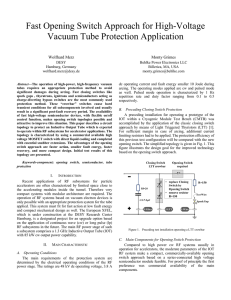
Fast Opening Switch Approach for High-Voltage Vacuum
... caused by the ineligible power supply, which is optimized for clean dc operation only. To improve this situation an appropriate upgrade is underway. At the final design the long pulse mode will be controlled by the RF drive of the IOT. The opening switch has to withstand all resulting load condition ...
... caused by the ineligible power supply, which is optimized for clean dc operation only. To improve this situation an appropriate upgrade is underway. At the final design the long pulse mode will be controlled by the RF drive of the IOT. The opening switch has to withstand all resulting load condition ...
Programmable shunt voltage reference
... pins of the device with no external series resistor (internal resistor < 5 Ω). This is done for all couples of connected pin combinations while the other pins are floating. ...
... pins of the device with no external series resistor (internal resistor < 5 Ω). This is done for all couples of connected pin combinations while the other pins are floating. ...
electrical current
... (b) There is loop to and from the light bulb, but there is no potential difference. (c) Nothing wrong here. The bulb will light up. ...
... (b) There is loop to and from the light bulb, but there is no potential difference. (c) Nothing wrong here. The bulb will light up. ...
chapter 4 - work and energy
... the switch so that current cannot flow. If the connection is made so that current can flow, the circuit is said to be closed. Before electrons were discovered, it was believed that electric currents consisted of movement of positive charge. Because of this misconception, conventional current is said ...
... the switch so that current cannot flow. If the connection is made so that current can flow, the circuit is said to be closed. Before electrons were discovered, it was believed that electric currents consisted of movement of positive charge. Because of this misconception, conventional current is said ...
Chapter 27
... (b) There is loop to and from the light bulb, but there is no potential difference. (c) Nothing wrong here. The bulb will light up. ...
... (b) There is loop to and from the light bulb, but there is no potential difference. (c) Nothing wrong here. The bulb will light up. ...
MAX1916 Low-Dropout, Constant-Current Triple White LED Bias Supply General Description
... The MAX1916 low-dropout bias supply for white LEDs is a high-performance alternative to the simple ballast resistors used in conventional white LED designs. The MAX1916 uses a single resistor to set the bias current for three LEDs, which are matched to 0.3%. The MAX1916 consumes only 40µA of supply ...
... The MAX1916 low-dropout bias supply for white LEDs is a high-performance alternative to the simple ballast resistors used in conventional white LED designs. The MAX1916 uses a single resistor to set the bias current for three LEDs, which are matched to 0.3%. The MAX1916 consumes only 40µA of supply ...
Circuits
... ◆ lectures will be posted frequently, mostly every day if I can remember to do so l l l l ...
... ◆ lectures will be posted frequently, mostly every day if I can remember to do so l l l l ...
2.2.5 uses of capacitors Measuring Capacitor Discharge When
... As the voltage increases the charge increases in the same manner (from Q = CV) In this case the time constant RC is at 0.63 Q0/V0 (0.37 more to reach Q0/V0) Charge (Q) and pd (V) graphs have exactly the same shape The current graph is gradient of the charge graph (since I=Q/t) & hence decreases exp ...
... As the voltage increases the charge increases in the same manner (from Q = CV) In this case the time constant RC is at 0.63 Q0/V0 (0.37 more to reach Q0/V0) Charge (Q) and pd (V) graphs have exactly the same shape The current graph is gradient of the charge graph (since I=Q/t) & hence decreases exp ...
Resistor Inductor Capacitor Series Circuits
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.