Gross Appearance of Cerebellum
... Efferents fibers: projects to the fastigial and interposed nuclei → vestibular nuclei, reticular formation and red nucleus → vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tract and rubrospinal tract → motor neurons of anterior horn ...
... Efferents fibers: projects to the fastigial and interposed nuclei → vestibular nuclei, reticular formation and red nucleus → vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tract and rubrospinal tract → motor neurons of anterior horn ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Non-essential activities are dampened (GI/urinary). Promotes adjustments during exercise – blood flow to organs is reduced, flow to muscles is increased. Its activity is illustrated by a person who is threatened • Heart rate increases, and breathing is rapid and deep. • The skin is cold and sweaty, ...
... Non-essential activities are dampened (GI/urinary). Promotes adjustments during exercise – blood flow to organs is reduced, flow to muscles is increased. Its activity is illustrated by a person who is threatened • Heart rate increases, and breathing is rapid and deep. • The skin is cold and sweaty, ...
Sensory System
... Area 3a and 3b (aka S1) are the first recipients of sensory information. Area 1 and 2 (aka S2 (?)) receive input from Areas 3a and 3b. Thus 1 and 2 are higher up in the processing of somatic sensation. o For example, Areas 1 and 2 can discriminate selectivity of movement of a finger across the s ...
... Area 3a and 3b (aka S1) are the first recipients of sensory information. Area 1 and 2 (aka S2 (?)) receive input from Areas 3a and 3b. Thus 1 and 2 are higher up in the processing of somatic sensation. o For example, Areas 1 and 2 can discriminate selectivity of movement of a finger across the s ...
Acutouch Therapy
... Neurons carry impulses between the body periphery and the central nervous system. ...
... Neurons carry impulses between the body periphery and the central nervous system. ...
12-2cut
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
Document
... • A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates • Three types of motor units (muscles): • Fast fatigable (FF) Powerful, but fatigue with repetitive stimulation muscle fiber: thick, large, white (anaerobic, use glycolytic pathway to generate ATP) Motor neuron large, ...
... • A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates • Three types of motor units (muscles): • Fast fatigable (FF) Powerful, but fatigue with repetitive stimulation muscle fiber: thick, large, white (anaerobic, use glycolytic pathway to generate ATP) Motor neuron large, ...
7. Nervous Tissue, Overview of the Nervous System.
... Functioning of dendrites and axons. The sheer number of dendrites against the single axon gives us an insight into their functioning. Dendrites can collect information from a vast number of sources (other neurons), add it up and pass it along the body to the axon. An axon, in general, transmits what ...
... Functioning of dendrites and axons. The sheer number of dendrites against the single axon gives us an insight into their functioning. Dendrites can collect information from a vast number of sources (other neurons), add it up and pass it along the body to the axon. An axon, in general, transmits what ...
2 m – 32. Autonomous part of the peripheral nervous system
... 4. Tasks for independent work during preparation for classes. 4.1. The list of key terms, parameters, characteristics which the student is to assimilate while preparing for classes Sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (PARS SYMPATHICA- is part of the sympathetic adaptation to changes in ...
... 4. Tasks for independent work during preparation for classes. 4.1. The list of key terms, parameters, characteristics which the student is to assimilate while preparing for classes Sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (PARS SYMPATHICA- is part of the sympathetic adaptation to changes in ...
NEUROSCIENCE Review Questions CHOOSE THE LETTER THAT
... D. are the receptors for muscle pain. E. are found in flexors but not extensors. 11. Each motoneuron pool: A. contains motoneurons that all have the same axon diameter B. consists of a population of motoneurons that all have the same size cell body. C. contains only one type of muscle fiber. D. is c ...
... D. are the receptors for muscle pain. E. are found in flexors but not extensors. 11. Each motoneuron pool: A. contains motoneurons that all have the same axon diameter B. consists of a population of motoneurons that all have the same size cell body. C. contains only one type of muscle fiber. D. is c ...
07 Cranial nerves, their functional division into three groups. Organ
... stimulus and its location • The stronger the stimulus, the higher the frequency of action potentials • Some receptors adapt, that is their sensitivity to a stimulus is reduced if the stimulus is continually applied (smell) – The RAS can heighten or reduce awareness of sensory information ...
... stimulus and its location • The stronger the stimulus, the higher the frequency of action potentials • Some receptors adapt, that is their sensitivity to a stimulus is reduced if the stimulus is continually applied (smell) – The RAS can heighten or reduce awareness of sensory information ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... language ability; when these areas are damaged, characteristic types of aphasias result. A. Wernicke’s area is involved in speech comprehension, whereas Broca’s area is required for the mechanical performance of speech. B. Wernicke’s area is believed to control Broca’s area by means of the arcuate f ...
... language ability; when these areas are damaged, characteristic types of aphasias result. A. Wernicke’s area is involved in speech comprehension, whereas Broca’s area is required for the mechanical performance of speech. B. Wernicke’s area is believed to control Broca’s area by means of the arcuate f ...
Muscles - Lever Systems
... muscle contracts, it must be pulled back to its original length by another muscle shortening itself in the other direction. ...
... muscle contracts, it must be pulled back to its original length by another muscle shortening itself in the other direction. ...
Motor Cortex
... because the selection of a particular movement is impaired. Supplementary motor area (medial area 6): Patient cannot tie shoe laces (impaired selection of a particular movement sequence). Parietal association: Patient has no sock on one foot because of sensory neglect. Patient has ataxia (inaccurate ...
