30V Internal Switch LCD Bias Supply MAX1605 General Description Features
... Negative Voltage for LCD Bias The MAX1605 can also generate a negative output by adding a diode-capacitor charge-pump circuit (D1, D2, and C3) to the LX pin as shown in Figure 4. Feedback is still connected to the positive output, which is not loaded, allowing a very small capacitor value at C4. For ...
... Negative Voltage for LCD Bias The MAX1605 can also generate a negative output by adding a diode-capacitor charge-pump circuit (D1, D2, and C3) to the LX pin as shown in Figure 4. Feedback is still connected to the positive output, which is not loaded, allowing a very small capacitor value at C4. For ...
Pressure-sensitive electrical switch and application therefor
... recti?ers. At this stage, silicon-controlled recti?er 82, for to be progressively decreased as the magnetic flux operat example, has not yet been triggered so that it will not ing thereon is increased. Consequently, a current ?ows conduct, and the other recti?er, e.g. 83 is positioned in through the ...
... recti?ers. At this stage, silicon-controlled recti?er 82, for to be progressively decreased as the magnetic flux operat example, has not yet been triggered so that it will not ing thereon is increased. Consequently, a current ?ows conduct, and the other recti?er, e.g. 83 is positioned in through the ...
romanian journal of physics - Romanian Reports in Physics
... transient regime is done through a graph presenting the energy variation in time, from the capacitor, and the energy dissipated in the resistor. For a comparative analysis a graph is drawn, overlaying the curves of the time dependence in case of the capacitor voltage from three different RC circuits ...
... transient regime is done through a graph presenting the energy variation in time, from the capacitor, and the energy dissipated in the resistor. For a comparative analysis a graph is drawn, overlaying the curves of the time dependence in case of the capacitor voltage from three different RC circuits ...
ZXTC6717MC Features Mechanical Data
... 6. For a dual device surface mounted on 28mm x 28mm (8cm2) FR4 PCB with high coverage of single sided 2 oz copper, in still air conditions; the device is measured when operating in a steady-state condition. The heatsink is split in half with the exposed collector pads connected to each half. 7. Same ...
... 6. For a dual device surface mounted on 28mm x 28mm (8cm2) FR4 PCB with high coverage of single sided 2 oz copper, in still air conditions; the device is measured when operating in a steady-state condition. The heatsink is split in half with the exposed collector pads connected to each half. 7. Same ...
AMS2954 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Figure 1 gives a timing diagram depicting the ERROR signal and the regulator output voltage as the AMS2954 input is ramped up and down. For 5V versions the ERROR signal becomes valid (low) at about 1.3V input. It goes high at about 5V input (the input voltage at which Vout = 4.75 ). ...
... Figure 1 gives a timing diagram depicting the ERROR signal and the regulator output voltage as the AMS2954 input is ramped up and down. For 5V versions the ERROR signal becomes valid (low) at about 1.3V input. It goes high at about 5V input (the input voltage at which Vout = 4.75 ). ...
High-Speed, 4-A, 600-V High-Side Low
... negative voltages of up to –8 VDC on HS pin (at VDD = 12 V). The device accepts a wide range bias supply input from 10 V to 20 V and offers UVLO protection for both the VCC and HB bias supply pins. UCC27714 is available in SOIC-14 package and rated to operate from –40°C to 125°C. ...
... negative voltages of up to –8 VDC on HS pin (at VDD = 12 V). The device accepts a wide range bias supply input from 10 V to 20 V and offers UVLO protection for both the VCC and HB bias supply pins. UCC27714 is available in SOIC-14 package and rated to operate from –40°C to 125°C. ...
MAX1645/MAX1645A Advanced Chemistry-Independent, Level 2 Battery Chargers with Input Current Limiting General Description
... The MAX1645 are high-efficiency battery chargers capable of charging batteries of any chemistry type. It uses the Intel System Management Bus (SMBus) to control voltage and current charge outputs. When charging lithium-ion (Li+) batteries, the MAX1645 automatically transition from regulating curren ...
... The MAX1645 are high-efficiency battery chargers capable of charging batteries of any chemistry type. It uses the Intel System Management Bus (SMBus) to control voltage and current charge outputs. When charging lithium-ion (Li+) batteries, the MAX1645 automatically transition from regulating curren ...
OPA3832
... provides an output swing to within 30mV of ground and 60mV of the positive supply. The high output drive current and low differential gain and phase errors also make it ideal for single-supply consumer video products. Low distortion operation is ensured by high bandwidth (80MHz) and slew rate (350V/ ...
... provides an output swing to within 30mV of ground and 60mV of the positive supply. The high output drive current and low differential gain and phase errors also make it ideal for single-supply consumer video products. Low distortion operation is ensured by high bandwidth (80MHz) and slew rate (350V/ ...
Maxim Design Support Technical Documents Application Notes
... small as possible. Some applications may even use Schottky diodes because they have a much lower forward voltage. Finally, choosing a diode with a short reverse-recovery time will limit the output charge lost back to the input when the diode switches from the conducting to the nonconducting stage. ...
... small as possible. Some applications may even use Schottky diodes because they have a much lower forward voltage. Finally, choosing a diode with a short reverse-recovery time will limit the output charge lost back to the input when the diode switches from the conducting to the nonconducting stage. ...
High Speed Switching / QSK for the TL-922 and SB
... switching, a necessary attribute for operating AMTOR, QSK-CW, or SSB-VOX modes. In its balky factory-stock configuration, the TL-922 hot-switches with many of the current crop of QSK-rated transceivers. Another factor is relay noise. The relay clacking in a stock TL-922 is loud, if not stentorian--a ...
... switching, a necessary attribute for operating AMTOR, QSK-CW, or SSB-VOX modes. In its balky factory-stock configuration, the TL-922 hot-switches with many of the current crop of QSK-rated transceivers. Another factor is relay noise. The relay clacking in a stock TL-922 is loud, if not stentorian--a ...
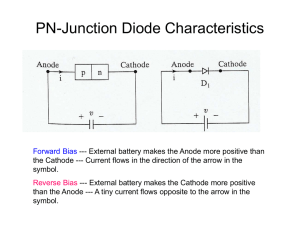
Diode Characteristics
... ta is the time to remove the charge stored in the depletion region of the junction tb is the time to remove the charge stored in the bulk semiconductor material ...
... ta is the time to remove the charge stored in the depletion region of the junction tb is the time to remove the charge stored in the bulk semiconductor material ...
DC and AC Load Line
... common-emitter amplifier. In another words, the ac load line will tell the maximum possible peakto-peak output voltage (VPP) from a given amplifier. This maximum VPP is referred to as the compliance of the amplifier. • The compliance of an amplifier is found by determine the maximum possible of IC a ...
... common-emitter amplifier. In another words, the ac load line will tell the maximum possible peakto-peak output voltage (VPP) from a given amplifier. This maximum VPP is referred to as the compliance of the amplifier. • The compliance of an amplifier is found by determine the maximum possible of IC a ...
LTC3619 - Linear Technology
... The input supply voltage range is 2.5V to 5.5V, making it ideal for Li-Ion and USB powered applications. 100% duty cycle capability provides low dropout operation, extending the run time in battery-operated systems. Low output voltages are supported with the 0.6V feedback reference voltage. Channel ...
... The input supply voltage range is 2.5V to 5.5V, making it ideal for Li-Ion and USB powered applications. 100% duty cycle capability provides low dropout operation, extending the run time in battery-operated systems. Low output voltages are supported with the 0.6V feedback reference voltage. Channel ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.