current - Irion County ISD
... • Has two or more paths for electrons to flow down • Current is shared between the branches • Sum of the current in each branch = total current • Voltage loss is the same across all components ...
... • Has two or more paths for electrons to flow down • Current is shared between the branches • Sum of the current in each branch = total current • Voltage loss is the same across all components ...
HCPL3700, An optocoupler with a difference
... Incoming Inspection when they buy a batch of such parts. Out of every hundred they may check a few to see that they operate as expected. This is one parameter they would likely check. At a set input current they should get a known output current at a predictable output voltage. Speed We have a limit ...
... Incoming Inspection when they buy a batch of such parts. Out of every hundred they may check a few to see that they operate as expected. This is one parameter they would likely check. At a set input current they should get a known output current at a predictable output voltage. Speed We have a limit ...
Unit 7_Electric current (unit guide)
... (or resistivity) for conductors, semiconductors and insulators, and to note that while the resistivity of a metallic conductor increases with temperature, the resistivity of a semiconductor decreases when the temperature increases. The existence of an electric current through wires that constitute a ...
... (or resistivity) for conductors, semiconductors and insulators, and to note that while the resistivity of a metallic conductor increases with temperature, the resistivity of a semiconductor decreases when the temperature increases. The existence of an electric current through wires that constitute a ...
Section C4: BJT Characteristic Curves
... It is sometimes helpful to view the characteristic curves of the transistor in graphical form. This is very similar to the graphical approach used with diodes, but now we have three possible points where something could be happening (base, emitter, collector). We’re still going to concentrate on nor ...
... It is sometimes helpful to view the characteristic curves of the transistor in graphical form. This is very similar to the graphical approach used with diodes, but now we have three possible points where something could be happening (base, emitter, collector). We’re still going to concentrate on nor ...
Electronic - Physics4IGCSE
... 7) The “reversed biased” diode is also placed in the circuit to act as a “_______” to prevent current flowing back into the transistor when the relay is switched _____ Words – base, buffer, on, increases, damaging, relay, off, larger, voltage, drop, NOT ...
... 7) The “reversed biased” diode is also placed in the circuit to act as a “_______” to prevent current flowing back into the transistor when the relay is switched _____ Words – base, buffer, on, increases, damaging, relay, off, larger, voltage, drop, NOT ...
Ohm`s Law Lab
... 1. Connect the source of current, the switch (opened), an ammeter, and a low ohm resistor in series. Place the voltmeter in parallel across the resistance. 2. Use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 3 volts through the resistor. You will have to change this each time. 3. NOTE Leave the switch ...
... 1. Connect the source of current, the switch (opened), an ammeter, and a low ohm resistor in series. Place the voltmeter in parallel across the resistance. 2. Use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 3 volts through the resistor. You will have to change this each time. 3. NOTE Leave the switch ...
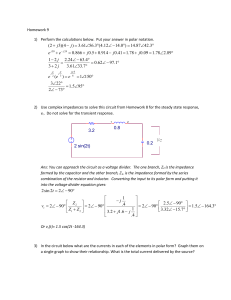
2 sin 2 2 90 1 2.5 90 .4 2 90 2 90 2 90 1.5 164.3 1 3.32 15.7 3.2 1.6
... 2) Use complex impedances to solve this circuit from Homework 8 for the steady state response, vc. Do not solve for the transient response. ...
... 2) Use complex impedances to solve this circuit from Homework 8 for the steady state response, vc. Do not solve for the transient response. ...
Chapter 27 Current and Resistance The Development of Voltage
... The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω). 1 Ω=1 V/A The electric field within a wire accelerates the electrons. However their velocities do not increase indefinitely because they collide with the array of positive ions that form the crystal lattice. This steady drift is analogous to the terminal vel ...
... The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω). 1 Ω=1 V/A The electric field within a wire accelerates the electrons. However their velocities do not increase indefinitely because they collide with the array of positive ions that form the crystal lattice. This steady drift is analogous to the terminal vel ...
Semester 1 Final Review
... What is electricity? What is the difference between parallel and series circuits? What is the total charge of an object with 18 electrons and 17 protons?__________ An atom that loses electrons becomes positive/negative. An atom that gains electrons becomes positive/negative. ...
... What is electricity? What is the difference between parallel and series circuits? What is the total charge of an object with 18 electrons and 17 protons?__________ An atom that loses electrons becomes positive/negative. An atom that gains electrons becomes positive/negative. ...
A LED Exercise
... with 40 mA through the diode there is a 2.0 V drop across it, leaving a 4 V drop across the resistor which needs to have a current of 40 mA flowing through it. Thus R = V/I = 4/40 = 0.1 k = 100 2. In a similar way, find the minimum value of the resistor that could be used without damaging the LED ...
... with 40 mA through the diode there is a 2.0 V drop across it, leaving a 4 V drop across the resistor which needs to have a current of 40 mA flowing through it. Thus R = V/I = 4/40 = 0.1 k = 100 2. In a similar way, find the minimum value of the resistor that could be used without damaging the LED ...
01-02MurraysOhmsLaw
... A 3.0 V battery with a capacity of 350 mAh (350 milli amp hours) is drained in 4 hours and 27 minutes. What is the resistance of the circuit that it is attached to? Given: R=V I I = q t R = ?? V = 3.0 V I = ?? q = (.350e-3)(3600) = 1260 C t = 4*3600 + 27*60 = 16020 s R = 38.14286 = 38 ...
... A 3.0 V battery with a capacity of 350 mAh (350 milli amp hours) is drained in 4 hours and 27 minutes. What is the resistance of the circuit that it is attached to? Given: R=V I I = q t R = ?? V = 3.0 V I = ?? q = (.350e-3)(3600) = 1260 C t = 4*3600 + 27*60 = 16020 s R = 38.14286 = 38 ...
Exercise 4
... Exercise 4: Kirchoff’s Current and Voltage Laws Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ...
... Exercise 4: Kirchoff’s Current and Voltage Laws Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ...
Ch 2 PPt 2 Basic Theories
... • Voltage applied to each leg is the same • Voltage dropped across each leg will be the same – If more that one resistor in a leg, voltage drop will depend on the resistance of each resistor in that leg ...
... • Voltage applied to each leg is the same • Voltage dropped across each leg will be the same – If more that one resistor in a leg, voltage drop will depend on the resistance of each resistor in that leg ...
Determining β for a 2N2222 transistor
... Horowitz and Hill [1]. In a transistor, the current Ib flowing into the base controls the current Ic that flows from the collector to the emitter. A picture of a transistor, along with its circuit drawing is shown in Figure 1. Ic ...
... Horowitz and Hill [1]. In a transistor, the current Ib flowing into the base controls the current Ic that flows from the collector to the emitter. A picture of a transistor, along with its circuit drawing is shown in Figure 1. Ic ...
www.physicspaathshala.org
... choke required. 15. A 100 mH inductor, a 25 µF capacitor and a 15 ohm resistor are connected in series to a 120 V, 50hz a.c. source. Calculate (i) impedance of the circuit at resonance, (ii) current at resonance (iii) Resonant frequency. 16. A 25·0 µF capacitor, a 0·10H inductor and a 25· 0 ohm resi ...
... choke required. 15. A 100 mH inductor, a 25 µF capacitor and a 15 ohm resistor are connected in series to a 120 V, 50hz a.c. source. Calculate (i) impedance of the circuit at resonance, (ii) current at resonance (iii) Resonant frequency. 16. A 25·0 µF capacitor, a 0·10H inductor and a 25· 0 ohm resi ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.