AP Physics HW Name: Photon Scattering and X
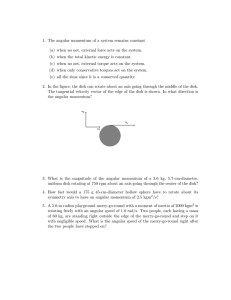
... shown above left. After the collision, the photon is shifted in wavelength by an amount Δ = 2h/mec, and reversed in direction, as shown above right. (a) Determine the energy in joules of the incident photon. ...
... shown above left. After the collision, the photon is shifted in wavelength by an amount Δ = 2h/mec, and reversed in direction, as shown above right. (a) Determine the energy in joules of the incident photon. ...
Homework set 1, due September 4, 11:40 am
... 5. (20 points) Consider a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x-direction in free space having as its plane of vibration the xy plane. Given that its frequency is 10 MHz and its amplitude is E0= 0.08 V/m (a) Find the period and wavelength of the wave. (b) Write an express ...
... 5. (20 points) Consider a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x-direction in free space having as its plane of vibration the xy plane. Given that its frequency is 10 MHz and its amplitude is E0= 0.08 V/m (a) Find the period and wavelength of the wave. (b) Write an express ...
Problem-Solving Strategy
... where is the angle between the incident polarization direction and the filter’s polarizing axis. ...
... where is the angle between the incident polarization direction and the filter’s polarizing axis. ...
Introductory Quantum Optics
... clear understanding. The diagrams are good. However, I felt that the mathematical analyses would be easier for those with good backgrounds if done on a higher level, and some of the physical discussions seemed obscure. Given the authors’ intended audience, it may be unreasonable to quarrel with thei ...
... clear understanding. The diagrams are good. However, I felt that the mathematical analyses would be easier for those with good backgrounds if done on a higher level, and some of the physical discussions seemed obscure. Given the authors’ intended audience, it may be unreasonable to quarrel with thei ...
Modern physics 2330
... 4- ( ) The number, strength, and exact position of the lines in the spectrum of an element depend only upon temperature. 5- ( ) According to de Broglie, the electron of the Bohr atom forms a standing h wave around the nucleus with . p 6- ( ) Davisson-Germer experiment (1927) is a direct experime ...
... 4- ( ) The number, strength, and exact position of the lines in the spectrum of an element depend only upon temperature. 5- ( ) According to de Broglie, the electron of the Bohr atom forms a standing h wave around the nucleus with . p 6- ( ) Davisson-Germer experiment (1927) is a direct experime ...
Notes27and29January2014BasicQuantumMechanics
... Quantum Theory for Semiconductors How to determine the behavior of electrons in the semiconductor? • Mathematical description of motion of electrons in quantum mechanics ─ Schrödinger’s Equation • Solution of Schrödinger’s Equation energy band structure and probability of finding a electron at a pa ...
... Quantum Theory for Semiconductors How to determine the behavior of electrons in the semiconductor? • Mathematical description of motion of electrons in quantum mechanics ─ Schrödinger’s Equation • Solution of Schrödinger’s Equation energy band structure and probability of finding a electron at a pa ...
Atomic Diffraction Dr. Janine Shertzer College of the Holy Cross
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...
Lesson 1 - Tarleton State University
... Many lines were not seen. This indicated that there were selection rules that determined what lines were present. ...
... Many lines were not seen. This indicated that there were selection rules that determined what lines were present. ...
Problem set 2
... is real, so that we are justified in calling it a phase angle. Here ψn (t) are orthonormal eigenstates of the hamiltonians H(t) for each t with eigenvalues En (t). 2. With the same notation as above, show that Ėn = hψn |Ḣ|ψn i. ...
... is real, so that we are justified in calling it a phase angle. Here ψn (t) are orthonormal eigenstates of the hamiltonians H(t) for each t with eigenvalues En (t). 2. With the same notation as above, show that Ėn = hψn |Ḣ|ψn i. ...
Homework 2
... (b) According to the Bohr model, electrons move on circular orbits and the angular momentum L can assume the values L = n~, n ∈ {1, 2, . . .}. Determine the possible energies En , orbital radii rn , and velocity ratios vn /c, where c is the speed of light. (c) Bohr assumed that only radiation of fre ...
... (b) According to the Bohr model, electrons move on circular orbits and the angular momentum L can assume the values L = n~, n ∈ {1, 2, . . .}. Determine the possible energies En , orbital radii rn , and velocity ratios vn /c, where c is the speed of light. (c) Bohr assumed that only radiation of fre ...