Reference Directions in Voltage and Current Division
... current: downward or upward. Similarly, there are two possible reference directions for the resistor current: downward or upward. Taken together, there are four possibilities for the source and resistor current reference directions. All four are illustrated by these two circuits. ...
... current: downward or upward. Similarly, there are two possible reference directions for the resistor current: downward or upward. Taken together, there are four possibilities for the source and resistor current reference directions. All four are illustrated by these two circuits. ...
Science Journals 4-18 to 5-5
... the current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across each resistor? If three resistors, 12 Ω , 24 Ω, and 6 Ω, are connected in parallel across a 24V battery, what is the current through each branch of the circuit? What is the total current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across e ...
... the current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across each resistor? If three resistors, 12 Ω , 24 Ω, and 6 Ω, are connected in parallel across a 24V battery, what is the current through each branch of the circuit? What is the total current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across e ...
PROBLEM SET Current, Voltage, and Resistance
... Solve the following problems on another sheet of paper. All answers should be expressed in four significant digits with correct units. ...
... Solve the following problems on another sheet of paper. All answers should be expressed in four significant digits with correct units. ...
Name: ___________________________________ Date: _________________________ Define the following terms:
... 8) You are doing yard work and listening to the radio. The radio seems to malfunction when you have it out in the hot sun. You decide to take a break and move the radio with you under an umbrella. Why does the radio start to work normally again? Explain using temperature and particles. ...
... 8) You are doing yard work and listening to the radio. The radio seems to malfunction when you have it out in the hot sun. You decide to take a break and move the radio with you under an umbrella. Why does the radio start to work normally again? Explain using temperature and particles. ...
LT6108/LT6109 - Current Sense System
... Precise, Rugged and Fast Current Monitor and Control Linear Technology’s LT ®6108 and LT6109 are complete high side current sense devices that combine a high precision current sense amplifier with comparators and a precision voltage reference. When connected to a current shunt resistor, the high sid ...
... Precise, Rugged and Fast Current Monitor and Control Linear Technology’s LT ®6108 and LT6109 are complete high side current sense devices that combine a high precision current sense amplifier with comparators and a precision voltage reference. When connected to a current shunt resistor, the high sid ...
A LED Exercise
... An LED which has the characteristics shown in this graph is to be used in the circuit below in which both VS and R can be varied. For this LED the switch on voltage (VD) is 1.7 volt which produces a current of 10 mA at which point the LED will just glow dimly. Let us say that the diode operates best ...
... An LED which has the characteristics shown in this graph is to be used in the circuit below in which both VS and R can be varied. For this LED the switch on voltage (VD) is 1.7 volt which produces a current of 10 mA at which point the LED will just glow dimly. Let us say that the diode operates best ...
Student Guide
... In this lab an NPN transistor will be used to show its characteristics as a switch and amplifier. NPN transistors are also used for its amplification properties. Figure 1 illustrates and example of the type of transistor you will be using. Take the transistor in front of you and look at the bottom. ...
... In this lab an NPN transistor will be used to show its characteristics as a switch and amplifier. NPN transistors are also used for its amplification properties. Figure 1 illustrates and example of the type of transistor you will be using. Take the transistor in front of you and look at the bottom. ...
Ohm`s Law
... 5. A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element (the resistance is 16 Ω) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
... 5. A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element (the resistance is 16 Ω) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
Gate Drive
... Info about LTC1910 (and how it works with LTC6101) A generic gate driver accepts low power input and converts it to a higher current gate driving MOSFET. In our circuit, we are using the gate driver in conjunction with an operational amplifier as a smart switch that can monitor the current reading. ...
... Info about LTC1910 (and how it works with LTC6101) A generic gate driver accepts low power input and converts it to a higher current gate driving MOSFET. In our circuit, we are using the gate driver in conjunction with an operational amplifier as a smart switch that can monitor the current reading. ...
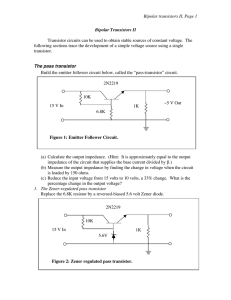
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with two or three transistors in a fast negative feedback circuit are u ...
... Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with two or three transistors in a fast negative feedback circuit are u ...
Bipolar Transistors I – Page 1 Bipolar Transistors I
... junction and then to read the voltage across it. For a silicon transistor like the 2N2219 you expect to find a forward voltage of 0.6 or 0.7 volts. Test both the basecollector and the base-emitter junctions of your transistor. (Note: With the multimeter in diode-test mode, you can determine which me ...
... junction and then to read the voltage across it. For a silicon transistor like the 2N2219 you expect to find a forward voltage of 0.6 or 0.7 volts. Test both the basecollector and the base-emitter junctions of your transistor. (Note: With the multimeter in diode-test mode, you can determine which me ...
FIGURE 4.2-1 Circuit with an independent voltage source and an
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
Pulukuri`s Report
... impossible. Moreover at a thickness equal to 5 atoms, where each silicon atom is 0.26 nm in diameter, the insulating layer was already creating a problem of current leakage by letting electrons rain through it. This caused a power drain and unwanted heat. Most of the advanced chips were getting heat ...
... impossible. Moreover at a thickness equal to 5 atoms, where each silicon atom is 0.26 nm in diameter, the insulating layer was already creating a problem of current leakage by letting electrons rain through it. This caused a power drain and unwanted heat. Most of the advanced chips were getting heat ...
project2 - UTK-EECS
... (b) Design, build, and test current mirror circuits using either MOSFETs or BJTs. Procedure example using a 2N7000 MOSFET: (1) Use HP 4145B to plot transfer function (ID~VGS) and output characteristic (ID~VDS) curve of the transistor, and estimate VTH, Kn, etc. for the subsequent PSPICE simulation. ...
... (b) Design, build, and test current mirror circuits using either MOSFETs or BJTs. Procedure example using a 2N7000 MOSFET: (1) Use HP 4145B to plot transfer function (ID~VGS) and output characteristic (ID~VDS) curve of the transistor, and estimate VTH, Kn, etc. for the subsequent PSPICE simulation. ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.