Momentum, Energy and Collisions
... For two interacting objects, if there is no net external force then we expect the total momentum of the system to be conserved. In contrast, energy is only conserved when certain types of forces are exerted between the objects. Collisions are classified as elastic (kinetic energy is conserved), inel ...
... For two interacting objects, if there is no net external force then we expect the total momentum of the system to be conserved. In contrast, energy is only conserved when certain types of forces are exerted between the objects. Collisions are classified as elastic (kinetic energy is conserved), inel ...
L07_Synchrotron_Radiation
... For the horizontal emittance h there is heating term due to the horizontal dispersion. What would stop dE and v of damping to zero? For v there is no heating term. So v can get very small. Coupling with motion in the horizontal plane finally limits the vertical beam size ...
... For the horizontal emittance h there is heating term due to the horizontal dispersion. What would stop dE and v of damping to zero? For v there is no heating term. So v can get very small. Coupling with motion in the horizontal plane finally limits the vertical beam size ...
Near-band-gap photo-induced nuclear spin
... responsible for our observations: One type of defect is a deep defect characterized by a longrange (tens of nm), non-uniform electric field gradient. The higher localization associated with deep defects gives rise to strong electric field gradients and thus efficient quadrupolar relaxation. This str ...
... responsible for our observations: One type of defect is a deep defect characterized by a longrange (tens of nm), non-uniform electric field gradient. The higher localization associated with deep defects gives rise to strong electric field gradients and thus efficient quadrupolar relaxation. This str ...
2.5 kg m/s - Purdue Physics
... escape from the gravitational attraction of all objects that affect it’s path. Or, for example, to leave the moon after landing. Conventional rockets are ~90% fuel by weight most of which is used escaping from the earth. Very small satellites might be put into orbit using a powerful laser beam Nucle ...
... escape from the gravitational attraction of all objects that affect it’s path. Or, for example, to leave the moon after landing. Conventional rockets are ~90% fuel by weight most of which is used escaping from the earth. Very small satellites might be put into orbit using a powerful laser beam Nucle ...
Chapter 6
... has mass 1/2 m and speed 2v, they will both have the same momentum. However, since KE = 1/2 mv2, we see that object #2 has twice the kinetic energy of ...
... has mass 1/2 m and speed 2v, they will both have the same momentum. However, since KE = 1/2 mv2, we see that object #2 has twice the kinetic energy of ...
Particle Physics
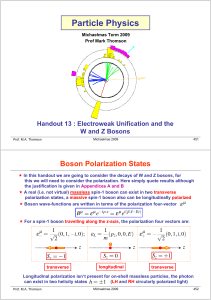
... In this handout we are going to consider the decays of W and Z bosons, for this we will need to consider the polarization. Here simply quote results although the justification is given in Appendices A and B A real (i.e. not virtual) massless spin-1 boson can exist in two transverse polarization ...
... In this handout we are going to consider the decays of W and Z bosons, for this we will need to consider the polarization. Here simply quote results although the justification is given in Appendices A and B A real (i.e. not virtual) massless spin-1 boson can exist in two transverse polarization ...
2008
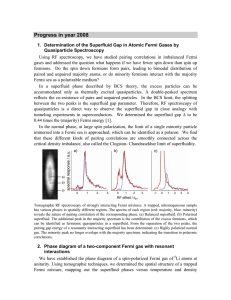
... fermions. Do the spin down fermions form pairs, leading to bimodal distribution of paired and unpaired majority atoms, or do minority fermions interact with the majority Fermi sea as a polarizable medium? In a superfluid phase described by BCS theory, the excess particles can be accommodated only as ...
... fermions. Do the spin down fermions form pairs, leading to bimodal distribution of paired and unpaired majority atoms, or do minority fermions interact with the majority Fermi sea as a polarizable medium? In a superfluid phase described by BCS theory, the excess particles can be accommodated only as ...
FE_Review_Dynamics - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... the work done is independent of the path taken Another way to state it: The work depends only on the initial and final positions, not on the route taken. ...
... the work done is independent of the path taken Another way to state it: The work depends only on the initial and final positions, not on the route taken. ...
Lecture-11-10
... Motion about the Center of Mass The center of mass of a complex or composite object follows a trajectory as if it were a single particle - with mass equal to the complex object, and experiencing a force equal to the sum of all external forces on that complex object ...
... Motion about the Center of Mass The center of mass of a complex or composite object follows a trajectory as if it were a single particle - with mass equal to the complex object, and experiencing a force equal to the sum of all external forces on that complex object ...