File - Biology with Radjewski
... – It insulates the axon – It speeds up the transmission of action potentials – Produced by Schwann cells that surround the axon – Gaps in the myelin sheath are called the Nodes of Ranvier ...
... – It insulates the axon – It speeds up the transmission of action potentials – Produced by Schwann cells that surround the axon – Gaps in the myelin sheath are called the Nodes of Ranvier ...
PNS/Reflexes
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
Neuroscience, 4e
... Figure 9.10 Somatic sensory portions of the thalamus and their cortical targets in postcentral gyrus ...
... Figure 9.10 Somatic sensory portions of the thalamus and their cortical targets in postcentral gyrus ...
The Central Nervous System
... A. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant in language and analytical ability, whereas the right hemisphere is more important in pattern recognition, musical creation, singing, and the recognition of faces. B. The two hemispheres cooperate in their functions; this is aided by communication b ...
... A. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant in language and analytical ability, whereas the right hemisphere is more important in pattern recognition, musical creation, singing, and the recognition of faces. B. The two hemispheres cooperate in their functions; this is aided by communication b ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 1. Unipolar – have a single process that emerges from the cell body. Functions mainly as an axon for the PNS. 2. Bipolar – have two processes- one axon, one dendrite. Found in the retina of the eye and the olfactory mucosa. 3. Multipolar – have many (at least 2) dendrites and one axon. Most common n ...
... 1. Unipolar – have a single process that emerges from the cell body. Functions mainly as an axon for the PNS. 2. Bipolar – have two processes- one axon, one dendrite. Found in the retina of the eye and the olfactory mucosa. 3. Multipolar – have many (at least 2) dendrites and one axon. Most common n ...
BOX 25.3 GIANT SYNAPTIC TERMINALS: ENDBULBS AND
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
... ventral cochlear nucleus (Fig. 25.18A), and (2) calyceal endings, which are found in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Calyces are so large that it is possible to use patch electrodes to record and clamp the presynaptic terminal while simultaneously doing the same with their postsynaptic tar ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System ppt - Jamestown Public Schools
... shape, to help you adjust your eyes’ focus to see near or distant objects Retina - where light is focused onto from the lens; here, light energy is converted into nerve impulses that are carried to the CNS ...
... shape, to help you adjust your eyes’ focus to see near or distant objects Retina - where light is focused onto from the lens; here, light energy is converted into nerve impulses that are carried to the CNS ...
To allow an immediate response to stimuli in the
... Structures associated with Vision: The photoreceptors: two types – Rods which detect low intensity light in degrees of “black and white”, and Cones which detect color, but only in high intensity light The Retina: The back wall of the eyeball, which contains all the photoreceptors The fovea centralis ...
... Structures associated with Vision: The photoreceptors: two types – Rods which detect low intensity light in degrees of “black and white”, and Cones which detect color, but only in high intensity light The Retina: The back wall of the eyeball, which contains all the photoreceptors The fovea centralis ...
A monument of inefficiency: The presumed course of the recurrent
... if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nervous system function has been demonstrated for living animals (More et al. 2010), but it probably reached its ultimate ex− p ...
... if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nervous system function has been demonstrated for living animals (More et al. 2010), but it probably reached its ultimate ex− p ...
Chapter 13
... neuron produces a change in membrane potential such that the potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane, this is referred to as ________________ ...
... neuron produces a change in membrane potential such that the potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane, this is referred to as ________________ ...
Nervous System - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... As well, these experiments indicated that the response is often an all-or-none response In other words, either the response (such as muscle contraction) would either not be present (when the threshold level had not been reached) or at maximum intensity (at any level above the threshold level) ...
... As well, these experiments indicated that the response is often an all-or-none response In other words, either the response (such as muscle contraction) would either not be present (when the threshold level had not been reached) or at maximum intensity (at any level above the threshold level) ...
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
... The cell body of a neuron consists of a nucleus surrounded by granular cytoplasm that contains the usual organelles found in other cells. Neuron cell bodies are gray in color and may be referred to as gray matter. Clusters of neuron cell bodies within the CNS are called nuclei; within the PNS they a ...
... The cell body of a neuron consists of a nucleus surrounded by granular cytoplasm that contains the usual organelles found in other cells. Neuron cell bodies are gray in color and may be referred to as gray matter. Clusters of neuron cell bodies within the CNS are called nuclei; within the PNS they a ...
