are those appealing to external aids, such as reminders in order to facili ...
... techniques of compensatory strategies for memory disorders are effective in individuals with minor traumatic brain injuries (Gordon et al. 2006). In moderately or severely injured individuals, the most effective interventions are those appealing to external aids, such as reminders in order to facili ...
tractus corticomuscularis
... afferent part (which accepts information) central part (that keeps information) efferent part (that creates response) As a result we have a circle – like structure - receptor (primary information centre) – programme centre – executive apparatus ...
... afferent part (which accepts information) central part (that keeps information) efferent part (that creates response) As a result we have a circle – like structure - receptor (primary information centre) – programme centre – executive apparatus ...
MND Australia International Research Update
... Can we fix motor neurone disease with electrical tape? Shin Kang and colleagues at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, USA have discovered that oligodendrocytes may play an important role in motor neurone disease. They investigated these glial cells (which are mainly responsible for my ...
... Can we fix motor neurone disease with electrical tape? Shin Kang and colleagues at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, USA have discovered that oligodendrocytes may play an important role in motor neurone disease. They investigated these glial cells (which are mainly responsible for my ...
A phase I trial of deep brain stimulation of memory
... Advances in neurosurgical techniques and the introduction of deep brain stimulation have made possible the modulation of the activity of several brain circuits, including pain circuits,23 motor circuits in patients with Parkinson disease,24,25 essential tremor,26 dystonia,27 and Huntington disease,2 ...
... Advances in neurosurgical techniques and the introduction of deep brain stimulation have made possible the modulation of the activity of several brain circuits, including pain circuits,23 motor circuits in patients with Parkinson disease,24,25 essential tremor,26 dystonia,27 and Huntington disease,2 ...
Information transmission and recovery in neural communications
... may be recovered at a later waystation and thus become useful again. Our discussion of the transmission properties of active neural channels is phrased in the context of an idealized channel composed on one neuron N1 that receives information in the form of a spike train and passes this on, modulate ...
... may be recovered at a later waystation and thus become useful again. Our discussion of the transmission properties of active neural channels is phrased in the context of an idealized channel composed on one neuron N1 that receives information in the form of a spike train and passes this on, modulate ...
Coupled Noisy Spiking Neurons as Velocity-Controlled
... Hasselmo, 2008; Hasselmo, 2008; Welinder et al., 2008; Burak and Fiete, 2009; Zilli et al., 2009) is that they are presented in terms of abstract, perfect oscillators, whereas oscillators in the brain are noisy and have more complicated dynamics. Zilli et al. (2009) showed that experimentally measur ...
... Hasselmo, 2008; Hasselmo, 2008; Welinder et al., 2008; Burak and Fiete, 2009; Zilli et al., 2009) is that they are presented in terms of abstract, perfect oscillators, whereas oscillators in the brain are noisy and have more complicated dynamics. Zilli et al. (2009) showed that experimentally measur ...
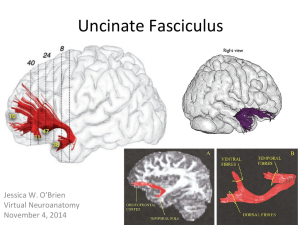
Uncinate Fasciculus
... neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to their behavioral significance, and some were condiOonal – E.g., neuron responds only if parOcular sOmulus is present AND that sOmulus signifies rewa ...
... neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to their behavioral significance, and some were condiOonal – E.g., neuron responds only if parOcular sOmulus is present AND that sOmulus signifies rewa ...
PDF of article - Janelia Research Campus
... Overview of sensorimotor processing. Example sensorimotor behavior: locust escape response. (a) As the image of a looming stimulus expands across a locust’s retina, it sequentially modulates the activity of each photoreceptor (two schematized examples shown). (b) The resulting pattern of photorecept ...
... Overview of sensorimotor processing. Example sensorimotor behavior: locust escape response. (a) As the image of a looming stimulus expands across a locust’s retina, it sequentially modulates the activity of each photoreceptor (two schematized examples shown). (b) The resulting pattern of photorecept ...