... because the selection of a particular movement is impaired. Supplementary motor area (medial area 6): Patient cannot tie shoe laces (impaired selection of a particular movement sequence). Parietal association: Patient has no sock on one foot because of sensory neglect. Patient has ataxia (inaccurate ...
Jackson Rancheria Casino Shooting
... A brain tumor is found in a CT scan of Mr. Child’s head. The physician is assuming that it is not a secondary tumor (i.e. it did not spread from another part of the body) because an exhaustive workup has revealed no signs of cancer elsewhere in Mr. Child’s body. Is the brain tumor more likely to hav ...
... A brain tumor is found in a CT scan of Mr. Child’s head. The physician is assuming that it is not a secondary tumor (i.e. it did not spread from another part of the body) because an exhaustive workup has revealed no signs of cancer elsewhere in Mr. Child’s body. Is the brain tumor more likely to hav ...
important ascending tracts
... three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract an ...
... three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract an ...
Nervous System Review ANSWERS File
... 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be produced by an electric shock or a sudden change in pH C. The action potential ends when the polarity across the membrane reaches +40mV ...
... 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be produced by an electric shock or a sudden change in pH C. The action potential ends when the polarity across the membrane reaches +40mV ...
Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... Diffuse modulatory system in part corresponds to the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) that is a physiological concept. The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire ...
... Diffuse modulatory system in part corresponds to the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) that is a physiological concept. The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
doc GIT
... In the esophagus, there is a peristaltic wave moving over the entire organ (moves down). The innervation & the responses of the musculature are diff. (striated and smooth). If you cut the vagus nerve high up in the neck so that the somatic and the autonomic fibers are disrupted, you can no longer ge ...
... In the esophagus, there is a peristaltic wave moving over the entire organ (moves down). The innervation & the responses of the musculature are diff. (striated and smooth). If you cut the vagus nerve high up in the neck so that the somatic and the autonomic fibers are disrupted, you can no longer ge ...
the autonomic nervous system
... often causes secretion of both epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla. The sympathetic division diverges more than parasympathetic division. Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine ...
... often causes secretion of both epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla. The sympathetic division diverges more than parasympathetic division. Sympathetic stimulation often activates many different kinds of effector organs at the same time as a result of CNS stimulation or epinephrine ...
Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
... Table 46–1 lists and classifies most of the body’s sensory receptors. This table shows that there are five basic types of sensory receptors: (1) mechanoreceptors, which detect mechanical compression or stretching of the receptor or of tissues adjacent to the receptor; (2) thermoreceptors, which dete ...
... Table 46–1 lists and classifies most of the body’s sensory receptors. This table shows that there are five basic types of sensory receptors: (1) mechanoreceptors, which detect mechanical compression or stretching of the receptor or of tissues adjacent to the receptor; (2) thermoreceptors, which dete ...
Reflexes and Homeostasis
... interneurons fall into two general categories. In long re exes, the interneuron is in a central nervous system (CNS) structure such as the brain or spinal cord. In short re exes, the interneuron is located in a peripheral ganglion, bypassing the CNS, as shown in Figure 1 (Short and Long Re exes ). F ...
... interneurons fall into two general categories. In long re exes, the interneuron is in a central nervous system (CNS) structure such as the brain or spinal cord. In short re exes, the interneuron is located in a peripheral ganglion, bypassing the CNS, as shown in Figure 1 (Short and Long Re exes ). F ...
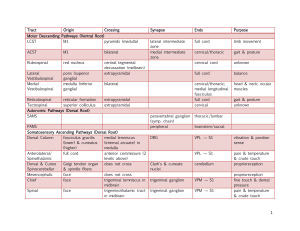
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... rest: increased gamma MN activity enhances muscle tone → shortens spindle, increasing Ia gain stretch: Ia activity elevation is abnormally high → sudden movements leads to spasticity & clonus Babinski's sign: extensor (toes fanned) plantar response sensory neurons touch: mechanoreceptors with differ ...
... rest: increased gamma MN activity enhances muscle tone → shortens spindle, increasing Ia gain stretch: Ia activity elevation is abnormally high → sudden movements leads to spasticity & clonus Babinski's sign: extensor (toes fanned) plantar response sensory neurons touch: mechanoreceptors with differ ...
Unit 4 Test Study sheet
... While there will be some questions on the overall organization of the NS, we will mostly focus on NS function of overall body control and sensory interpretation. There will be questions on reflexes, and a heavy emphasize on skeletal muscle structure and function. Topics in general covered in this un ...
... While there will be some questions on the overall organization of the NS, we will mostly focus on NS function of overall body control and sensory interpretation. There will be questions on reflexes, and a heavy emphasize on skeletal muscle structure and function. Topics in general covered in this un ...
The Nervous System - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... from outside to inside of axon (i.e. "depolarization" occurs -- the inside of the axon becomes positive). In the downswing (+40 mV to -60 mV), membrane becomes permeable to K+. K+ moves from outside to inside of axon. This is called repolarization (since the inside of axon becomes negative again). R ...
... from outside to inside of axon (i.e. "depolarization" occurs -- the inside of the axon becomes positive). In the downswing (+40 mV to -60 mV), membrane becomes permeable to K+. K+ moves from outside to inside of axon. This is called repolarization (since the inside of axon becomes negative again). R ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.