Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... ossicles, tympanic reflex Normal conduction, air conduction, and bone conduction; classification of deafness Cochlear structure: basilar membrane, organ of Corti, hair cells, tectorial membrane, fluid ...
... ossicles, tympanic reflex Normal conduction, air conduction, and bone conduction; classification of deafness Cochlear structure: basilar membrane, organ of Corti, hair cells, tectorial membrane, fluid ...
The Brain and Behavior
... FIGURE 2.1 A neuron, or nerve cell. In the right foreground you can see a nerve cell fiber in cross section. The upper left photo gives a more realistic picture of the shape of neurons. Nerve impulses usually travel from the dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The nerve cell shown ...
... FIGURE 2.1 A neuron, or nerve cell. In the right foreground you can see a nerve cell fiber in cross section. The upper left photo gives a more realistic picture of the shape of neurons. Nerve impulses usually travel from the dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The nerve cell shown ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... A sensory neuron, that conducts the afferent (sensory) impulses to the CNS; The integration center, consisting of one to several synapses in the CNS; A motor neuron, that conducts the efferent (motor) impulses from the CNS to an effector; An effector, the muscle fibers or gland that respond to the m ...
... A sensory neuron, that conducts the afferent (sensory) impulses to the CNS; The integration center, consisting of one to several synapses in the CNS; A motor neuron, that conducts the efferent (motor) impulses from the CNS to an effector; An effector, the muscle fibers or gland that respond to the m ...
Chapter 02
... understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
... understand that humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
Lecture - Lawrence Moon
... Anti-growth pathways switched on Inhospitable extrinsic environment Growth-inhibitory molecules (intact & injured) Lack of growth factors, permissive substrates ...
... Anti-growth pathways switched on Inhospitable extrinsic environment Growth-inhibitory molecules (intact & injured) Lack of growth factors, permissive substrates ...
The Nervous System
... show that you understand what you are saying. Also, make it a habit to answer in full sentences whenever it is appropriate for the question. You will also be responsible for the vocabulary words listed on p239. 1. What structures make up the central nervous system? 2. What structures make up the per ...
... show that you understand what you are saying. Also, make it a habit to answer in full sentences whenever it is appropriate for the question. You will also be responsible for the vocabulary words listed on p239. 1. What structures make up the central nervous system? 2. What structures make up the per ...
The Nervous System
... glands, among other tissues. In the nervous system, diphtheria toxin damages Schwann cells and destroys myelin sheaths in the PNS. This demyelination leads to sensory and motor problems that may ultimately produce a fatal paralysis. The toxin also affects cardiac muscle cells, and heart enlargement ...
... glands, among other tissues. In the nervous system, diphtheria toxin damages Schwann cells and destroys myelin sheaths in the PNS. This demyelination leads to sensory and motor problems that may ultimately produce a fatal paralysis. The toxin also affects cardiac muscle cells, and heart enlargement ...
Keshara Senanayake Towle Notes Chapter 50 "Nervous System
... >hair cells that respond to high frequency sound are most vulnerable -Balance is maintained with the help of mechanoreceptors in the 3 semicircular canals of the inner ear. These canals are filled with fluid, and their interiors are lined with hair cells that have tiny particles of CaCO3 (calcium ca ...
... >hair cells that respond to high frequency sound are most vulnerable -Balance is maintained with the help of mechanoreceptors in the 3 semicircular canals of the inner ear. These canals are filled with fluid, and their interiors are lined with hair cells that have tiny particles of CaCO3 (calcium ca ...
HEAD/NECK: Cranial Nerves
... IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
... IX: Glosso- • Sensory to carotid body/sinus pharyngeal • Taste to posterior tongue • Sensory to ear opening/middle ear • Parotid salivary gland X: Vagus ...
What is Superior Laryngeal Nerve Paresis
... larynx and sends the signal to the Cricothyroid muscle (the v-shaped muscle above) responsible for stretching the vocal folds and changing pitch. The SLN is particularly susceptible to viral infections for some reason, and this kind of weakness is fairly common. When a virus affects the nerve, it sw ...
... larynx and sends the signal to the Cricothyroid muscle (the v-shaped muscle above) responsible for stretching the vocal folds and changing pitch. The SLN is particularly susceptible to viral infections for some reason, and this kind of weakness is fairly common. When a virus affects the nerve, it sw ...
Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... Spreading out from the cell body are short, branched extensions called dendrites, which RECEIVE information. ...
... Spreading out from the cell body are short, branched extensions called dendrites, which RECEIVE information. ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
Slide ()
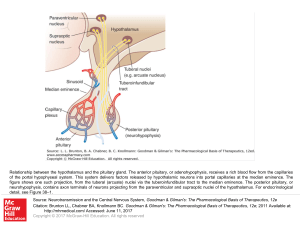
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
presentation
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...
... Two astrocytic microdomains connected to two networks are able to interact with each other. The network connected to M1 spikes at a higher frequency and is able to trigger SICs (Slow Inward Currents) in b ...
Neurology, Neurons, and EEG
... physical parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is most easily described by what it is not…it is everything BUT the spinal cord and brain. The central nervous system [CNS] is made of the spinal cord and the brain (including the brain stem). ...
... physical parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is most easily described by what it is not…it is everything BUT the spinal cord and brain. The central nervous system [CNS] is made of the spinal cord and the brain (including the brain stem). ...
The Nervous System http://www.gmstigers.com/apps/pages/index
... brain to all parts of your body. The messages are carried through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons are made up of three main parts, the cell body, axons, and dendrites. Axons and dendrites branch out to messages to be sent and received to all parts of the body. The spinal cord is the long bu ...
... brain to all parts of your body. The messages are carried through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons are made up of three main parts, the cell body, axons, and dendrites. Axons and dendrites branch out to messages to be sent and received to all parts of the body. The spinal cord is the long bu ...
Nervous Tissue - Manasquan Public Schools
... fuse together into a single process - single process divides into two branches a short distance from cell body ...
... fuse together into a single process - single process divides into two branches a short distance from cell body ...
Introduction of the Nervous System
... the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually given is walking in a shallow pond and stepping on a sharp object. The foot immediately raises before you are voluntarily aware of pending dange ...
... the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually given is walking in a shallow pond and stepping on a sharp object. The foot immediately raises before you are voluntarily aware of pending dange ...
PCL - mmc7
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEX ACTIVITY
... • The segmental level is the lowest level on the motor control hierarchy and consists of the spinal cord circuits • The projection level has direct control of the spinal cord • The precommand level is made up of the cerebellum and the basal nuclei and is the highest level of the motor system ...
... • The segmental level is the lowest level on the motor control hierarchy and consists of the spinal cord circuits • The projection level has direct control of the spinal cord • The precommand level is made up of the cerebellum and the basal nuclei and is the highest level of the motor system ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... Discussion Questions Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
... Discussion Questions Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
Position of Larval Tapeworms, Polypocephalus sp., in the Ganglia of
... Polypocephalus sp. within the ganglia might be extremely specific, for two reasons. First, being closer to the functionally important area of the nervous system would allow a greater probability of manipulation (i.e., ‘‘access to the control panel’’), particularly if the mechanism of manipulation in ...
... Polypocephalus sp. within the ganglia might be extremely specific, for two reasons. First, being closer to the functionally important area of the nervous system would allow a greater probability of manipulation (i.e., ‘‘access to the control panel’’), particularly if the mechanism of manipulation in ...