20030115154916
... • The atoms of the gas absorb incident photons of certain wavelength and re-emit photons of the same wavelength almost immediately, but in all directions. • Consequently, the intensity of light of these wavelengths, in the original direction is reduced and ‘dark’ lines are produced. ...
... • The atoms of the gas absorb incident photons of certain wavelength and re-emit photons of the same wavelength almost immediately, but in all directions. • Consequently, the intensity of light of these wavelengths, in the original direction is reduced and ‘dark’ lines are produced. ...
W11Physics1CLec24Afkw
... of multitude of atoms located there. Each atom produces a wave with its own orientation of the electric field. All directions of the electric field vector are equally possible and are in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. This type of wave is known as an unpolarized wave. ...
... of multitude of atoms located there. Each atom produces a wave with its own orientation of the electric field. All directions of the electric field vector are equally possible and are in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. This type of wave is known as an unpolarized wave. ...
Rotational Motion Objectives: After reviewing this section you should
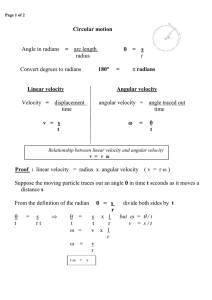
... 'angular' is used to describe motion in a circular path. If you are moving in a curved path, you are passing through some angle if you take the center of the path as the center of circle. Circular motion and rotational motion might seem like the same thing - and they are very similar. A familiar exa ...
... 'angular' is used to describe motion in a circular path. If you are moving in a curved path, you are passing through some angle if you take the center of the path as the center of circle. Circular motion and rotational motion might seem like the same thing - and they are very similar. A familiar exa ...
D (t-t
... The quantity ’() gives the part of the current which is in phase with the field and which therefore leads to absorption of energy. Hence, this quantity is comparable with ’’(). The quantity ’’() gives the part of the current with a phase difference of with respect to the field. Thus, ’’() is ...
... The quantity ’() gives the part of the current which is in phase with the field and which therefore leads to absorption of energy. Hence, this quantity is comparable with ’’(). The quantity ’’() gives the part of the current with a phase difference of with respect to the field. Thus, ’’() is ...
dark energy stars - at www.arxiv.org.
... quantum mechanics and GR is the lack of a universal time in GR. A number of arguments can be advanced as to why quantum mechanics requires a universal time. The simplest argument is what time does one mean when one writes down Schrodinger's equation? More subtle arguments involve the existence of no ...
... quantum mechanics and GR is the lack of a universal time in GR. A number of arguments can be advanced as to why quantum mechanics requires a universal time. The simplest argument is what time does one mean when one writes down Schrodinger's equation? More subtle arguments involve the existence of no ...
Discussion Short Questions Explicit Calculations
... (a) Consider a cone defined by the equation θ = β. Any point that has azimuthal angle larger than β is inside the conductor. Find the most general solution for the electrostatic potential in spherical coordinate. (10 points) (b) For points close to the tip, r is very small and hence only the leading ...
... (a) Consider a cone defined by the equation θ = β. Any point that has azimuthal angle larger than β is inside the conductor. Find the most general solution for the electrostatic potential in spherical coordinate. (10 points) (b) For points close to the tip, r is very small and hence only the leading ...
Evidence for Rescattering in Intense, Femtosecond - DORAS
... The main experimental difficulty in studying recollision in negative ions stems from the fact that neutralization will occur before the intensity of the pulse becomes sufficiently high for excitation or ionization of the core. At the wavelength used for our experiments (800 nm), the laser intensity ...
... The main experimental difficulty in studying recollision in negative ions stems from the fact that neutralization will occur before the intensity of the pulse becomes sufficiently high for excitation or ionization of the core. At the wavelength used for our experiments (800 nm), the laser intensity ...