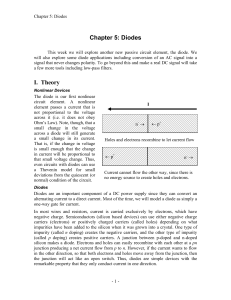
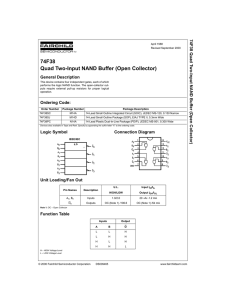
Unit Wise Questions
... one of the plates is raised from 0 to 5 V in 1 ns at a uniform rate with respect to the other. After this duration, the potential difference between the plates is suddenly dropped to 0 V and remains the same thereafter. Find (a) The position of the electron, which started with zero initial velocity ...
... one of the plates is raised from 0 to 5 V in 1 ns at a uniform rate with respect to the other. After this duration, the potential difference between the plates is suddenly dropped to 0 V and remains the same thereafter. Find (a) The position of the electron, which started with zero initial velocity ...
Ohms Law and Basic Circuit Theory
... across the switch. How much energy is lost per coulomb of electrons as they pass through the switch. Ohm’s Law was discussed previously. Apply this law to the light bulb. You know its resistance and you know the voltage drop across it. The current in the circuit is the same everywhere. You can check ...
... across the switch. How much energy is lost per coulomb of electrons as they pass through the switch. Ohm’s Law was discussed previously. Apply this law to the light bulb. You know its resistance and you know the voltage drop across it. The current in the circuit is the same everywhere. You can check ...
MJ2955
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any ...
Document
... used as voltage regulator. The regulating action takes place because of the fact that in reverse breakdown region, a very small change in voltage produces large change in current. This causes a sufficient increase in voltage drop across the resistance to lower voltage back to normal. Similarly, when ...
... used as voltage regulator. The regulating action takes place because of the fact that in reverse breakdown region, a very small change in voltage produces large change in current. This causes a sufficient increase in voltage drop across the resistance to lower voltage back to normal. Similarly, when ...
EUP3651 4-Channel, 1X/1.5X Charge Pump White LED Driver
... with lower VF is recommended in order to improve the efficiency by keeping the driver in 1X mode longer as the battery voltage decreases. For example, if a white LED with a VF of 3.3V is selected over one with VF of 3.5V, the EUP3651 will stay in 1X mode for lower supply voltage of 0.2V. This helps ...
... with lower VF is recommended in order to improve the efficiency by keeping the driver in 1X mode longer as the battery voltage decreases. For example, if a white LED with a VF of 3.3V is selected over one with VF of 3.5V, the EUP3651 will stay in 1X mode for lower supply voltage of 0.2V. This helps ...
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 18 Physics: Principles with
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. • Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current: ...
... • Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge. • Conventional current is in the direction that positive charge would flow. • Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current: ...
Resistance - Leaving Cert Physics
... Now let's go back and try again to understand the Wheatstone bridge: The galvanometer in the middle is used to detect current. If it reads zero then no current flows between the two points. We say that the bridge is balanced. Now the key to this is to realise that not only can the bridge be balance ...
... Now let's go back and try again to understand the Wheatstone bridge: The galvanometer in the middle is used to detect current. If it reads zero then no current flows between the two points. We say that the bridge is balanced. Now the key to this is to realise that not only can the bridge be balance ...
Series Parallel Circ - Red Hook Central Schools
... • Resistors all connected across the V , all V equal to the battery voltage. • V1 = V2 =V3 = Vtot • Current (I), charges reach a junction, they divide. • Itot in the circuit = S currents in each branch. • Itot = I1 + I2 + I3 … ...
... • Resistors all connected across the V , all V equal to the battery voltage. • V1 = V2 =V3 = Vtot • Current (I), charges reach a junction, they divide. • Itot in the circuit = S currents in each branch. • Itot = I1 + I2 + I3 … ...
London Model Railroad Group SCR Throttle
... will be able to deliver its maximum voltage. If the trimmer resistance is set too low the SCR will not trigger on every cycle of the full wave DC at full output voltage and could be damaged by high current spikes. Notes * NOTE 1 At full throttle and with no load this circuit will deliver more than 2 ...
... will be able to deliver its maximum voltage. If the trimmer resistance is set too low the SCR will not trigger on every cycle of the full wave DC at full output voltage and could be damaged by high current spikes. Notes * NOTE 1 At full throttle and with no load this circuit will deliver more than 2 ...
1 - אתר מורי הפיזיקה
... move through the circuit. The rate at which the electrons move is called current. Make a general rule about the relationship between current and resistance. For instance: The higher the resistance the ________ the current. 3. Build another circuit. - Add another resistor to your circuit, making it a ...
... move through the circuit. The rate at which the electrons move is called current. Make a general rule about the relationship between current and resistance. For instance: The higher the resistance the ________ the current. 3. Build another circuit. - Add another resistor to your circuit, making it a ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.