The Nervous System
... hormones to be produced, carried by blood to target organ, and for response to occur ...
... hormones to be produced, carried by blood to target organ, and for response to occur ...
Lower Extremity Nerve Roots Pain Distribution Causative lesions
... Fibularis Longus & Brevis (Sup Fibular ...
... Fibularis Longus & Brevis (Sup Fibular ...
Review Questions
... of the gracilis and cuneatus, is likely to result in loss of A. fine discriminative touch ipsilaterally. B. eye movements. C. diffuse touch bilaterally. D. pain and temperature universally. E. motor control bilaterally. ...
... of the gracilis and cuneatus, is likely to result in loss of A. fine discriminative touch ipsilaterally. B. eye movements. C. diffuse touch bilaterally. D. pain and temperature universally. E. motor control bilaterally. ...
Nervous System Function
... Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and can depolarize as a result ...
... Myelinated neurons allow action potentials to ‘jump’ between unmyelinated gaps (Node of Ranvier) along the neuron Action potential and nerve impulse are faster Myelin sheath acts as insulation prevents depolarization Nodes of Ranvier are not insulated and can depolarize as a result ...
Document
... CNS Moderation of Reflexes • Upper CNS (brain) normally produces an inhibitory effect on the reflex arcs (muffled effect) • With injury, intact reflex arcs caudal to spinal cord trauma ...
... CNS Moderation of Reflexes • Upper CNS (brain) normally produces an inhibitory effect on the reflex arcs (muffled effect) • With injury, intact reflex arcs caudal to spinal cord trauma ...
Taste and Smell - Liberty Hill High School
... Taste triggers reflex involved in digestion; causes an increase of saliva in mouth (amylase) and gastric juice in stomach acids cause strong salivary reflex bad tasting food causes gagging or reflexive vomiting taste can change over time taste is 80% smell ...
... Taste triggers reflex involved in digestion; causes an increase of saliva in mouth (amylase) and gastric juice in stomach acids cause strong salivary reflex bad tasting food causes gagging or reflexive vomiting taste can change over time taste is 80% smell ...
The Nervous System
... Divisions of the Nervous System • 1. Central Nervous System – Spinal Chord and Brain – Processing coordination of stimulus and response 2. Peripheral Nervous System - All neural tissue outside the CNS - Delivers sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to the effectors ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System • 1. Central Nervous System – Spinal Chord and Brain – Processing coordination of stimulus and response 2. Peripheral Nervous System - All neural tissue outside the CNS - Delivers sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to the effectors ...
Document
... A weight lifter is straining to lift a 200-kg barbell. Shortly after he lifts it to chest height, his muscles appear to relax and he drops the barbell. Which reflex has occurred? ...
... A weight lifter is straining to lift a 200-kg barbell. Shortly after he lifts it to chest height, his muscles appear to relax and he drops the barbell. Which reflex has occurred? ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES
... formed from the fusion of dorsal and ventral roots as they pass through the intervertebral foramen • Nerves then divide into several branches ...
... formed from the fusion of dorsal and ventral roots as they pass through the intervertebral foramen • Nerves then divide into several branches ...
Sensation and Perception
... limbs report phantom limb pain • May involve activation of nerves in the stump of missing limb • May also involve reorganization of motor and somatosensory cortex ...
... limbs report phantom limb pain • May involve activation of nerves in the stump of missing limb • May also involve reorganization of motor and somatosensory cortex ...
Babinski reflex and corticospinal tract lesion
... Activation of gamma MN during active muscle contraction enables the muscle spindles to continue sensing changes in muscle length •Activation of the gamma motor neurons leads to contraction of the ends of the fibers, which stretch of the central regions. •This allows the spindle to respond to change ...
... Activation of gamma MN during active muscle contraction enables the muscle spindles to continue sensing changes in muscle length •Activation of the gamma motor neurons leads to contraction of the ends of the fibers, which stretch of the central regions. •This allows the spindle to respond to change ...
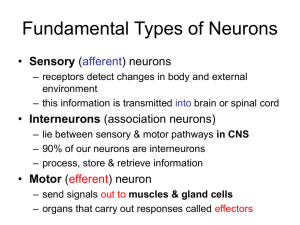
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.