Sample
... students watch the pulse travel to the other end. Tie a bit a red yarn to a coil in the Slinky and ask students to compare the motion of the pulse with the motion of the yarn. The pulse moves from one end to the other; the yarn just moves up and down. A wave is the propagation of a disturbance, not ...
... students watch the pulse travel to the other end. Tie a bit a red yarn to a coil in the Slinky and ask students to compare the motion of the pulse with the motion of the yarn. The pulse moves from one end to the other; the yarn just moves up and down. A wave is the propagation of a disturbance, not ...
The Physics of Polarization
... where E1, E2, ϕ 1, and ϕ 2 are constants. These oscillations combine in such a way that the tip of the electric filed vector describes an ellipse. ...
... where E1, E2, ϕ 1, and ϕ 2 are constants. These oscillations combine in such a way that the tip of the electric filed vector describes an ellipse. ...
Polarized light imaging of tissues
... twice retain significant information about the tissue structures that scatter light. A significant information remains in the trajectories of scattered photons and in their wavelength-dependent polarization and coherence properties. Such singly or doubly scattered photons offer a contrast mechanism ...
... twice retain significant information about the tissue structures that scatter light. A significant information remains in the trajectories of scattered photons and in their wavelength-dependent polarization and coherence properties. Such singly or doubly scattered photons offer a contrast mechanism ...
Pulse shaping control of spatially aligned
... the revivals using pulses with a modified temporal structure. We show control on the structure of the revivals in N2 and O2 at room temperature; for instance, enhancement of alignment at the expense of antialignment or vice versa. The results are discussed with reference to theoretical simulations t ...
... the revivals using pulses with a modified temporal structure. We show control on the structure of the revivals in N2 and O2 at room temperature; for instance, enhancement of alignment at the expense of antialignment or vice versa. The results are discussed with reference to theoretical simulations t ...
Momemtum/Impulse/ Conservation of Momentum
... Air bags are used in automobiles because they are able to minimize the affect of the force on an object involved in a collision. Air bags accomplish this by extending the time required to stop the momentum of the driver and passenger (bigger t, less F). Without airbags the driver and passenger tend ...
... Air bags are used in automobiles because they are able to minimize the affect of the force on an object involved in a collision. Air bags accomplish this by extending the time required to stop the momentum of the driver and passenger (bigger t, less F). Without airbags the driver and passenger tend ...
5 Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students
... kilogram (kg) as our unit of mass, the meter (m) as our unit of length, and the second (s) as our unit of time. This combination is known as “S.I. units”. All other mechanical quantities, such as force, energy, power, etc. will then be defined in terms of appropriate combinations of these three basi ...
... kilogram (kg) as our unit of mass, the meter (m) as our unit of length, and the second (s) as our unit of time. This combination is known as “S.I. units”. All other mechanical quantities, such as force, energy, power, etc. will then be defined in terms of appropriate combinations of these three basi ...
Degree Applicable Glendale Community College
... Prior to enrolling in the course, the student should be able to: 1. understand basic concepts and laws of mechanics, thermodynamics, and acoustics and apply this understanding to the solution of algebra-based problems in physics; 2. understand the scientific method and apply it to observations of ph ...
... Prior to enrolling in the course, the student should be able to: 1. understand basic concepts and laws of mechanics, thermodynamics, and acoustics and apply this understanding to the solution of algebra-based problems in physics; 2. understand the scientific method and apply it to observations of ph ...
DCAS Review of Energy Across the Systems
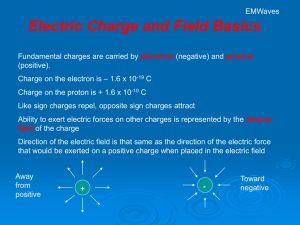
... Electric force and magnetic force are closely related. This is because both are caused by negative and positive charges in matter. Atoms, which make up all matter, contain a positively charged nucleus and a negatively charged cloud of electrons. When charges from one piece of matter interact with th ...
... Electric force and magnetic force are closely related. This is because both are caused by negative and positive charges in matter. Atoms, which make up all matter, contain a positively charged nucleus and a negatively charged cloud of electrons. When charges from one piece of matter interact with th ...
Physical Quantities and Units
... Oscillatory / Vibratory motion – Moving back and forth over the same path Free Oscillations – Oscillations where no frictional forces act on the oscillating particle Harmonic Motion – Motion where the displacement of the particle can be expressed in harmonic functions (sine and cosine functions). Pe ...
... Oscillatory / Vibratory motion – Moving back and forth over the same path Free Oscillations – Oscillations where no frictional forces act on the oscillating particle Harmonic Motion – Motion where the displacement of the particle can be expressed in harmonic functions (sine and cosine functions). Pe ...
Energy and Power
... net force in vertical direction is Fsin2 - Fsin 1 but sin~ ~tan when is small net vertical force on segment is F(tan2 - tan 1 ) but slope S of string is S=tan = y/x net force is F(S2 - S1) = F S = ma = x2y/t2 ...
... net force in vertical direction is Fsin2 - Fsin 1 but sin~ ~tan when is small net vertical force on segment is F(tan2 - tan 1 ) but slope S of string is S=tan = y/x net force is F(S2 - S1) = F S = ma = x2y/t2 ...